Abstract
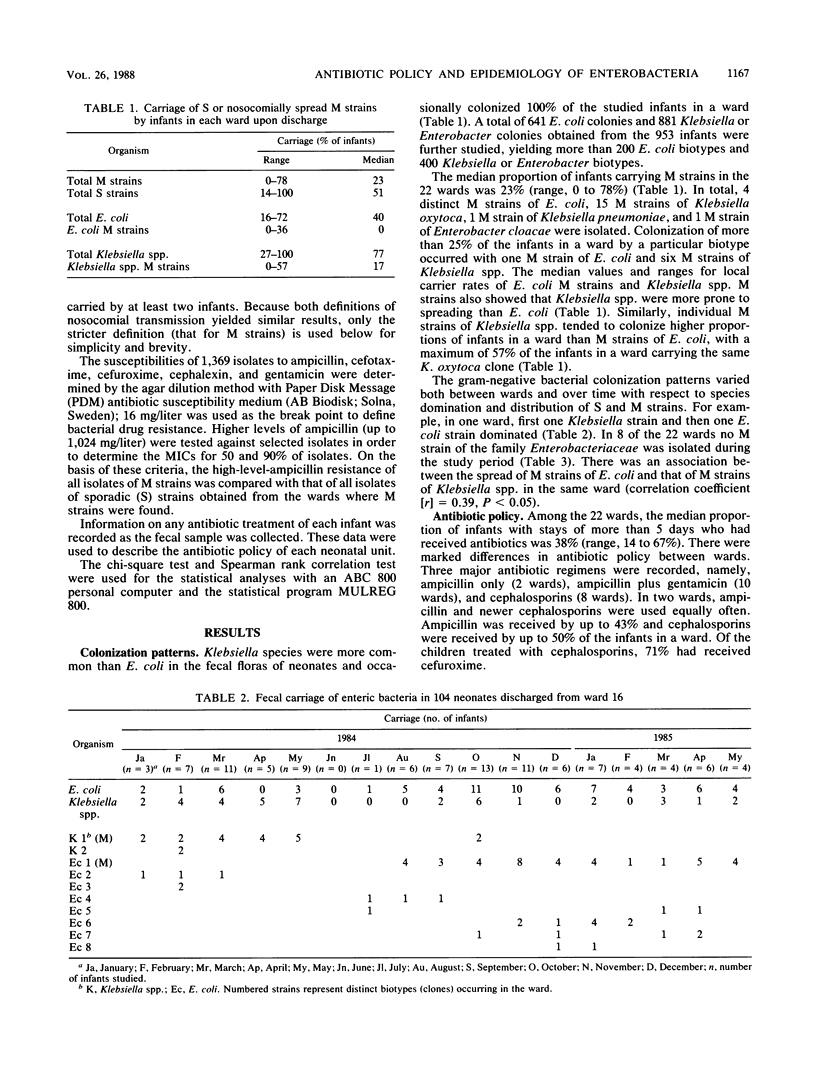
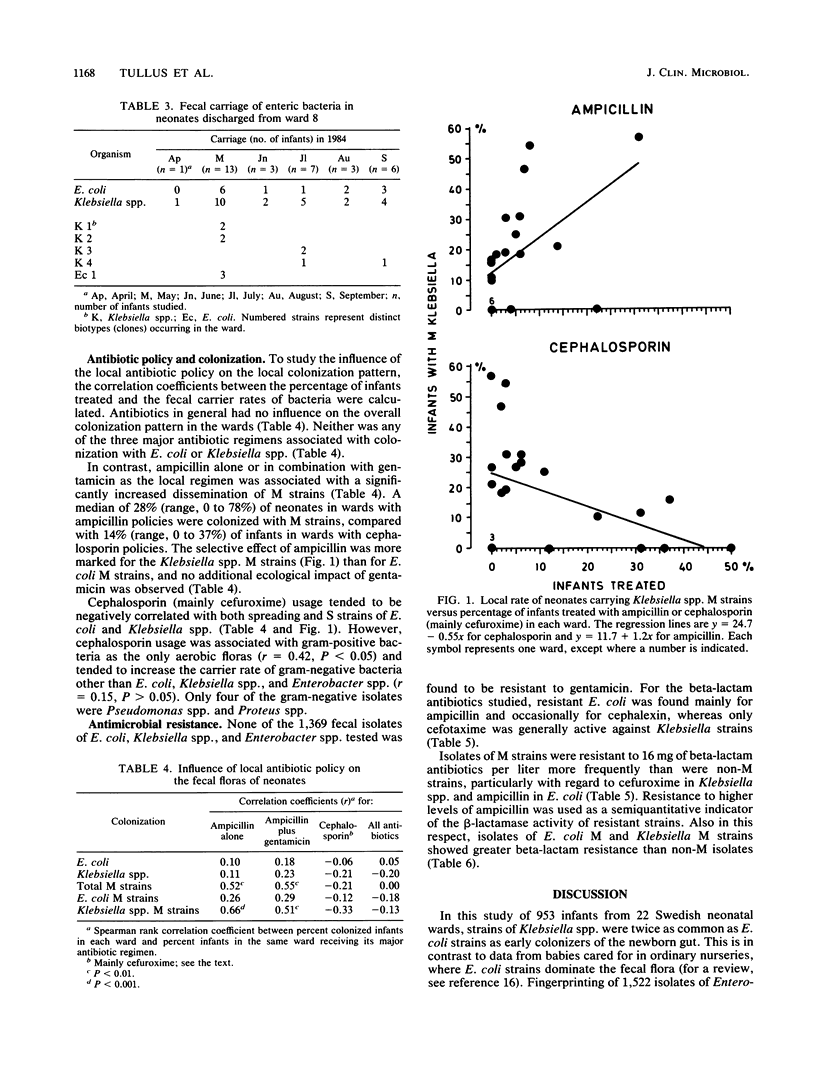
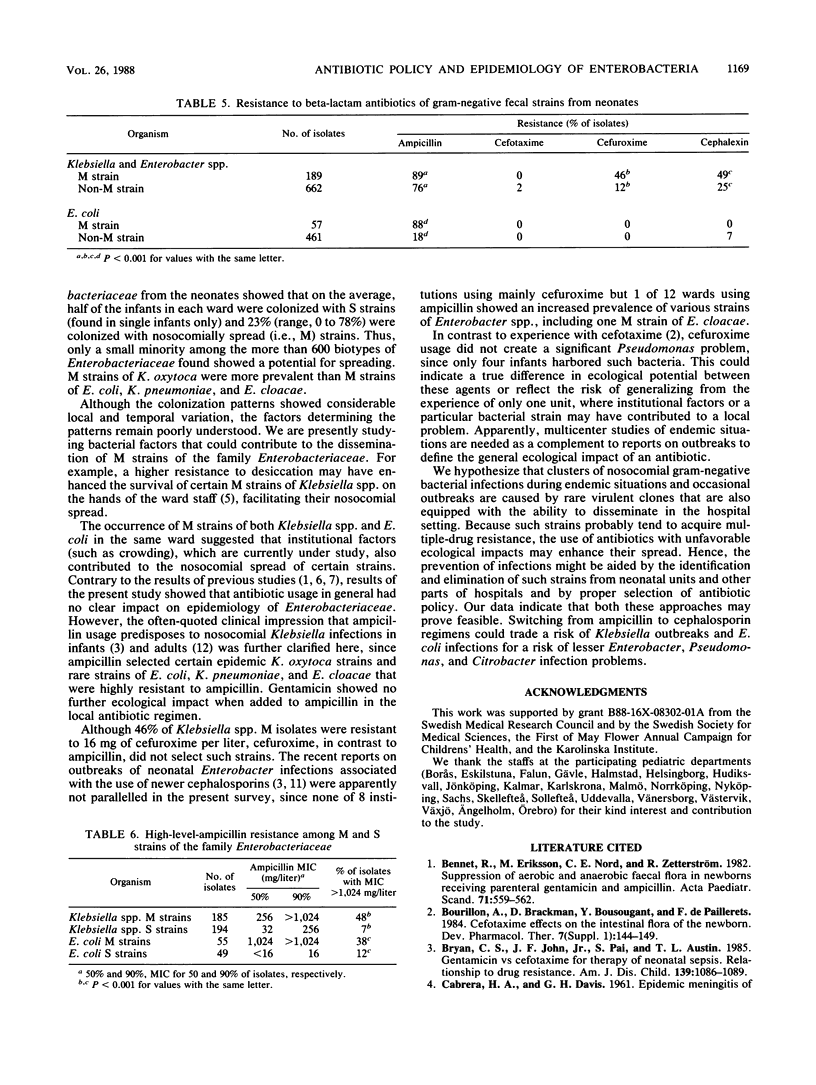
The gram-negative fecal floras from 953 infants were studied upon discharge of the infants from 22 neonatal wards. More than 600 distinct phenotypes of Escherichia coli, Klebsiella spp., and Enterobacter spp. were distinguished by high-resolution biotyping. The colonization patterns observed showed considerable local and temporal variation. The major (M) strains (phenotypes), which colonized more than 10% and up to 78% of the infants in a ward (median, 23%), were Klebsiella oxytoca (15 strains), E. coli (4 strains), Klebsiella pneumoniae (1 strain), and Enterobacter cloacae (1 strain). Resistance to beta-lactam antibiotics was more pronounced among M strains than among strains of enteric bacteria colonizing few or single infants only. Local antibiotic policy influenced the colonization patterns. Despite the fact that M strains of Klebsiella spp. were usually resistant to ampicillin as well as to cephalexin and cefuroxime, their local dissemination was associated with the use of ampicillin with or without gentamicin but not with the use of cefuroxime. It thus appeared that in the neonatal setting, ampicillin posed a greater risk of local spread of certain drug-resistant bacterial clones than a newer cephalosporin, such as cefuroxime.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bennet R., Eriksson M., Nord C. E., Zetterström R. Suppression of aerobic and anaerobic faecal flora in newborns receiving parenteral gentamicin and ampicillin. Acta Paediatr Scand. 1982 Jul;71(4):559–562. doi: 10.1111/j.1651-2227.1982.tb09474.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bourrillon A., Brackman D., Boussougant Y., de Paillerets F. Cefotaxime effects on the intestinal flora of the newborn. Dev Pharmacol Ther. 1984;7 (Suppl 1):144–149. doi: 10.1159/000457245. