Abstract
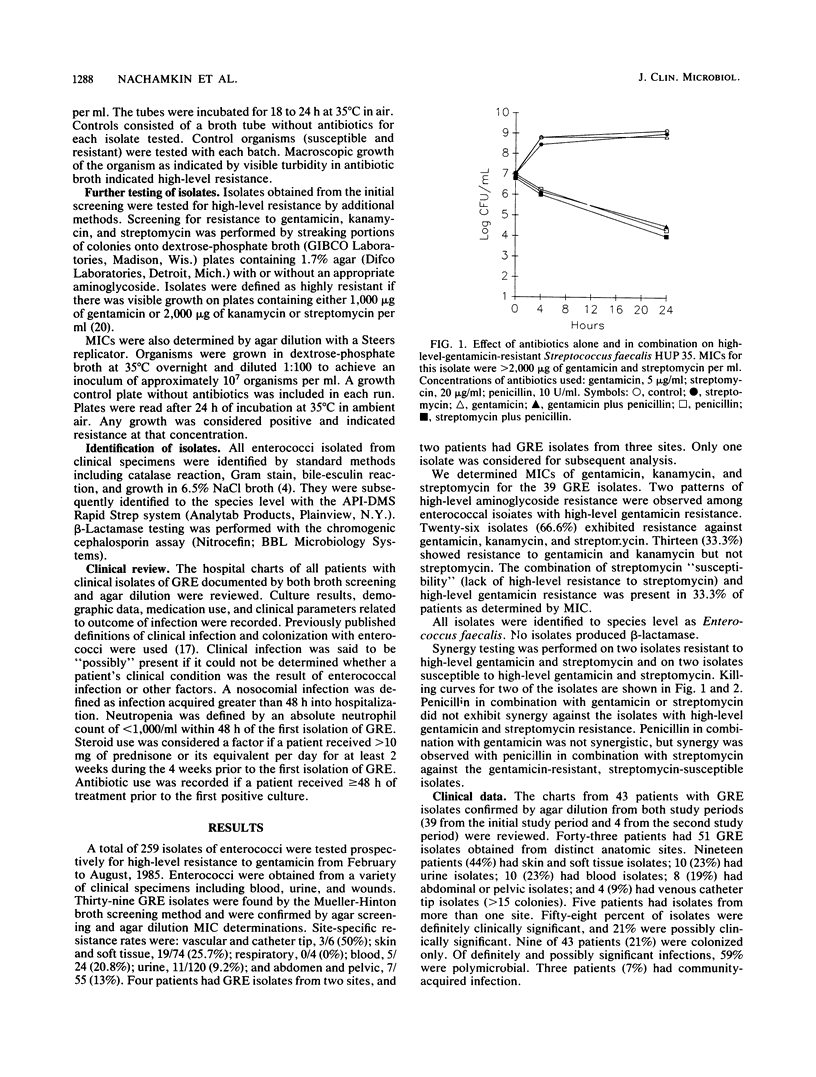
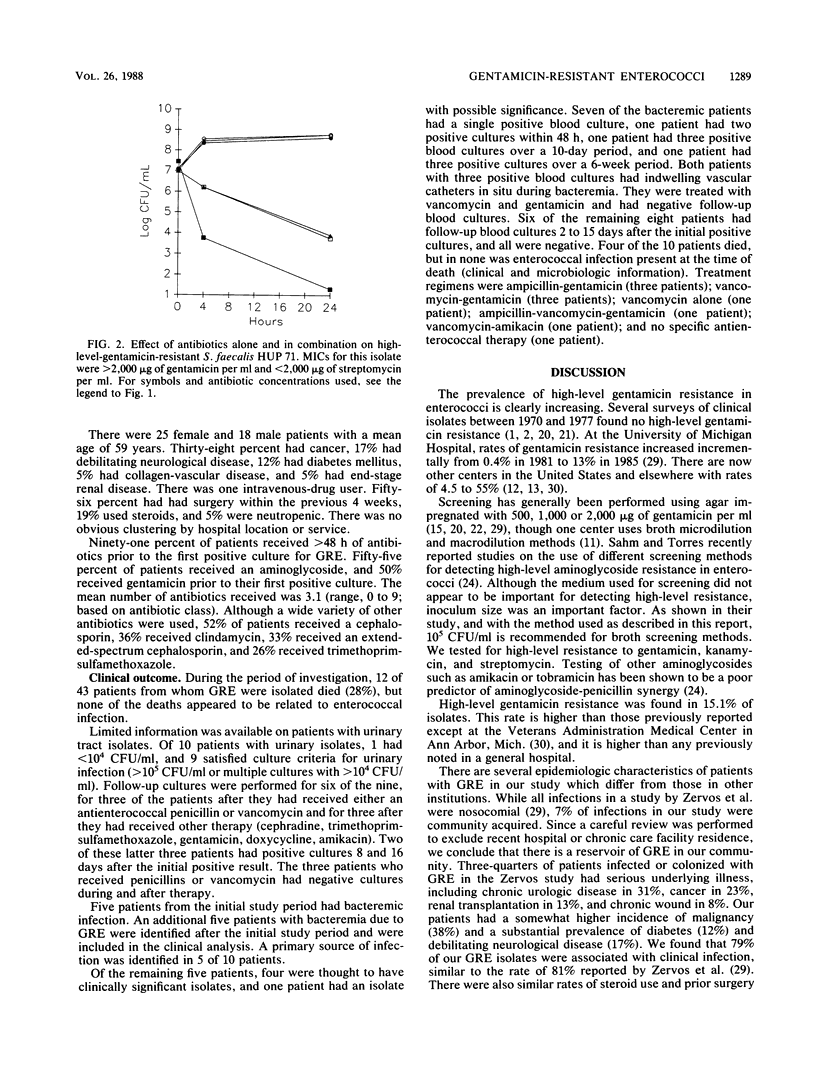
Enterococci isolated from different body sites were tested for high-level gentamicin resistance. A total of 259 enterococcal isolates were screened for resistance (MIC, greater than 2,000 micrograms/ml) by a broth-tube method. Thirty-nine (15.1%) were found to exhibit resistance and were confirmed by agar screening (1,000 micrograms/ml) and agar dilution MIC determinations. The majority of isolates also showed high-level resistance to kanamycin and streptomycin. The remaining isolates showed high-level resistance to gentamicin and kanamycin but not streptomycin. Synergy testing of several isolates confirmed the correlation between lack of synergy and high-level resistance. A retrospective clinical review was performed. Most patients had a source of definite or likely infection (79%). Serious infections such as endocarditis or meningitis were not observed during the course of this study. Retrospective clinical data suggest that in cases not involving endocarditis or meningitis, neither infection refractory to therapy nor relapse of infection is a common sequela of infection with gentamicin-resistant enterococci in hospitalized patients.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Basker M. J., Slocombe B., Sutherland R. Aminoglycoside-resistant enterococci. J Clin Pathol. 1977 Apr;30(4):375–380. doi: 10.1136/jcp.30.4.375. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calderwood S. A., Wennersten C., Moellering R. C., Jr, Kunz L. J., Krogstad D. J. Resistance to six aminoglycosidic aminocyclitol antibiotics among enterococci: prevalence, evolution, and relationship to synergism with penicillin. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1977 Sep;12(3):401–405. doi: 10.1128/aac.12.3.401. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen H. Y., Williams J. D. Transferable resistance and aminoglycoside-modifying enzymes in enterococci. J Med Microbiol. 1985 Oct;20(2):187–196. doi: 10.1099/00222615-20-2-187. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gross P. A., Harkavy L. M., Barden G. E., Flower M. F. The epidemiology of nosocomial enterococcal urinary tract infection. Am J Med Sci. 1976 Jul-Aug;272(1):75–81. doi: 10.1097/00000441-197607000-00009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris J. A., Cobbs C. G. Persistent gram-negative bacteremia. Observations in twenty patients. Am J Surg. 1973 Jun;125(6):705–717. doi: 10.1016/0002-9610(73)90169-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herzstein J., Ryan J. L., Mangi R. J., Greco T. P., Andriole V. T. Optimal therapy for enterococcal endocarditis. Am J Med. 1984 Feb;76(2):186–191. