Abstract
Murine monoclonal antibodies (MAbs) were produced which were specific for Pasteurella haemolytica serotype 1 lipopolysaccharide (LPS). The MAbs also reacted with LPS present in a partially purified antigen derived from a saline extract of the organism. The epitope to which the MAbs were directed was a carbohydrate which was sensitive to oxidation with periodate, had a molecular weight between 14,000 and 25,000 as determined by immunoblotting, and was present in a crude O-antigen preparation of P. haemolytica LPS. The MAbs did not react with purified capsular polysaccharide from P. haemolytica serotype 1. In an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay, reaction of the MAbs with LPS obtained from 14 gram-negative bacteria failed to detect any cross-reactivity with P. haemolytica LPS. However, the MAbs detected antigenic similarities among P. haemolytica serotypes 1, 5, 6, 7, 8, and 12 and, to a lesser extent, 4 and 14. These studies indicate that the LPS-O-antigens from several P. haemolytica serotypes have similar epitopes and may be partially responsible for shared antigenicity among serotypes.
Full text
PDF

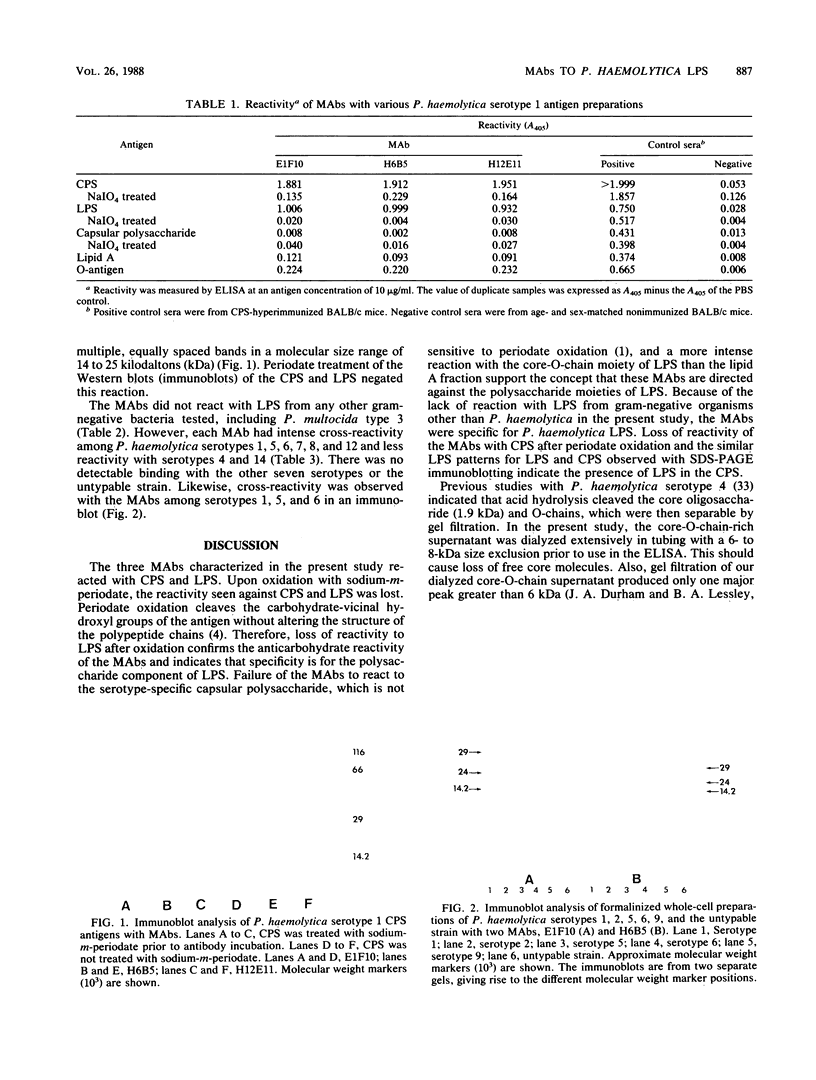
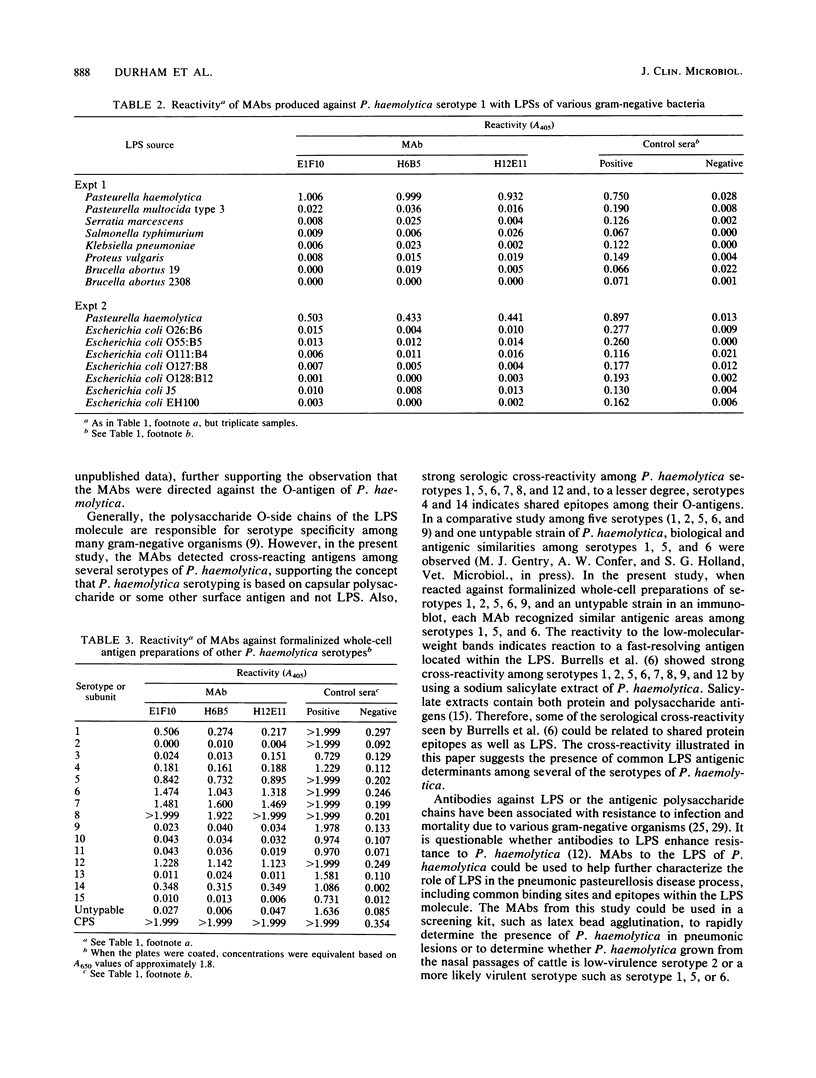

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adlam C., Knights J. M., Mugridge A., Lindon J. C., Baker P. R., Beesley J. E., Spacey B., Craig G. R., Nagy L. K. Purification, characterization and immunological properties of the serotype-specific capsular polysaccharide of Pasteurella haemolytica (serotype A1) organisms. J Gen Microbiol. 1984 Sep;130(9):2415–2426. doi: 10.1099/00221287-130-9-2415. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BIBERSTEIN E. L., GILLS M., KNIGHT H. Serological types of Pasteurella hemolytica. Cornell Vet. 1960 Jul;50:283–300. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BOBBITT J. M. Periodate oxidation of carbohydrates. Adv Carbohydr Chem. 1956;48(11):1–41. doi: 10.1016/s0096-5332(08)60115-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biberstein E. L., Francis C. K. Nucleic acid homologies between the A and T types of Pasteurella haemolytica. J Med Microbiol. 1968 Aug;1(1):105–108. doi: 10.1099/00222615-1-1-105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burrells C., Evans H. B., Dawson A. M. Antigenic relationships between the serotypes of Pasteurella haemolytica demonstrable by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA). Vet Microbiol. 1983 Apr;8(2):187–198. doi: 10.1016/0378-1135(83)90065-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caroff M., Bundle D. R., Perry M. B., Cherwonogrodzky J. W., Duncan J. R. Antigenic S-type lipopolysaccharide of Brucella abortus 1119-3. Infect Immun. 1984 Nov;46(2):384–388. doi: 10.1128/iai.46.2.384-388.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caroff M., Bundle D. R., Perry M. B. Structure of the O-chain of the phenol-phase soluble cellular lipopolysaccharide of Yersinia enterocolitica serotype O:9. Eur J Biochem. 1984 Feb 15;139(1):195–200. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1984.tb07994.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chester I. R., Meadow P. M., Pitt T. L. The relationship between the O-antigenic lipopolysaccharides and serological specificity in strains of Pseudomonas aeruginosa of different O-serotypes. J Gen Microbiol. 