Abstract
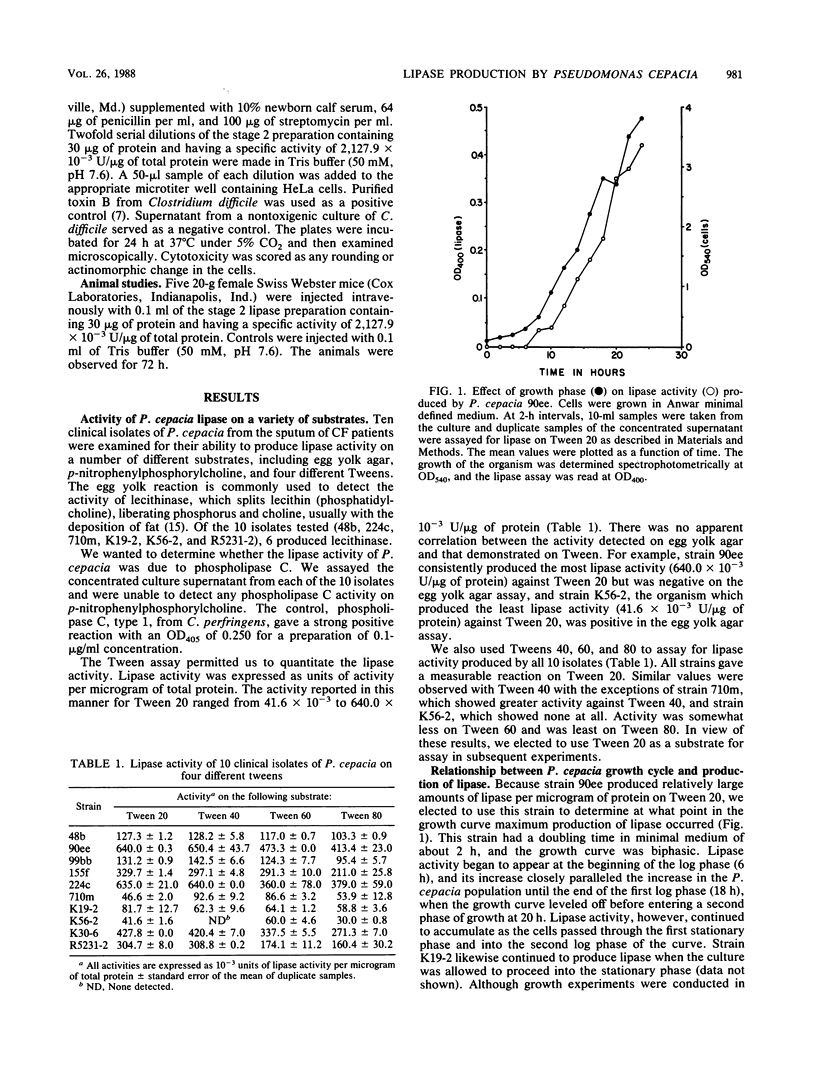
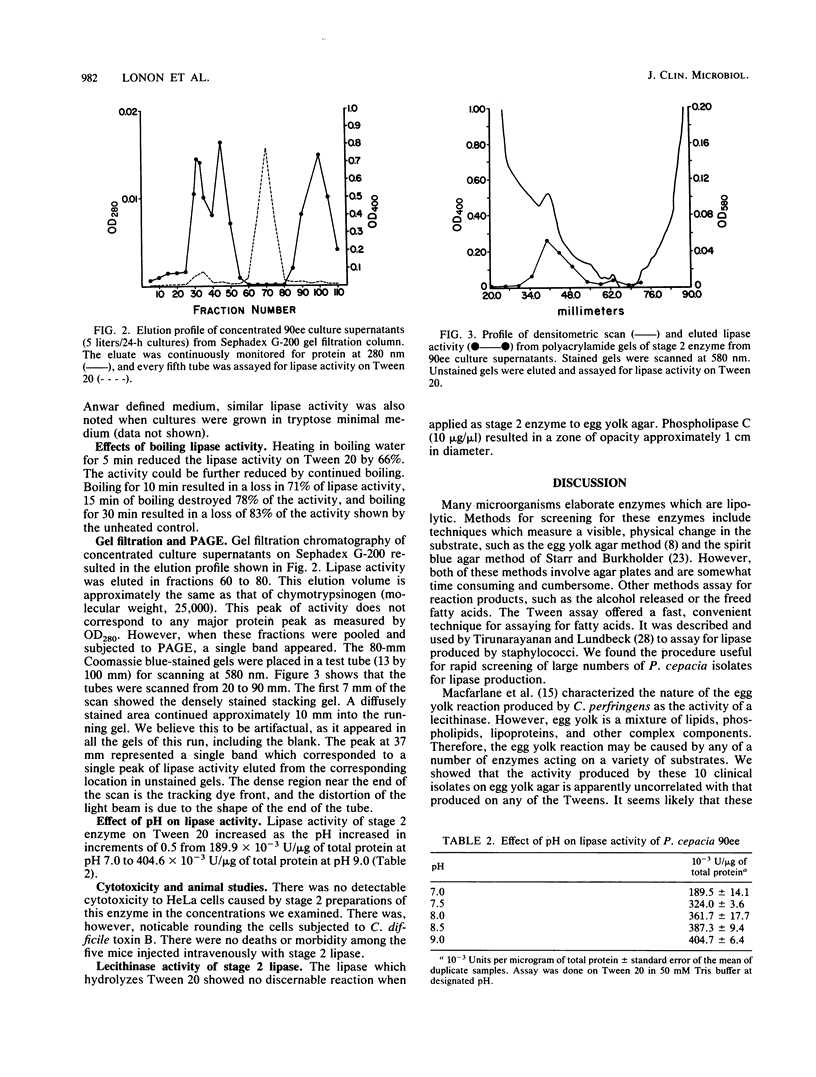
Ten clinical isolates of Pseudomonas cepacia from the sputum of cystic fibrosis patients were examined for the ability to produce lipase. Lipase substrates used included egg yolk agar, four different polyoxyethylene sorbitans (Tweens), and p-nitrophenylphosphorylcholine, a chromogenic substrate used to assay for phospholipase C. Lipase activity was detected in the filtrates of organisms grown to the exponential phase in either tryptose minimal medium or chemically defined medium. Lipase activity increased in the filtrates if the cultures were allowed to proceed into the stationary phase. None of the isolates produced phospholipase C. Lipase activity on Tween 20 ranged from 41.6 X 10(-3) to 640.0 X 10(-3) U/micrograms of protein. The activity was similar or slightly lower when Tween 40, 60, or 80 was used as the substrate. There was no correlation between lipase activity on Tween and that demonstrated on egg yolk agar. Lipase activity increased as pH increased from 7.0 to 9.0. Boiling for 5 min resulted in 66% loss of enzyme activity. The remaining activity continued to decrease with increasing boiling time. The enzyme was purified by gel filtration on Sephadex G-200, and the resultant preparation, when subjected to polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis, resulted in a single protein band (molecular weight, approximately 25,000) from which lipase activity could be eluted. The purified lipase was not cytotoxic to HeLa cells, nor was it toxic when injected intravenously into mice.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anwar H., Brown M. R., Lambert P. A. Effect of nutrient depletion on sensitivity of Pseudomonas cepacia to phagocytosis and serum bactericidal activity at different temperatures. J Gen Microbiol. 1983 Jul;129(7):2021–2027. doi: 10.1099/00221287-129-7-2021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ballard R. W., Palleroni N. J., Doudoroff M., Stanier R. Y., Mandel M. Taxonomy of the aerobic pseudomonads: Pseudomonas cepacia, P. marginata, P. alliicola and P. caryophylli. J Gen Microbiol. 1970 Feb;60(2):199–214. doi: 10.1099/00221287-60-2-199. