Abstract
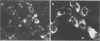
The Cowden strain of porcine group C rotavirus (pararotavirus) was adapted to serial passage in a continuous monkey kidney cell line (MA104). Key factors in its successful adaptation included use of virus passaged in primary porcine kidney cells as the initial inoculum, use of roller tubes, and addition of pancreatin to the maintenance medium. A cell culture immunofluorescence test was used to quantitate the virus at each passage level, since a possible cytopathic effect was obscured by the effects of pancreatin. The virus titers dropped after initial passage into MA104 cells but increased thereafter, with peak titers evident after 16 passages (10(7) immunofluorescence U/ml). Immune electron microscopy and genome electropherotyping were used to identify group C rotavirus particles and confirm group C rotavirus double-stranded RNA gel migration patterns, respectively, from infected cell culture supernatants. The electropherotype of the cell culture-propagated group C rotavirus was identical to that of the gut virulent virus from which it was derived. The cell culture-passaged group C rotavirus also retained its infectivity for gnotobiotic pigs. No group A rotavirus was detected in the intestinal contents of the pigs or in cell culture fluids from group C rotavirus-inoculated monolayers with the two former techniques or the cell culture immunofluorescence test. This is the first verified report of serial propagation of a non-group A rotavirus in a continuous cell line.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Almeida J. D., Hall T., Banatvala J. E., Totterdell B. M., Chrystie I. L. The effect of trypsin on the growth of rotavirus. J Gen Virol. 1978 Jul;40(1):213–218. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-40-1-213. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Askaa J., Bloch B. Infection in piglets with a porcine rotavirus-like virus. Experimental inoculation and ultrastructural examination. Arch Virol. 1984;80(4):291–303. doi: 10.1007/BF01311220. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Babiuk L. A., Mohammed K., Spence L., Fauvel M., Petro R. Rotavirus isolation and cultivation in the presence of trypsin. J Clin Microbiol. 1977 Dec;6(6):610–617. doi: 10.1128/jcm.6.6.610-617.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bohl E. H., Saif L. J., Theil K. W., Agnes A. G., Cross R. F. Porcine pararotavirus: detection, differentiation from rotavirus, and pathogenesis in gnotobiotic pigs. J Clin Microbiol. 1982 Feb;15(2):312–319. doi: 10.1128/jcm.15.2.312-319.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bohl E. H., Theil K. W., Saif L. J. Isolation and serotyping of porcine rotaviruses and antigenic comparison with other rotaviruses. J Clin Microbiol. 1984 Feb;19(2):105–111. doi: 10.1128/jcm.19.2.105-111.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bridger J. C., Pedley S., McCrae M. A. Group C rotaviruses in humans. J Clin Microbiol. 1986 Apr;23(4):760–763. doi: 10.1128/jcm.23.4.760-763.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cross R. F., Moorhead P. D. An azure and eosin rapid staining technique. Can J Comp Med. 1969 Oct;33(4):317–317. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Estes M. K., Graham D. Y., Mason B. B. Proteolytic enhancement of rotavirus infectivity: molecular mechanisms. J Virol. 1981 Sep;39(3):879–888. doi: 10.1128/jvi.39.3.879-888.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fernelius A. L., Ritchie A. E., Classick L. G., Norman J. O., Mebus C. A. Cell culture adaptation and propagation of a reovirus-like agent of calf diarrhea from a field outbreak in Nebraska. Arch Gesamte Virusforsch. 1972;37(1):114–130. doi: 10.1007/BF01241157. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fukusho A., Shimizu Y., Ito Y. Isolation of cytopathic porcine rotavirus in cell roller culture in the presence of trypsin. Arch Virol. 1981;69(1):49–60. doi: 10.1007/BF01315265. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenberg H. B., Kalica A. R., Wyatt R. G., Jones R. W., Kapikian A. Z., Chanock R. M. Rescue of noncultivatable human rotavirus by gene reassortment during mixed infection with ts mutants of a cultivatable bovine rotavirus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jan;78(1):420–424. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.1.420. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malherbe H. H., Strickland-Cholmley M. Simian virus SA11 and the related O agent. Arch Gesamte Virusforsch. 1967;22(1):235–245. doi: 10.1007/BF01240518. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McNulty M. S., Allan G. M., McFerran J. B. Cell culture studies with a cytopathic bovine rotavirus. Arch Virol. 1977;54(3):201–209. doi: 10.1007/BF01314786. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McNulty M. S., Allan G. M., Todd D., McFerran J. B., McCracken R. M. Isolation from chickens of a rotavirus lacking the rotavirus group antigen. J Gen Virol. 1981 Aug;55(Pt 2):405–413. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-55-2-405. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pedley S., Bridger J. C., Brown J. F., McCrae M. A. Molecular characterization of rotaviruses with distinct group antigens. J Gen Virol. 1983 Oct;64(Pt 10):2093–2101. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-64-10-2093. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pedley S., Bridger J. C., Chasey D., McCrae M. A. Definition of two new groups of atypical rotaviruses. J Gen Virol. 1986 Jan;67(Pt 1):131–137. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-67-1-131. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodger S. M., Bishop R. F., Holmes I. H. Detection of a rotavirus-like agent associated with diarrhea in an infant. J Clin Microbiol. 1982 Oct;16(4):724–726. doi: 10.1128/jcm.16.4.724-726.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saif L. J., Bohl E. H., Kohler E. M., Hughes J. H. Immune electron microscopy of transmissible gastroenteritis virus and rotavirus (reovirus-like agent) of swine. Am J Vet Res. 1977 Jan;38(1):13–20. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saif L. J., Bohl E. H., Theil K. W., Cross R. F., House J. A. Rotavirus-like, calicivirus-like, and 23-nm virus-like particles associated with diarrhea in young pigs. J Clin Microbiol. 1980 Jul;12(1):105–111. doi: 10.1128/jcm.12.1.105-111.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sato K., Inaba Y., Shinozaki T., Fujii R., Matumoto M. Isolation of human rotavirus in cell cultures: brief report. Arch Virol. 1981;69(2):155–160. doi: 10.1007/BF01315159. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Terrett L. A., Saif L. J. Serial propagation of porcine group C rotavirus (pararotavirus) in primary porcine kidney cell cultures. J Clin Microbiol. 1987 Jul;25(7):1316–1319. doi: 10.1128/jcm.25.7.1316-1319.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Terrett L. A., Saif L. J., Theil K. W., Kohler E. M. Physicochemical characterization of porcine pararotavirus and detection of virus and viral antibodies using cell culture immunofluorescence. J Clin Microbiol. 1987 Feb;25(2):268–272. doi: 10.1128/jcm.25.2.268-272.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Theil K. W., Bohl E. H., Agnes A. G. Cell culture propagation of porcine rotavirus (reovirus-like agent). Am J Vet Res. 1977 Nov;38(11):1765–1768. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Theil K. W., McCloskey C. M., Saif L. J., Redman D. R., Bohl E. H., Hancock D. D., Kohler E. M., Moorhead P. D. Rapid, simple method of preparing rotaviral double-stranded ribonucleic acid for analysis by polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. J Clin Microbiol. 1981 Sep;14(3):273–280. doi: 10.1128/jcm.14.3.273-280.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wyatt R. G., James W. D., Bohl E. H., Theil K. W., Saif L. J., Kalica A. R., Greenberg H. B., Kapikian A. Z., Chanock R. M. Human rotavirus type 2: cultivation in vitro. Science. 1980 Jan 11;207(4427):189–191. doi: 10.1126/science.6243190. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]