Abstract
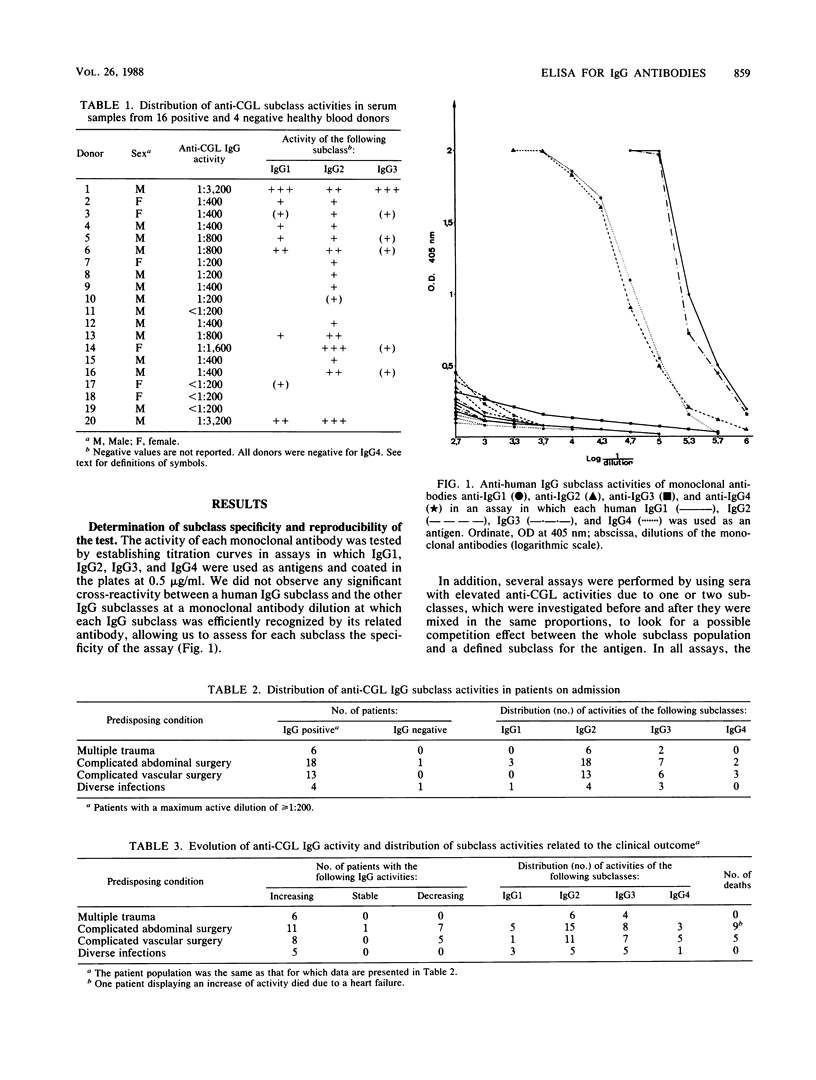
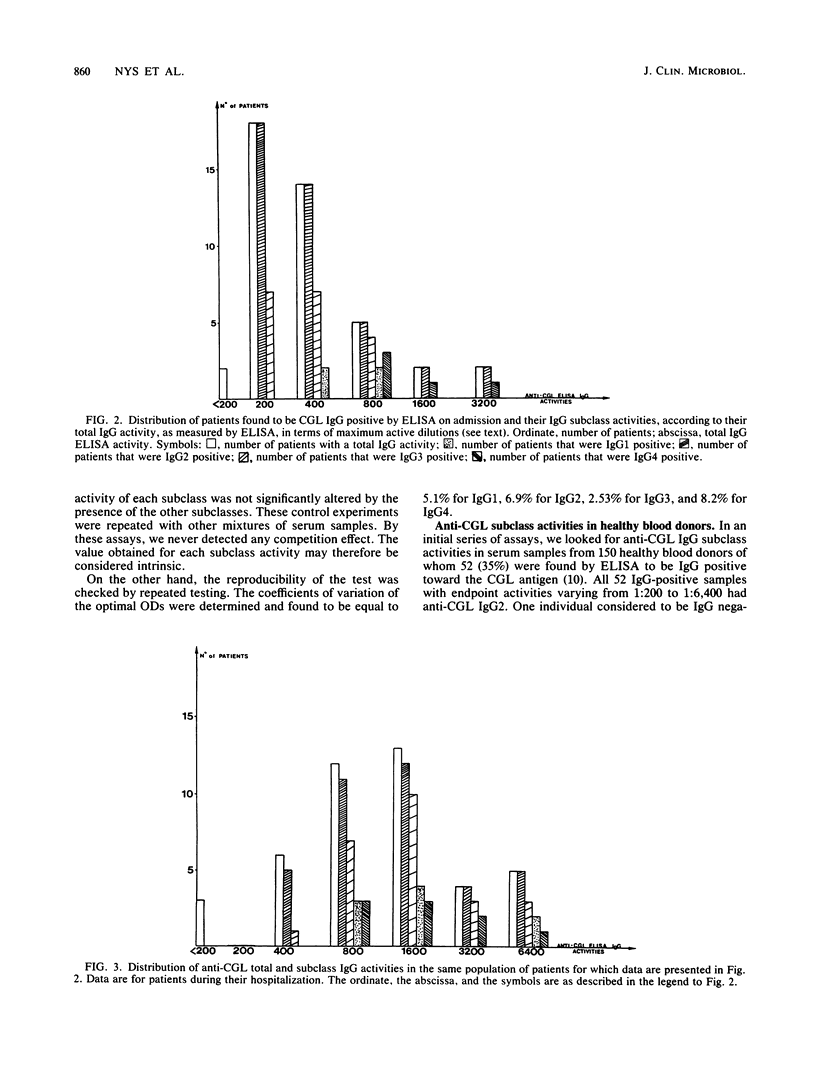
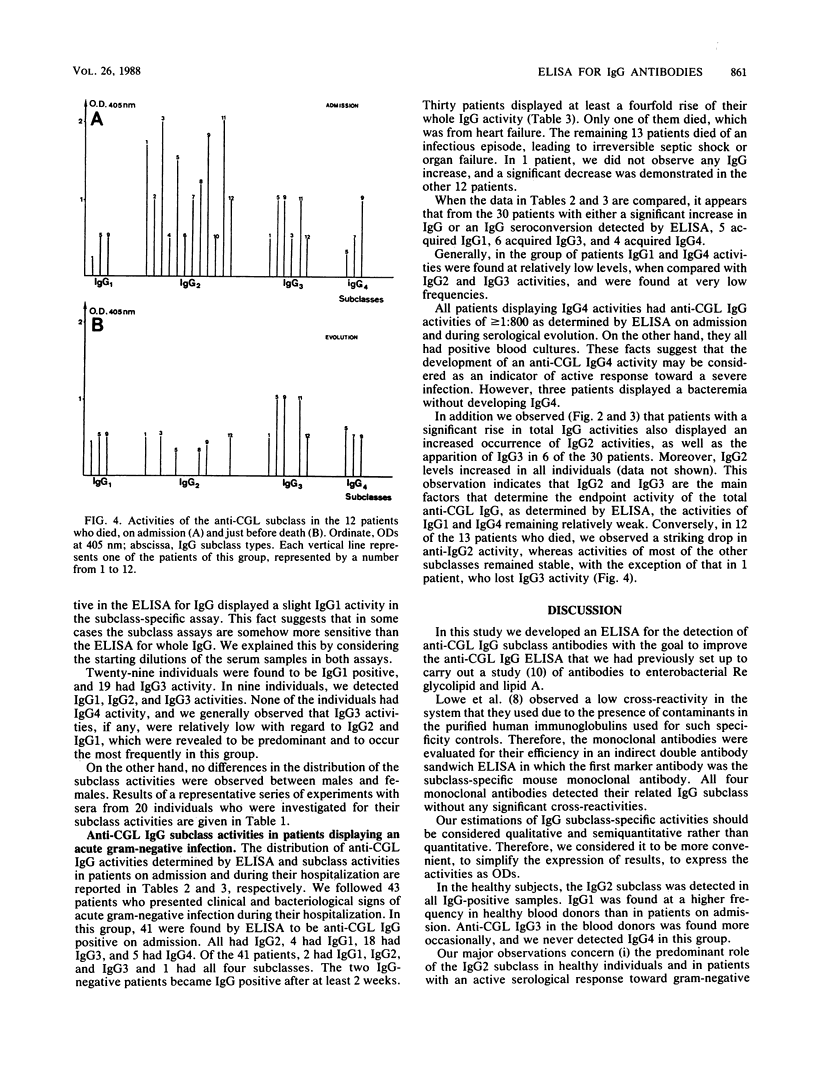
An enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay was developed to study the subclass distribution of immunoglobulin G (IgG) specific to the core glycolipid (CGL) of the Re mutant of Salmonella minnesota R595 in serum samples from individuals with an IgG response toward these antigens. In a group of healthy blood donors, we detected predominantly the IgG2 and IgG1 subclasses. In a group of patients in an intensive care unit who developed infectious complications due to gram-negative bacteria, the anti-CGL IgG activity was due mainly to the IgG2 and IgG3 subclasses. In all serum samples found to be IgG positive, the assay for anti-CGL IgG2 was positive. This subclass was revealed to play a predominant role in patients displaying a seroconversion or a significant rise in their antibody response toward CGL. IgG4 was found or appeared only in patients with confirmed bacteremia. In addition, we observed a drop in anti-CGL IgG2 before the death of patients undergoing a septic shock or an irreversible organ failure, suggesting that the anti-CGL IgG2 activity could be used as a marker of the evolution of the illness in this group of patients.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Galanos C., Lüderitz O., Westphal O. A new method for the extraction of R lipopolysaccharides. Eur J Biochem. 1969 Jun;9(2):245–249. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1969.tb00601.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hornsleth A., Bech-Thomsen N., Friis B. Detection by ELISA of IgG-subclass-specific antibodies in primary respiratory syncytial (RS) virus infections. J Med Virol. 1985 Aug;16(4):321–328. doi: 10.1002/jmv.1890160404. