Abstract
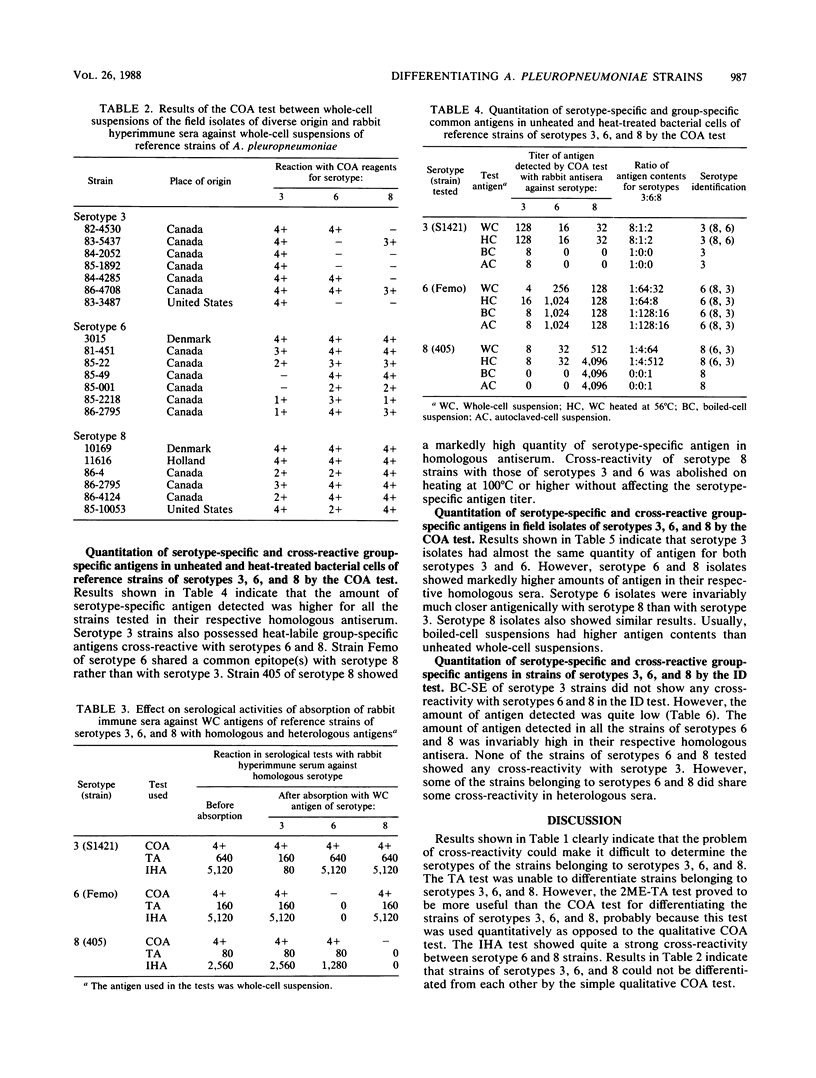
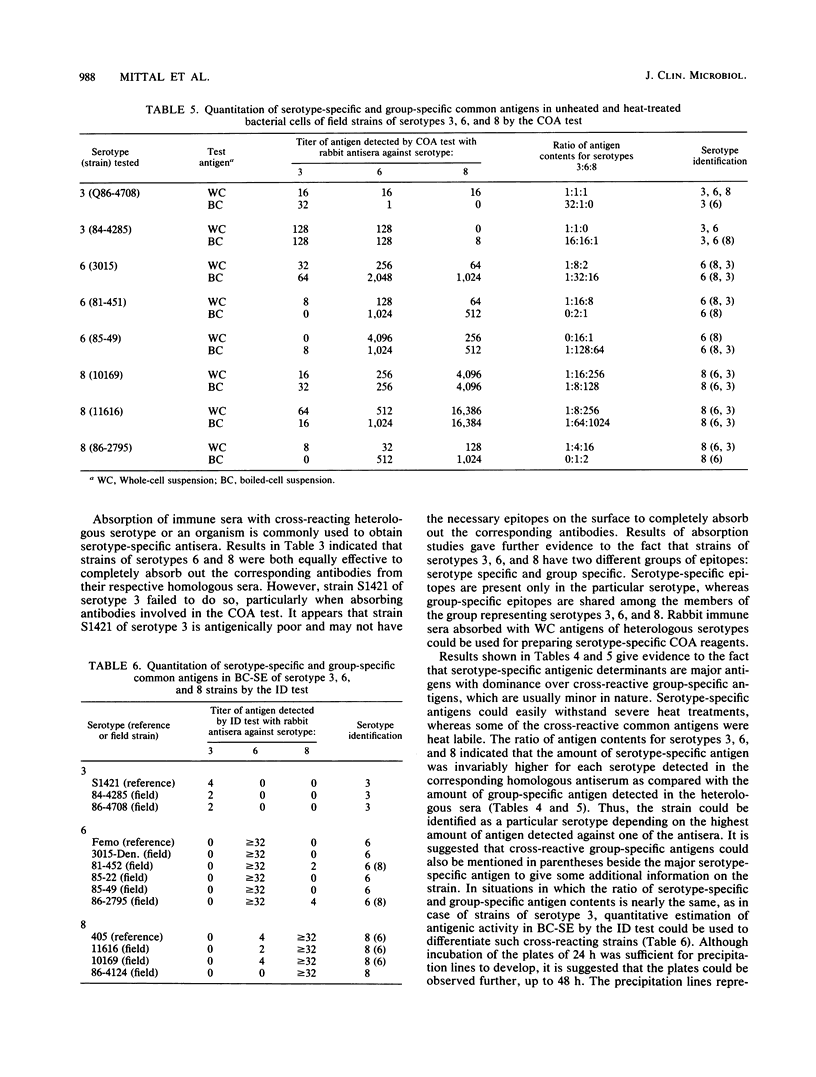
There are strong cross-reactions among strains of Actinobacillus pleuropneumoniae belonging to serotypes 3, 6, and 8. Various serological tests were used to differentiate these serotypes from each other. Tube agglutination, coagglutination, and indirect hemagglutination tests were not sufficiently sensitive to differentiate strains of serotypes 3, 6, and 8. However, higher antibody titers were obtained with a 2-mercaptoethanol agglutination test in homologous rabbit antisera. Absorption of immune sera with homologous and heterologous serotypes as well as quantitative estimation of antigenic activity in the unheated and heat-treated bacterial cell suspensions of reference strains with rabbit homologous and heterologous antisera revealed serotype-specific and cross-reacting group-specific antigens. Usually, serotype-specific antigens were major and dominant over group-specific antigens. The coagglutination test could be used quantitatively to measure the ratio of serotype-specific and group-specific antigens with rabbit hyperimmune sera against serotypes 3, 6, and 8. The highest antigen content for a particular serotype reflected serotype-specific antigen. For strains showing equal amounts of antigen for two or more serotypes in the coagglutination test, the immunodiffusion test with boiled cell-saline extract as the antigen and rabbit antisera against whole-cell suspensions of serotypes 3, 6, and 8 clearly revealed the serotype-specific antigen. It is suggested that coagglutination and immunodiffusion tests could be used successfully to determine the exact serotype of strains belonging to serotypes 3, 6, and 8.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Biberstein E. L., Gunnarsson A., Hurvell B. Cultural and biochemical criteria for the identification of haemophilus spp from swine. Am J Vet Res. 1977 Jan;38(1):7–11. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fenwick B. W., Osburn B. I. Immune responses to the lipopolysaccharides and capsular polysaccharides of Haemophilus pleuropneumoniae in convalescent and immunized pigs. Infect Immun. 1986 Nov;54(2):575–582. doi: 10.1128/iai.54.2.575-582.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gunnarsson A., Biberstein E. L., Hurvell B. Serologic studies on porcine strains of Haemophilus parahaemolyticus (pleuropneumoniae): agglutination reactions. Am J Vet Res. 1977 Aug;38(8):1111–1114. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunter D., Jones M. A., McKendry T. Serotyping of haemophilus pleuropneumonia isolates using ring precipitate tests. Vet Rec. 1983 Aug 13;113(7):158–158. doi: 10.1136/vr.113.7.158. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inzana T. J., Mathison B. Serotype specificity and immunogenicity of the capsular polymer of Haemophilus pleuropneumoniae serotype 5. Infect Immun. 