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berka R. M., Gray G. L., Vasil M. L. Studies of phospholipase C (heat-labile hemolysin) in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Infect Immun. 1981 Dec;34(3):1071–1074. doi: 10.1128/iai.34.3.1071-1074.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAVIS B. J. DISC ELECTROPHORESIS. II. METHOD AND APPLICATION TO HUMAN SERUM PROTEINS. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1964 Dec 28;121:404–427. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1964.tb14213.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donta S. T., Shaffer S. J. Effects of Clostridium difficile toxin on tissue-cultured cells. J Infect Dis. 1980 Feb;141(2):218–222. doi: 10.1093/infdis/141.2.218. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ESSELMANN M. T., LIU P. V. Lecithinase production by gramnegative bacteria. J Bacteriol. 1961 Jun;81:939–945. doi: 10.1128/jb.81.6.939-945.1961. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOERLEIN H., PILZ W. [Research on the enzymes of human blood. IV. Definition of a lipase in human serum (CE), its relation to the clearing factor (lipoprotein lipase) and its routine determination]. Hoppe Seylers Z Physiol Chem. 1962 May 4;327:256–273. doi: 10.1515/bchm2.1962.327.1.256. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isles A., Maclusky I., Corey M., Gold R., Prober C., Fleming P., Levison H. Pseudomonas cepacia infection in cystic fibrosis: an emerging problem. J Pediatr. 1984 Feb;104(2):206–210. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(84)80993-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurioka S., Matsuda M. Phospholipase C assay using p-nitrophenylphosphoryl-choline together with sorbitol and its application to studying the metal and detergent requirement of the enzyme. Anal Biochem. 1976 Sep;75(1):281–289. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90078-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lawrence R. C., Fryer T. F., Reiter B. The production and characterization of lipases from a micrococcus and a pseudomonad. J Gen Microbiol. 1967 Sep;48(3):401–418. doi: 10.1099/00221287-48-3-401. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MORRIS M. B., ROBERTS J. B. A group of pseudomonads able to synthesize poly-beta-hydroxybutyric acid. Nature. 