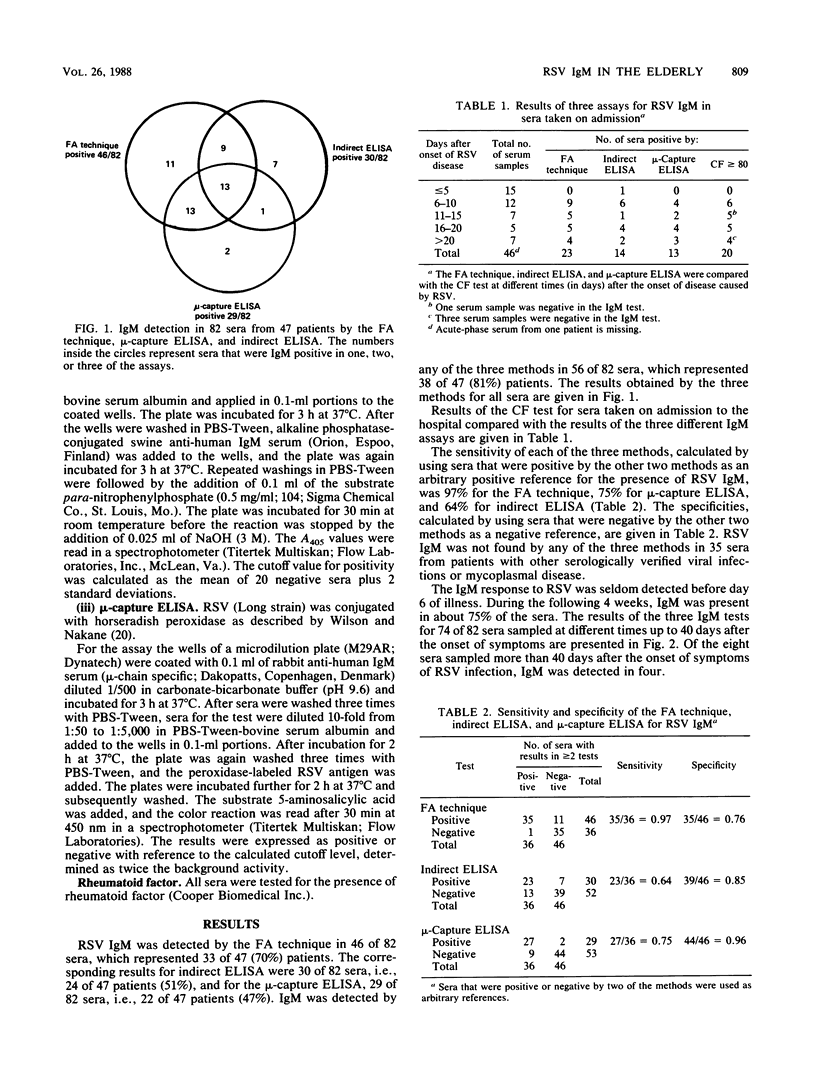
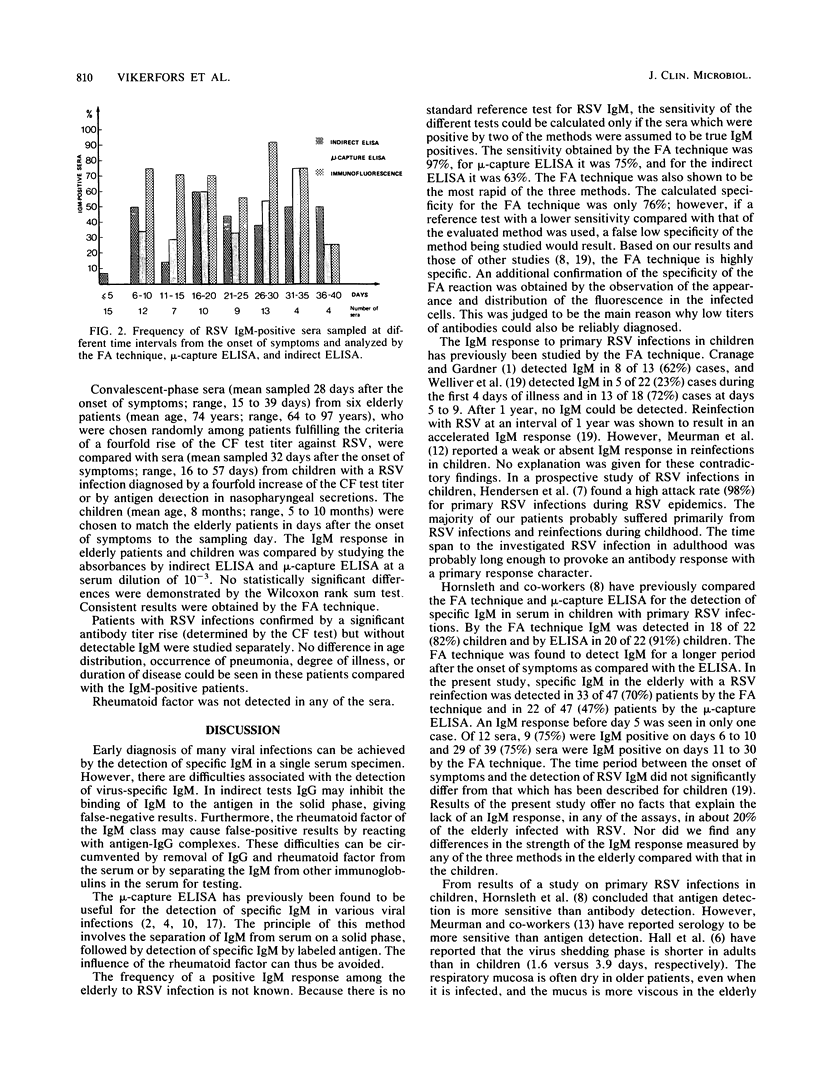
Abstract
The indirect fluorescent-antibody technique was compared with indirect and mu-capture enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays for the detection of respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) immunoglobulin M (IgM) in the elderly. Sera from 47 patients (mean age, 70 years) with acute lower respiratory tract infections caused by RSV were investigated. Specific IgM was detected in 81% (38 of 47) of the patients. The fluorescent-antibody technique, which gave 70% positive results, proved to be the most sensitive of the three methods. An IgM response was seldom seen in sera from the elderly within the first week of disease, but was present in 85% of sera (33 of 39) collected between days 11 and 30 of disease. In some patients it persisted for more than 6 weeks. Detection of IgM was found to be a useful tool for the diagnosis of RSV infections in elderly patients.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Cranage M. P., Gardner P. S. Systemic cell-mediated and antibody responses in infants with respiratory syncytial virus infections. J Med Virol. 1980;5(2):161–170. doi: 10.1002/jmv.1890050210. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duermeyer W., Wielaard F., van der Veen J. A new principle for the detection of specific IgM antibodies applied in an ELISA for hepatitis A. J Med Virol. 1979;4(1):25–32. doi: 10.1002/jmv.1890040104. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fransén H., Sterner G., Forsgren M., Heigl Z., Wolontis S., Svedmyr A., Tunevall G. Acute lower respiratory illness in elderly patients with respiratory syncytial virus infection. Acta Med Scand. 1967 Sep;182(3):323–330. doi: 10.1111/j.0954-6820.1967.tb11530.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldwater P. N., Webster M., Banatvala J. E. Use of a simple, new test for virus-specific IgM to investigate an outbreak of influenza B in a hospitalised aged community. J Virol Methods. 1982 Feb;4(1):9–18. doi: 10.1016/0166-0934(82)90049-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grandien M., Pettersson C. A., Gardner P. S., Linde A., Stanton A. Rapid viral diagnosis of acute respiratory infections: comparison of enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay and the immunofluorescence technique for detection of viral antigens in nasopharyngeal secretions. J Clin Microbiol. 1985 Nov;22(5):757–760. doi: 10.1128/jcm.22.5.757-760.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall C. B., Geiman J. M., Biggar R., Kotok D. I., Hogan P. M., Douglas G. R., Jr Respiratory syncytial virus infections within families. N Engl J Med. 1976 Feb 19;294(8):414–419. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197602192940803. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henderson F. W., Collier A. M., Clyde W. A., Jr, Denny F. W. Respiratory-syncytial-virus infections, reinfections and immunity. A prospective, longitudinal study in young children. N Engl J Med. 1979 Mar 8;300(10):530–534. