Abstract
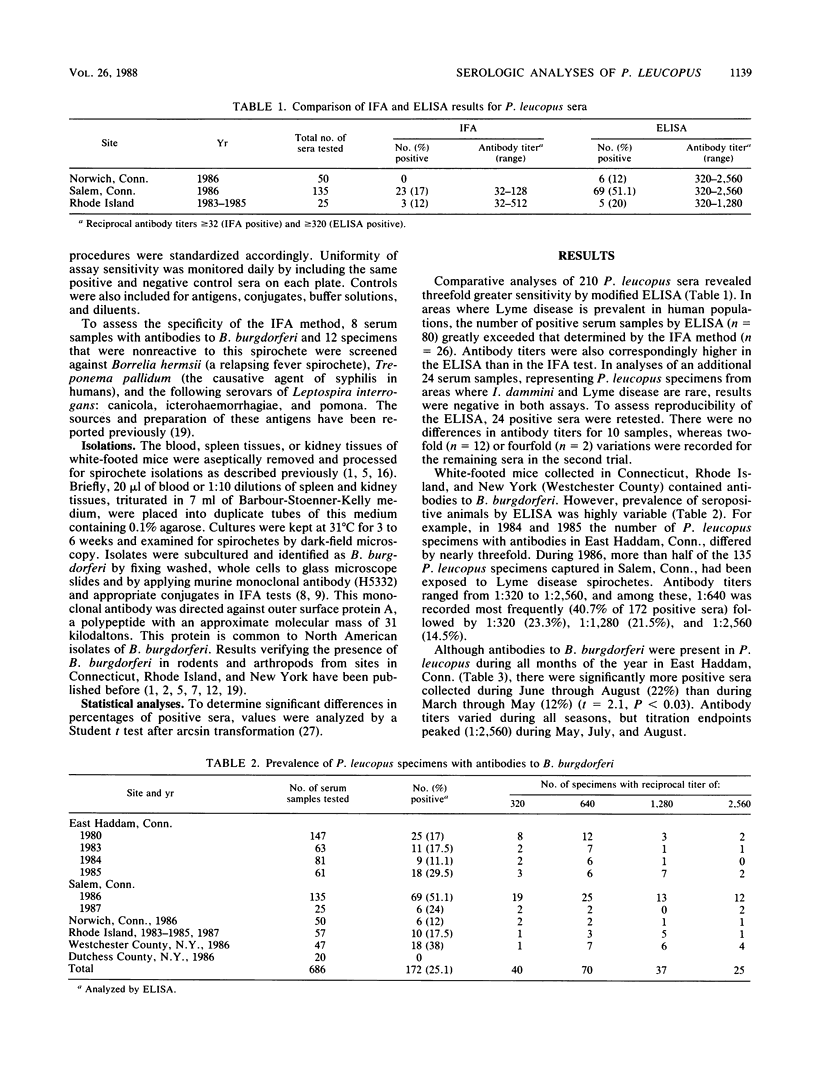
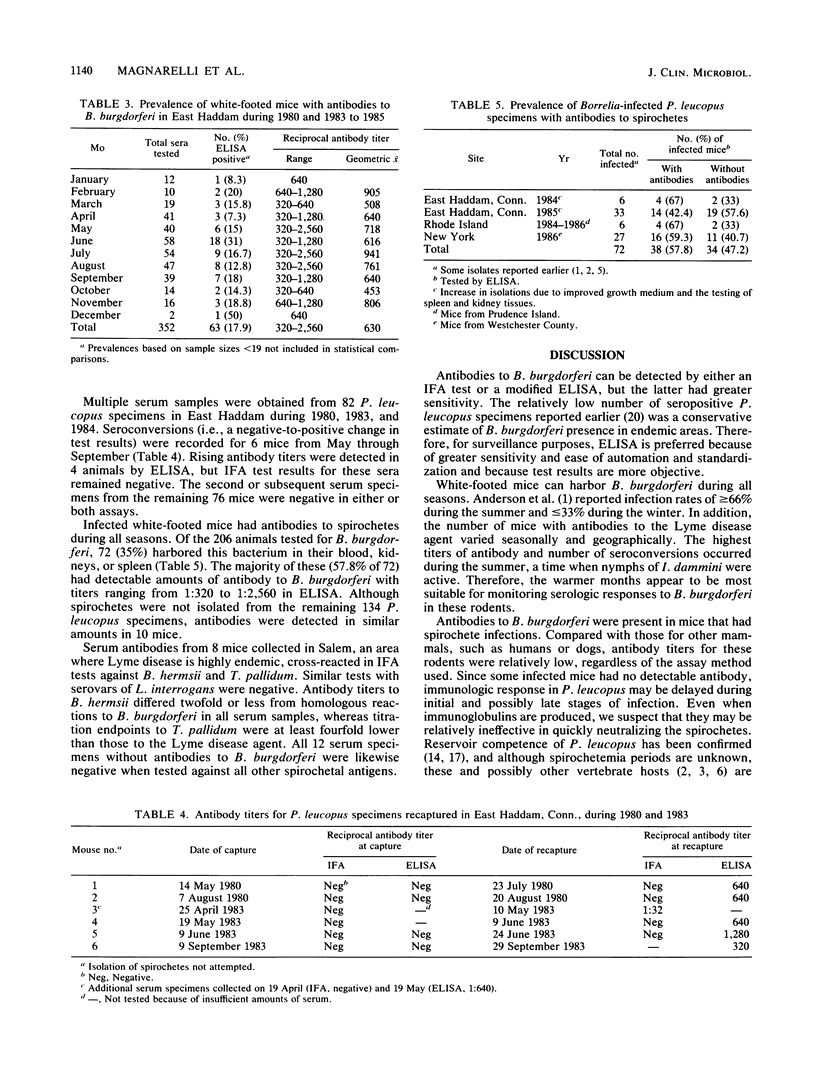
An enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) and indirect fluorescent-antibody test were used to detect antibodies to Borrelia burgdorferi, the causative agent of Lyme disease, in Peromyscus leucopus (white-footed mouse). Of the 661 mice captured in Connecticut, Rhode Island, and New York during 1980 and 1983 to 1987, 166 (25.1%) had antibodies to B. burgdorferi by ELISA. Comparative analyses of 210 serum specimens, collected in areas where Lyme disease is endemic, revealed a threefold difference in sensitivity between the ELISA (38.1% positive) and the indirect fluorescent-antibody method (12.4%). Although prevalence of seropositive P. leucopus was highest during June, elevated amounts of antibody (1:1,280 to 1:2,560) were detected in mice that harbored spirochetes during all seasons. Being reservoirs for B. burgdorferi, these rodents are suitable for monitoring spirochete infections at foci and should be included in field evaluations of control programs aimed at suppressing Lyme disease.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson J. F., Johnson R. C., Magnarelli L. A., Hyde F. W., Andreadis T. G. New infectious spirochete isolated from short-tailed shrews and white-footed mice. J Clin Microbiol. 1987 Aug;25(8):1490–1494. doi: 10.1128/jcm.25.8.1490-1494.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson J. F., Johnson R. C., Magnarelli L. A., Hyde F. W. Identification of endemic foci of Lyme disease: isolation of Borrelia burgdorferi from feral rodents and ticks (Dermacentor variabilis). J Clin Microbiol. 1985 Jul;22(1):36–38. doi: 10.1128/jcm.22.1.36-38.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson J. F., Johnson R. C., Magnarelli L. A., Hyde F. W. Involvement of birds in the epidemiology of the Lyme disease agent Borrelia burgdorferi. Infect Immun. 1986 Feb;51(2):394–396. doi: 10.1128/iai.51.2.394-396.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson J. F., Johnson R. C., Magnarelli L. A., Hyde F. W., Myers J. E. Prevalence of Borrelia burgdorferi and Babesia microti in mice on islands inhabited by white-tailed deer. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1987 Apr;53(4):892–894. doi: 10.1128/aem.53.4.892-894.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson J. F., Johnson R. C., Magnarelli L. A. Seasonal prevalence of Borrelia burgdorferi in natural populations of white-footed mice, Peromyscus leucopus. J Clin Microbiol. 1987 Aug;25(8):1564–1566. doi: 10.1128/jcm.25.8.1564-1566.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson J. F., Magnarelli L. A. Avian and mammalian hosts for spirochete-infected ticks and insects in a Lyme disease focus in Connecticut. Yale J Biol Med. 1984 Jul-Aug;57(4):627–641. