Abstract
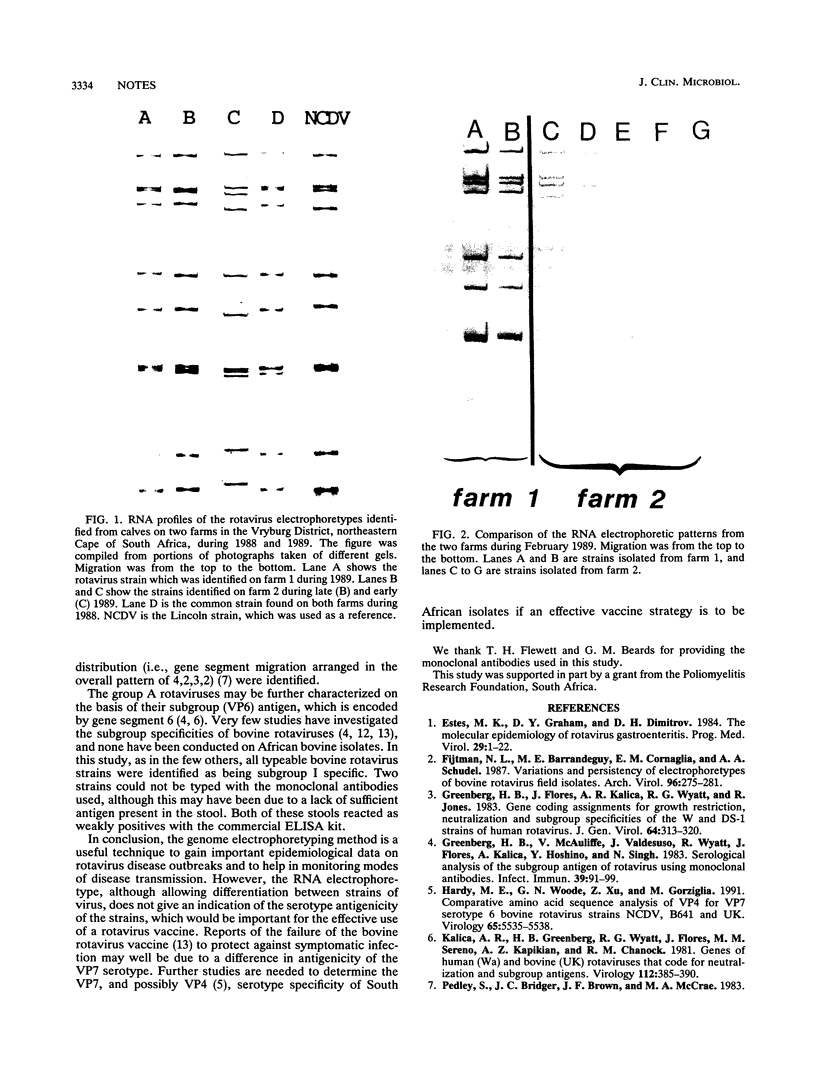
Rotavirus-positive specimens were recovered from 143 Afrikander calves on two farms in the northeastern Cape of South Africa during late 1988 and 1989. The rotavirus strains were analyzed by polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis of the RNA genome, and four rotavirus RNA electrophoretypes, each with a long profile, were identified. A distinct RNA profile was identified on the farms during 1988, but by early 1989, two patterns existed, one unique to each farm. Over the next 8 months a new electrophoretic pattern emerged on one farm, whereas the pattern on the other farm remained unchanged. The rotavirus subgroup I antigen was detected in all specimens examined with subgroup-specific monoclonal antibodies. Non-group A rotaviruses were not identified by RNA genome analysis of 82 specimens from calves with diarrhea negative for group A rotaviruses by an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Estes M. K., Graham D. Y., Dimitrov D. H. The molecular epidemiology of rotavirus gastroenteritis. Prog Med Virol. 1984;29:1–22. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fijtman N. L., Barrandeguy M. E., Cornaglia E. M., Schudel A. A. Variations and persistency of electropherotypes of bovine rotavirus field isolates. Brief report. Arch Virol. 1987;96(3-4):275–281. doi: 10.1007/BF01320968. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenberg H. B., Flores J., Kalica A. R., Wyatt R. G., Jones R. Gene coding assignments for growth restriction, neutralization and subgroup specificities of the W and DS-1 strains of human rotavirus. J Gen Virol. 1983 Feb;64(Pt 2):313–320. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-64-2-313. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenberg H., McAuliffe V., Valdesuso J., Wyatt R., Flores J., Kalica A., Hoshino Y., Singh N. Serological analysis of the subgroup protein of rotavirus, using monoclonal antibodies. Infect Immun. 1983 Jan;39(1):91–99. doi: 10.1128/iai.39.1.91-99.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hardy M. E., Woode G. N., Xu Z. C., Gorziglia M. Comparative amino acid sequence analysis of VP4 for VP7 serotype 6 bovine rotavirus strains NCDV, B641, and UK. J Virol. 1991 Oct;65(10):5535–5538. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.10.5535-5538.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kalica A. R., Greenberg H. B., Wyatt R. G., Flores J., Sereno M. M., Kapikian A. Z., Chanock R. M. Genes of human (strain Wa) and bovine (strain UK) rotaviruses that code for neutralization and subgroup antigens. Virology. 1981 Jul 30;112(2):385–390. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(81)90285-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pocock D. H. Characterisation of rotavirus isolates from sub-clinically infected calves by genome profile analysis. Vet Microbiol. 1987 Jan;13(1):27–34. doi: 10.1016/0378-1135(87)90095-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodger S. M., Holmes I. H. Comparison of the genomes of simian, bovine, and human rotaviruses by gel electrophoresis and detection of genomic variation among bovine isolates. J Virol. 1979 Jun;30(3):839–846. doi: 10.1128/jvi.30.3.839-846.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sabara M., Deregt D., Babiuk L. A., Misra V. Genetic heterogeneity within individual bovine rotavirus isolates. J Virol. 1982 Dec;44(3):813–822. doi: 10.1128/jvi.44.3.813-822.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snodgrass D. R., Herring A. J., Campbell I., Inglis J. M., Hargreaves F. D. Comparison of atypical rotaviruses from calves, piglets, lambs and man. J Gen Virol. 1984 May;65(Pt 5):909–914. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-65-5-909. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Theil K. W., McCloskey C. M. Molecular epidemiology and subgroup determination of bovine group A rotaviruses associated with diarrhea in dairy and beef calves. J Clin Microbiol. 1989 Jan;27(1):126–131. doi: 10.1128/jcm.27.1.126-131.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Theil K. W., McCloskey C. M. Partial characterization of a bovine group A rotavirus with a short genome electropherotype. J Clin Microbiol. 1988 Jun;26(6):1094–1099. doi: 10.1128/jcm.26.6.1094-1099.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Theodoridis A., Prozesky L., Els H. J. Studies on neonatal calf diarrhoea caused by rotavirus: transmission of the disease and attempted vaccination of colostrum-deprived calves. Onderstepoort J Vet Res. 1980 Mar;47(1):31–34. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Theodoridis A., Prozesky L., Els H. J. The isolation and cultivation of calf rotavirus in the Republic of South Africa. Onderstepoort J Vet Res. 1979 Jun;46(2):65–69. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsunemitsu H., Saif L. J., Jiang B. M., Shimizu M., Hiro M., Yamaguchi H., Ishiyama T., Hirai T. Isolation, characterization, and serial propagation of a bovine group C rotavirus in a monkey kidney cell line (MA104). J Clin Microbiol. 1991 Nov;29(11):2609–2613. doi: 10.1128/jcm.29.11.2609-2613.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verly E., Cohen J. Demonstration of size variation of RNA segments between different isolates of calf rotavirus. J Gen Virol. 1977 Jun;35(3):583–586. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-35-3-583. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]