1987 Jul;55(7):1580–1587. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.7.1580-1587.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mittal K. R., Higgins R., Lariviere S. Determination of antigenic specificity and relationship among Haemophilus pleuropneumoniae serotypes by an indirect hemagglutination test. J Clin Microbiol. 1983 May;17(5):787–790. doi: 10.1128/jcm.17.5.787-790.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mittal K. R., Higgins R., Lariviere S. Evaluation of slide agglutination and ring precipitation tests for capsular serotyping of Haemophilus pleuropneumoniae. J Clin Microbiol. 1982 Jun;15(6):1019–1023. doi: 10.1128/jcm.15.6.1019-1023.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mittal K. R., Higgins R., Larivière S. An evaluation of agglutination and coagglutination techniques for serotyping of Haemophilus pleuropneumoniae isolates. Am J Vet Res. 1987 Feb;48(2):219–226. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mittal K. R., Higgins R., Larivière S. Identification and serotyping of Haemophilus pleuropneumoniae by coagglutination test. J Clin Microbiol. 1983 Dec;18(6):1351–1354. doi: 10.1128/jcm.18.6.1351-1354.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mittal K. R., Higgins R., Larivière S., Leblanc D. A 2-mercaptoethanol tube agglutination test for diagnosis of Haemophilus pleuropneumoniae infection in pigs. Am J Vet Res. 1984 Apr;45(4):715–719. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mittal K. R., Higgins R., Larivière S. Serologic studies of Actinobacillus (Haemophilus) pleuropneumoniae strains of serotype-3 and their antigenic relationships with other A pleuropneumoniae serotypes in swine. Am J Vet Res. 1988 Feb;49(2):152–155. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicolet J. Sur l'hémophilose du pore. 3. Différenciation sérologique de Haemophilus parahaemolyticus. Zentralbl Bakteriol Orig. 1971;216(4):487–495. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nielsen R., O'Connor P. J. Serological characterization of 8 Haemophilus pleuropneumoniae strains and proposal of a new serotype: serotype 8. Acta Vet Scand. 1984;25(1):96–106. doi: 10.1186/BF03547283. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nielsen R. Serological characterization of Actinobacillus pleuropneumoniae strains and proposal of a new serotype: serotype 12. Acta Vet Scand. 1986;27(3):453–455. doi: 10.1186/BF03548158. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piffer I. A., Carter G. R., Botovchenco A. A. Identification of serotypes of Haemophilus pleuropneumoniae by counterimmunoelectrophoresis. Vet Rec. 1986 Mar 15;118(11):292–294. doi: 10.1136/vr.118.11.292. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosendal S., Boyd D. A. Haemophilus pleuropneumoniae serotyping. J Clin Microbiol. 1982 Nov;16(5):840–843. doi: 10.1128/jcm.16.5.840-843.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