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(84)90772-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horodniceanu T., Bougueleret L., El-Solh N., Bieth G., Delbos F. High-level, plasmid-borne resistance to gentamicin in Streptococcus faecalis subsp. zymogenes. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1979 Nov;16(5):686–689. doi: 10.1128/aac.16.5.686. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ikeda D. P., Barry A. L., Andersen S. G. Emergence of Streptococcus faecalis isolates with high-level resistance to multiple aminocyclitol aminoglycosides. Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis. 1984 Jun;2(3):171–177. doi: 10.1016/0732-8893(84)90027-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaye D. Enterococci. Biologic and epidemiologic characteristics and in vitro susceptibility. Arch Intern Med. 1982 Oct 25;142(11):2006–2009. doi: 10.1001/archinte.142.11.2006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McHenry M. C., Gavan T. L., Hawk W. A., Van Ommen R. A., Ma C. A. Gram-negative bacteremia of long duration. Clinical study of 29 patients. Cleve Clin Q. 1973 Summer;40(2):47–56. doi: 10.3949/ccjm.40.2.47. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mederski-Samoraj B. D., Murray B. E. High-level resistance to gentamicin in clinical isolates of enterococci. J Infect Dis. 1983 Apr;147(4):751–757. doi: 10.1093/infdis/147.4.751. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moellering R. C., Jr Antibiotic synergism--lessons from the enterococcus. Trans Am Clin Climatol Assoc. 1983;94:55–62. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moellering R. C., Jr Enterococcal infections in patients treated with moxalactam. Rev Infect Dis. 1982 Nov-Dec;4 (Suppl):S708–S711. doi: 10.1093/clinids/4.supplement_3.s708. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moellering R. C., Jr, Korzeniowski O. M., Sande M. A., Wennersten C. B. Species-specific resistance to antimocrobial synergism in Streptococcus faecium and Streptococcus faecalis. J Infect Dis. 1979 Aug;140(2):203–208. doi: 10.1093/infdis/140.2.203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moellering R. C., Jr, Wennersten C., Medrek T., Weinberg A. N. Prevalence of high-level resistance to aminoglycosides in clinical isolates of enterococci. Antimicrob Agents Chemother (Bethesda) 1970;10:335–340. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moellering R. C., Jr, Wennersten C., Weinberg A. N. Synergy of penicillin and gentamicin against Enterococci. J Infect Dis. 1971 Dec;124 (Suppl):S207–S209. doi: 10.1093/infdis/124.supplement_1.s207. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray B. E., Tsao J., Panida J. Enterococci from Bangkok, Thailand, with high-level resistance to currently available aminoglycosides. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1983 Jun;23(6):799–802. doi: 10.1128/aac.23.6.799. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sahm D. F., Torres C. Effects of medium and inoculum variations on screening for high-level aminoglycoside resistance in Enterococcus faecalis. J Clin Microbiol. 1988 Feb;26(2):250–256. doi: 10.1128/jcm.26.2.250-256.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scheld W. M., Mandell G. L. Enigmatic enterococcal endocarditis. Ann Intern Med. 1984 Jun;100(6):904–905. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-100-6-904. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seligman S. Treatment of enterococcal endocarditis with oral amoxicillin and intramuscular gentamicin. J Infect Dis. 1974 Jun;129(0):suppl–suppl:S215. doi: 10.1093/infdis/129.supplement_2.s213. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Standiford H. D., De Maine J. B., Kirby W. M. Antibiotic synergism of enterococci. Relation to inhibitory concentrations. Arch Intern Med. 1970 Aug;126(2):255–259. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toala P., McDonald A., Wilcox C., Finland M. Susceptibility of group D streptococcus (enterococcus) to 21 antibiotics in vitro, with special reference to species differences. Am J Med Sci. 1969 Dec;258(6):416–430. doi: 10.1097/00000441-196912000-00006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tofte R. W., Solliday J. A., Crossley K. B. Susceptibilities of enterococci to twelve antibiotics. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1984 Apr;25(4):532–533. doi: 10.1128/aac.25.4.532. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zervos M. J., Dembinski S., Mikesell T., Schaberg D. R. High-level resistance to gentamicin in Streptococcus faecalis: risk factors and evidence for exogenous acquisition of infection. J Infect Dis. 1986 Jun;153(6):1075–1083. doi: 10.1093/infdis/153.6.1075. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zervos M. J., Kauffman C. A., Therasse P. M., Bergman A. G., Mikesell T. S., Schaberg D. R. Nosocomial infection by gentamicin-resistant Streptococcus faecalis. An epidemiologic study. Ann Intern Med. 1987 May;106(5):687–691. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-106-5-687. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