1973 Oct;78(2):305–318. doi: 10.1099/00221287-78-2-305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ciesielski C. A., Blaser M. J., Wang W. L. Serogroup specificity of Legionella pneumophila is related to lipopolysaccharide characteristics. Infect Immun. 1986 Feb;51(2):397–404. doi: 10.1128/iai.51.2.397-404.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Confer A. W., Panciera R. J., Mosier D. A. Serum antibodies to Pasteurella haemolytica lipopolysaccharide: relationship to experimental bovine pneumonic pasteurellosis. Am J Vet Res. 1986 May;47(5):1134–1138. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Confer A. W., Simons K. R. Effects of Pasteurella haemolytica lipopolysaccharide on selected functions of bovine leukocytes. Am J Vet Res. 1986 Jan;47(1):154–157. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cunningham M. W., Russell S. M. Study of heart-reactive antibody in antisera and hybridoma culture fluids against group A streptococci. Infect Immun. 1983 Nov;42(2):531–538. doi: 10.1128/iai.42.2.531-538.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Durham J. A., Confer A. W., Mosier D. A., Lessley B. A. Comparison of the antigens associated with saline solution, potassium thiocyanate, and sodium salicylate extracts of Pasteurella haemolytica serotype 1. Am J Vet Res. 1986 Sep;47(9):1946–1951. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emau P., Giri S. N., Bruss M. L. Comparative effects of smooth and rough Pasteurella hemolytica lipopolysaccharides on arachidonic acid, eicosanoids, serotonin, and histamine in calves. Circ Shock. 1986;20(3):239–253. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fox M. L., Thomson R. G., Magwood S. E. Pasteurella haemolytica of cattle: serotype, production of beta-galactosidase and antibacterial sensitivity. Can J Comp Med. 1971 Oct;35(4):313–317. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frank G. H., Smith P. C. Prevalence of Pasteurella haemolytica in transported calves. Am J Vet Res. 1983 Jun;44(6):981–985. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frank G. H., Wessman G. E. Rapid plate agglutination procedure for serotyping Pasteurella haemolytica. J Clin Microbiol. 1978 Feb;7(2):142–145. doi: 10.1128/jcm.7.2.142-145.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GROLLMAN A. P., OSBORN M. J. O-PHOSPHORYLETHANOLAMINE: A COMPONENT OF LIPOPOLYSACCHARIDE IN CERTAIN GRAM-NEGATIVE BACTERIA. Biochemistry. 1964 Oct;3:1571–1574. doi: 10.1021/bi00898a031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gentry M. J., Corstvet R. E., Panciera R. J. Extraction of capsular material from Pasteurella haemolytica. Am J Vet Res. 1982 Nov;43(11):2070–2073. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henricks P. A., van der Tol M. E., Thyssen R. M., van Asbeck B. S., Verhoef J. Escherichia coli lipopolysaccharides diminish and enhance cell function of human polymorphonuclear leukocytes. Infect Immun. 1983 Jul;41(1):294–301. doi: 10.1128/iai.41.1.294-301.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirkland T. N., Ziegler E. J. An immunoprotective monoclonal antibody to lipopolysaccharide. J Immunol. 1984 May;132(5):2590–2592. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klesius P. H., Chambers W. H., Schultz R. D. Effect of bacterial lipopolysaccharide on bovine polymorphonuclear neutrophil migration in vitro. Vet Immunol Immunopathol. 1984 Oct;7(3-4):239–244. doi: 10.1016/0165-2427(84)90082-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lessley B. A., Confer A. W., Mosier D. A., Gentry M. J., Durham J. A., Rummage J. A. Saline-extracted antigens of Pasteurella haemolytica: separation by chromatofocusing, preliminary characterization, and evaluation of immunogenicity. Vet Immunol Immunopathol. 1985 Nov;10(2-3):279–296. doi: 10.1016/0165-2427(85)90053-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrison D. C., Ryan J. L. Bacterial endotoxins and host immune responses. Adv Immunol. 1979;28:293–450. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60802-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrison D. C., Ulevitch R. J. The effects of bacterial endotoxins on host mediation systems. A review. Am J Pathol. 1978 Nov;93(2):526–618. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagao S., Tanaka A., Onozaki K., Hashimoto T. Differences between macrophage migration inhibitions by lymphokines and muramyl dipeptide (MDP) or lipopolysaccharide (LPS): migration enhancement by lymphokines. Cell Immunol. 1982 Jul 15;71(1):1–11. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(82)90491-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newman P. R., Corstvet R. E., Panciera R. J. Distribution of Pasteurella haemolytica and Pasteurella multocida in the bovine lung following vaccination and challenge exposure as an indicator of lung resistance. Am J Vet Res. 1982 Mar;43(3):417–422. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rimler R. B., Brown W. E. Comparisons of the serologic response of chickens to Pasteurella multocida and its lipopolysaccharide. Avian Dis. 1982 Oct-Dec;26(4):842–846. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rimsay R. L., Coyle-Dennis J. E., Lauerman L. H., Squire P. G. Purification and biological characterizationof endotoxin fractions from Pasteruella haemolytica. Am J Vet Res. 1981 Dec;42(12):2134–2138. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shoenfeld Y., Rauch J., Massicotte H., Datta S. K., André-Schwartz J., Stollar B. D., Schwartz R. S. Polyspecificity of monoclonal lupus autoantibodies produced by human-human hybridomas. N Engl J Med. 1983 Feb 24;308(8):414–420. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198302243080802. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stuart F. A., Corbel M. J. Identification of a serological cross-reaction between Brucella abortus and Escherichia coli 0:157. Vet Rec. 1982 Feb 27;110(9):202–203. doi: 10.1136/vr.110.9.202-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson D. A., Mould D. L. Protein electrophoretic pattern of Pasteurella haemolytica. Res Vet Sci. 1975 May;18(3):342–343. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woodward M. P., Young W. W., Jr, Bloodgood R. A. Detection of monoclonal antibodies specific for carbohydrate epitopes using periodate oxidation. J Immunol Methods. 1985 Apr 8;78(1):143–153. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(85)90337-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]