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bryan C. S., John J. F., Jr, Pai M. S., Austin T. L. Gentamicin vs cefotaxime for therapy of neonatal sepsis. Relationship to drug resistance. Am J Dis Child. 1985 Nov;139(11):1086–1089. doi: 10.1001/archpedi.1985.02140130024022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Casewell M. W., Desai N. Survival of multiply-resistant Klebsiella aerogenes and other gram-negative bacilli on finger-tips. J Hosp Infect. 1983 Dec;4(4):350–360. doi: 10.1016/0195-6701(83)90005-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldmann D. A., Leclair J., Macone A. Bacterial colonization of neonates admitted to an intensive care environment. J Pediatr. 1978 Aug;93(2):288–293. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(78)80523-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hable K. A., Matsen J. M., Wheeler D. J., Hunt C. E., Quie P. G. Klebsiella type 33 septicemia in an infant intensive care unit. J Pediatr. 1972 Jun;80(6):920–924. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(72)80002-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Markowitz S. M., Veazey J. M., Jr, Macrina F. L., Mayhall C. G., Lamb V. A. Sequential outbreaks of infection due to Klebsiella pneumoniae in a neonatal intensive care unit: implication of a conjugative R plasmid. J Infect Dis. 1980 Jul;142(1):106–112. doi: 10.1093/infdis/142.1.106. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Modi N., Damjanovic V., Cooke R. W. Outbreak of cephalosporin resistant Enterobacter cloacae infection in a neonatal intensive care unit. Arch Dis Child. 1987 Feb;62(2):148–151. doi: 10.1136/adc.62.2.148. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Price D. J., Sleigh J. D. Control of infection due to Klebsiella aerogenes in a neurosurgical unit by withdrawal of all antibiotics. Lancet. 