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson J. F., Magnarelli L. A., McAninch J. B. Ixodes dammini and Borrelia burgdorferi in northern New England and upstate New York. J Parasitol. 1987 Apr;73(2):419–421. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barbour A. G., Heiland R. A., Howe T. R. Heterogeneity of major proteins in Lyme disease borreliae: a molecular analysis of North American and European isolates. J Infect Dis. 1985 Sep;152(3):478–484. doi: 10.1093/infdis/152.3.478. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barbour A. G., Tessier S. L., Todd W. J. Lyme disease spirochetes and ixodid tick spirochetes share a common surface antigenic determinant defined by a monoclonal antibody. Infect Immun. 1983 Aug;41(2):795–804. doi: 10.1128/iai.41.2.795-804.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bosler E. M., Ormiston B. G., Coleman J. L., Hanrahan J. P., Benach J. L. Prevalence of the Lyme disease spirochete in populations of white-tailed deer and white-footed mice. Yale J Biol Med. 1984 Jul-Aug;57(4):651–659. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bosler E. M., Schulze T. L. The prevalence and significance of Borrelia burgdorferi in the urine of feral reservoir hosts. Zentralbl Bakteriol Mikrobiol Hyg A. 1986 Dec;263(1-2):40–44. doi: 10.1016/s0176-6724(86)80100-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burgdorfer W., Barbour A. G., Hayes S. F., Benach J. L., Grunwaldt E., Davis J. P. Lyme disease-a tick-borne spirochetosis? Science. 1982 Jun 18;216(4552):1317–1319. doi: 10.1126/science.7043737. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carey A. B., Krinsky W. L., Main A. J. Ixodes dammini (Acari: Ixodidae) and associated ixodid ticks in South-central Connecticut, USA. J Med Entomol. 1980 Jan 31;17(1):89–99. doi: 10.1093/jmedent/17.1.89. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donahue J. G., Piesman J., Spielman A. Reservoir competence of white-footed mice for Lyme disease spirochetes. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1987 Jan;36(1):92–96. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1987.36.92. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Godsey M. S., Jr, Amundson T. E., Burgess E. C., Schell W., Davis J. P., Kaslow R., Edelman R. Lyme disease ecology in Wisconsin: distribution and host preferences of Ixodes dammini, and prevalence of antibody to Borrelia burgdorferi in small mammals. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1987 Jul;37(1):180–187. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1987.37.180. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson R. C., Marek N., Kodner C. Infection of Syrian hamsters with Lyme disease spirochetes. J Clin Microbiol. 1984 Dec;20(6):1099–1101. doi: 10.1128/jcm.20.6.1099-1101.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levine J. F., Wilson M. L., Spielman A. Mice as reservoirs of the Lyme disease spirochete. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1985 Mar;34(2):355–360. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1985.34.355. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loken K. I., Wu C. C., Johnson R. C., Bey R. F. Isolation of the Lyme disease spirochete from mammals in Minnesota. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1985 Jul;179(3):300–302. doi: 10.3181/00379727-179-42100. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Magnarelli L. A., Anderson J. F., Apperson C. S., Fish D., Johnson R. C., Chappell W. A. Spirochetes in ticks and antibodies to Borrelia burgdorferi in white-tailed deer from Connecticut, New York State, and North Carolina. J Wildl Dis. 1986 Apr;22(2):178–188. doi: 10.7589/0090-3558-22.2.178. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Magnarelli L. A., Anderson J. F., Burgdorfer W., Chappell W. A. Parasitism by Ixodes dammini (Acari: Ixodidae) and antibodies to spirochetes in mammals at Lyme disease foci in Connecticut, USA. J Med Entomol. 1984 Jan 26;21(1):52–57. doi: 10.1093/jmedent/21.1.52. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Magnarelli L. A., Anderson J. F., Chappell W. A. Geographic distribution of humans, raccoons, and white-footed mice with antibodies to Lyme disease spirochetes in Connecticut. Yale J Biol Med. 1984 Jul-Aug;57(4):619–626. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Magnarelli L. A., Anderson J. F., Fish D. Transovarial transmission of Borrelia burgdorferi in Ixodes dammini (Acari:Ixodidae). J Infect Dis. 1987 Jul;156(1):234–236. doi: 10.1093/infdis/156.1.234. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Magnarelli L. A., Anderson J. F., Johnson R. C. Cross-reactivity in serological tests for Lyme disease and other spirochetal infections. J Infect Dis. 1987 Jul;156(1):183–188. doi: 10.1093/infdis/156.1.183. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Magnarelli L. A., Meegan J. M., Anderson J. F., Chappell W. A. Comparison of an indirect fluorescent-antibody test with an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for serological studies of Lyme disease. J Clin Microbiol. 1984 Aug;20(2):181–184. doi: 10.1128/jcm.20.2.181-184.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Main A. J., Carey A. B., Carey M. G., Goodwin R. H. Immature Ixodes dammini (acari: Ixodidae) on small animals in Connecticut, USA. J Med Entomol. 1982 Nov 30;19(6):655–664. doi: 10.1093/jmedent/19.6.655. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steere A. C., Malawista S. E. Cases of Lyme disease in the United States: locations correlated with distribution of Ixodes dammini. Ann Intern Med. 1979 Nov;91(5):730–733. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-91-5-730. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