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197903083001004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hornsleth A., Friis B., Grauballe P. C., Krasilnikof P. A. Detection by ELISA of IgA and IgM antibodies in secretion and IgM antibodies in serum in primary lower respiratory syncytial virus infection. J Med Virol. 1984;13(2):149–161. doi: 10.1002/jmv.1890130205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krech U., Wilhelm J. A. A solid-phase immunosorbent technique for the rapid detection of rubella IgM by haemagglutination inhibition. J Gen Virol. 1979 Aug;44(2):281–286. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-44-2-281. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McQuillin J., Gardner P. S. Rapid diagnosis of respiratory syncytial virus infection by immunofluorescent antibody techniques. Br Med J. 1968 Mar 9;1(5592):602–605. doi: 10.1136/bmj.1.5592.602. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meurman O., Ruuskanen O., Sarkkinen H., Hänninen P., Halonen P. Immunoglobulin class-specific antibody response in respiratory syncytial virus infection measured by enzyme immunoassay. J Med Virol. 1984;14(1):67–72. doi: 10.1002/jmv.1890140110. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meurman O., Sarkkinen H., Ruuskanen O., Hänninen P., Halonen P. Diagnosis of respiratory syncytial virus infection in children: comparison of viral antigen detection and serology. J Med Virol. 1984;14(1):61–65. doi: 10.1002/jmv.1890140109. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orvell C. Structural polypeptides of mumps virus. J Gen Virol. 1978 Dec;41(3):527–539. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-41-3-527. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skaug K., Gaarder P. I. An indirect immunofluorescent antibody test for determination of Rubella virus specific IgM antibodies. Elimination of secondary IgM rheumatoid factor staining after absorption of serum IgG with Staphylococcal protein A. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand C. 1978 Feb;86(1):33–35. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1978.tb02554.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spelman D. W., Stanley P. A. Respiratory syncytial virus pneumonitis in adults. Med J Aust. 1983 Apr 30;1(9):430–431. doi: 10.5694/j.1326-5377.1983.tb136145.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vikerfors T., Grandien M., Olcen P. Respiratory syncytial virus infections in adults. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1987 Sep;136(3):561–564. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm/136.3.561. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Welliver R. C., Kaul T. N., Putnam T. I., Sun M., Riddlesberger K., Ogra P. L. The antibody response to primary and secondary infection with respiratory syncytial virus: kinetics of class-specific responses. J Pediatr. 1980 May;96(5):808–813. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(80)80547-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van der Logt J. T., van Loon A. M., Heessen F. W., van der Veen J. Diagnosis of parainfluenza virus infection in children and older patients by detection of specific IgM antibody. J Med Virol. 1985 Jun;16(2):191–199. doi: 10.1002/jmv.1890160212. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