1970 Dec 12;2(7685):1213–1215. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(70)92179-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reybrouck G. Role of the hands in the spread of nosocomial infections. 1. J Hosp Infect. 1983 Jun;4(2):103–110. doi: 10.1016/0195-6701(83)90040-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selden R., Lee S., Wang W. L., Bennett J. V., Eickhoff T. C. Nosocomial klebsiella infections: intestinal colonization as a reservoir. Ann Intern Med. 1971 May;74(5):657–664. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-74-5-657. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Svenningsen N. W., Békássy A. N., Christensen P., Kamme C. Nosocomial Klebsiella pneumoniae infection: clinical and hygienic measures in a neonatal intensive care unit. Scand J Infect Dis. 1984;16(1):29–35. doi: 10.3109/00365548409068406. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tullus K. Fecal colonization with P-fimbriated Escherichia coli in newborn children and relation to development of extraintestinal E. coli infections. Acta Paediatr Scand Suppl. 1987;334:1–35. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tullus K., Hörlin K., Svenson S. B., Källenius G. Epidemic outbreaks of acute pyelonephritis caused by nosocomial spread of P fimbriated Escherichia coli in children. J Infect Dis. 1984 Nov;150(5):728–736. doi: 10.1093/infdis/150.5.728. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tullus K., Sjöberg P. Epidemiological aspects of P-fimbriated E. coli. II. Variations in incidence of E. coli infections in children attending a neonatal ward. Acta Paediatr Scand. 1986 Mar;75(2):205–210. doi: 10.1111/j.1651-2227.1986.tb10185.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