1959 May 30;183(4674):1538–1539. doi: 10.1038/1831538a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKevitt A. I., Woods D. E. Characterization of Pseudomonas cepacia isolates from patients with cystic fibrosis. J Clin Microbiol. 1984 Feb;19(2):291–293. doi: 10.1128/jcm.19.2.291-293.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phillips I., Eykyn S., Curtis M. A., Snell J. J. Pseudomonas cepacia (multivorans) septicaemia in an intensive-care unit. Lancet. 1971 Feb 20;1(7695):375–377. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(71)92212-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern P. M., Jr, Mays B. B., Pierce A. K., Sanford J. P. Pulmonary clearance of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Lab Clin Med. 1970 Oct;76(4):548–559. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Speller D. C., Stephens M. E., Viant A. C. Hospital infection by Pseudomonas cepacia. Lancet. 1971 Apr 17;1(7703):798–799. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(71)91236-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stinson M. W., Hayden C. Secretion of phospholipase C by Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Infect Immun. 1979 Aug;25(2):558–564. doi: 10.1128/iai.25.2.558-564.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tablan O. C., Chorba T. L., Schidlow D. V., White J. W., Hardy K. A., Gilligan P. H., Morgan W. M., Carson L. A., Martone W. J., Jason J. M. Pseudomonas cepacia colonization in patients with cystic fibrosis: risk factors and clinical outcome. J Pediatr. 1985 Sep;107(3):382–387. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(85)80511-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomassen M. J., Demko C. A., Klinger J. D., Stern R. C. Pseudomonas cepacia colonization among patients with cystic fibrosis. A new opportunist. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1985 May;131(5):791–796. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1985.131.5.791. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tirunarayanan M. O., Lundbeck H. Investigations on the enzymes and toxins of staphylococci. Assay of lipase using Tween as the substrate. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand. 1968;72(2):263–276. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1968.tb01342.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