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jefferis R., Reimer C. B., Skvaril F., de Lange G., Ling N. R., Lowe J., Walker M. R., Phillips D. J., Aloisio C. H., Wells T. W. Evaluation of monoclonal antibodies having specificity for human IgG sub-classes: results of an IUIS/WHO collaborative study. Immunol Lett. 1985;10(3-4):223–252. doi: 10.1016/0165-2478(85)90082-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linde G. A., Hammarström L., Persson M. A., Smith C. I., Sundqvist V. A., Wahren B. Virus-specific antibody activity of different subclasses of immunoglobulins G and A in cytomegalovirus infections. Infect Immun. 1983 Oct;42(1):237–244. doi: 10.1128/iai.42.1.237-244.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linde G. A. Subclass distribution of rubella virus-specific immunoglobulin G. J Clin Microbiol. 1985 Jan;21(1):117–121. doi: 10.1128/jcm.21.1.117-121.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lowe J., Bird P., Hardie D., Jefferis R., Ling N. R. Monoclonal antibodies (McAbs) to determinants on human gamma chains: properties of antibodies showing subclass restriction or subclass specificity. Immunology. 1982 Oct;47(2):329–336. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morell A., Roth-Wicky B., Skvaril F. Immunoglobulin G subclass restriction of antibodies against hepatitis B surface antigen. Infect Immun. 1983 Feb;39(2):565–568. doi: 10.1128/iai.39.2.565-568.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nys M., Damas P., Damas F., Joassin L., Demonty J. A direct enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) for antibodies to enterobacterial Re core glycolipid and lipid A. Results in healthy subjects and in patients infected by gram-negative bacteria. Med Microbiol Immunol. 1987;176(5):257–271. doi: 10.1007/BF00190532. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oxelius V. A. Chronic infections in a family with hereditary deficiency of IgG2 and IgG4. Clin Exp Immunol. 1974 May;17(1):19–27. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robbins D. L., Wistar R., Jr Comparative specificities of serum and synovial cell 19S IgM rheumatoid factors in rheumatoid arthritis. J Rheumatol. 1985 Jun;12(3):437–443. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schur P. H., Borel H., Gelfand E. W., Alper C. A., Rosen F. S. Selective gamma-g globulin deficiencies in patients with recurrent pyogenic infections. N Engl J Med. 1970 Sep 17;283(12):631–634. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197009172831205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shapiro S. S., Carroll K. S. Acquired factor 8 antibodies: further immunologic and electrophoretic studies. Science. 1968 May 17;160(3829):786–787. doi: 10.1126/science.160.3829.786. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siber G. R., Schur P. H., Aisenberg A. C., Weitzman S. A., Schiffman G. Correlation between serum IgG-2 concentrations and the antibody response to bacterial polysaccharide antigens. N Engl J Med. 1980 Jul 24;303(4):178–182. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198007243030402. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young L. S., Stevens P., Ingram J. Functional role of antibody against "core" glycolipid of Enterobacteriaceae. J Clin Invest. 1975 Oct;56(4):850–861. doi: 10.1172/JCI108164. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yount W. J., Dorner M. M., Kunkel H. G., Kabat E. A. Studies on human antibodies. VI. Selective variations in subgroup composition and genetic markers. J Exp Med. 1968 Mar 1;127(3):633–646. doi: 10.1084/jem.127.3.633. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


