Abstract
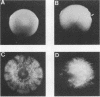
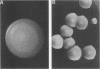
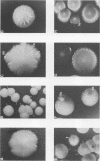
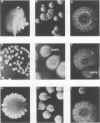
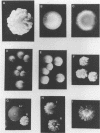
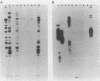
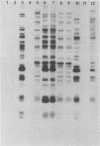
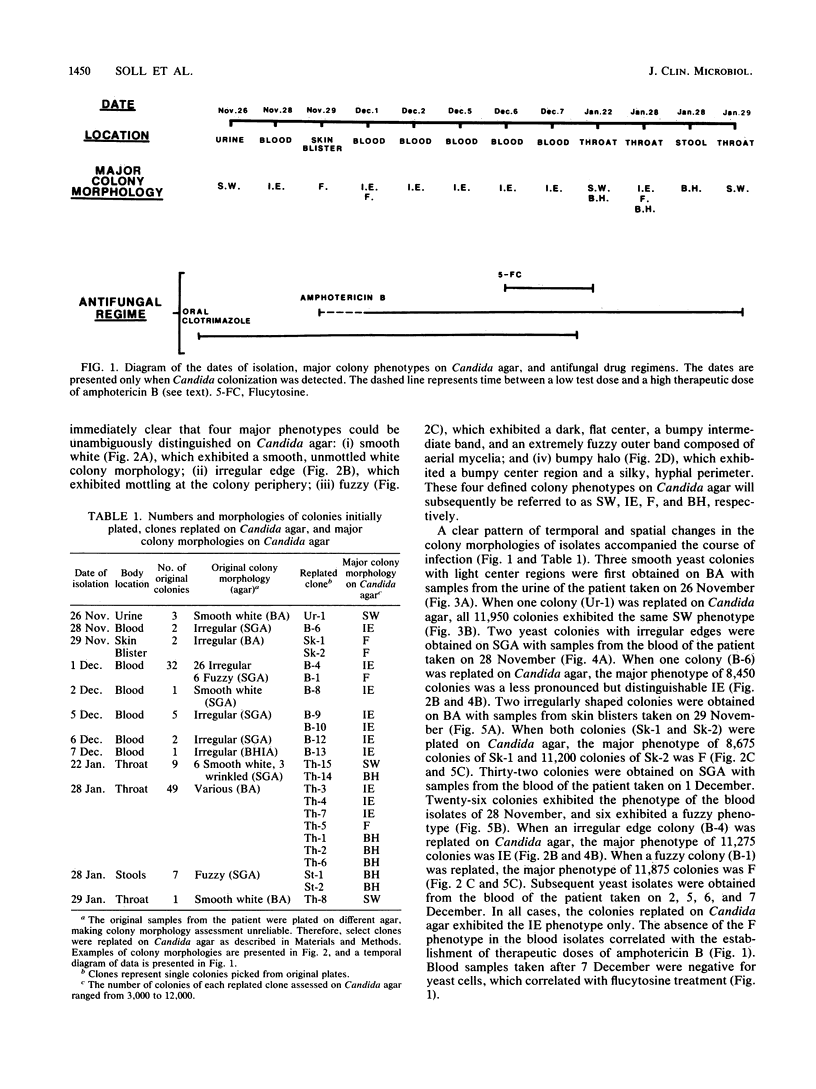
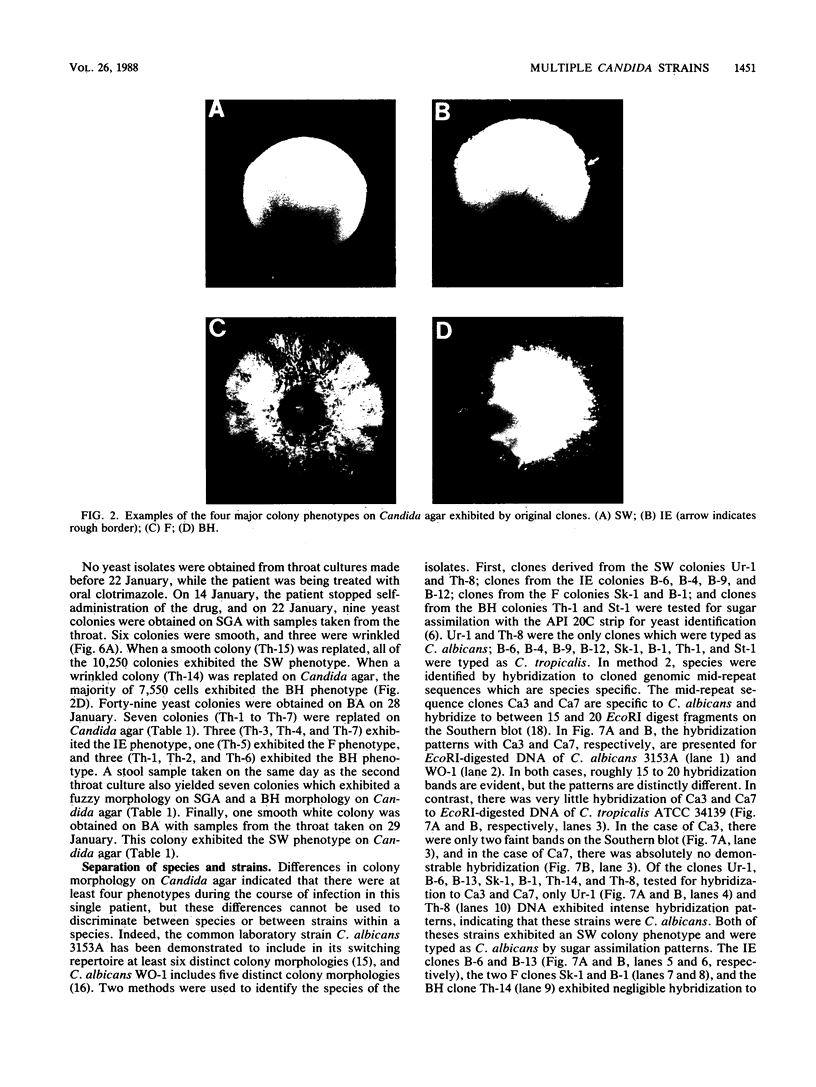
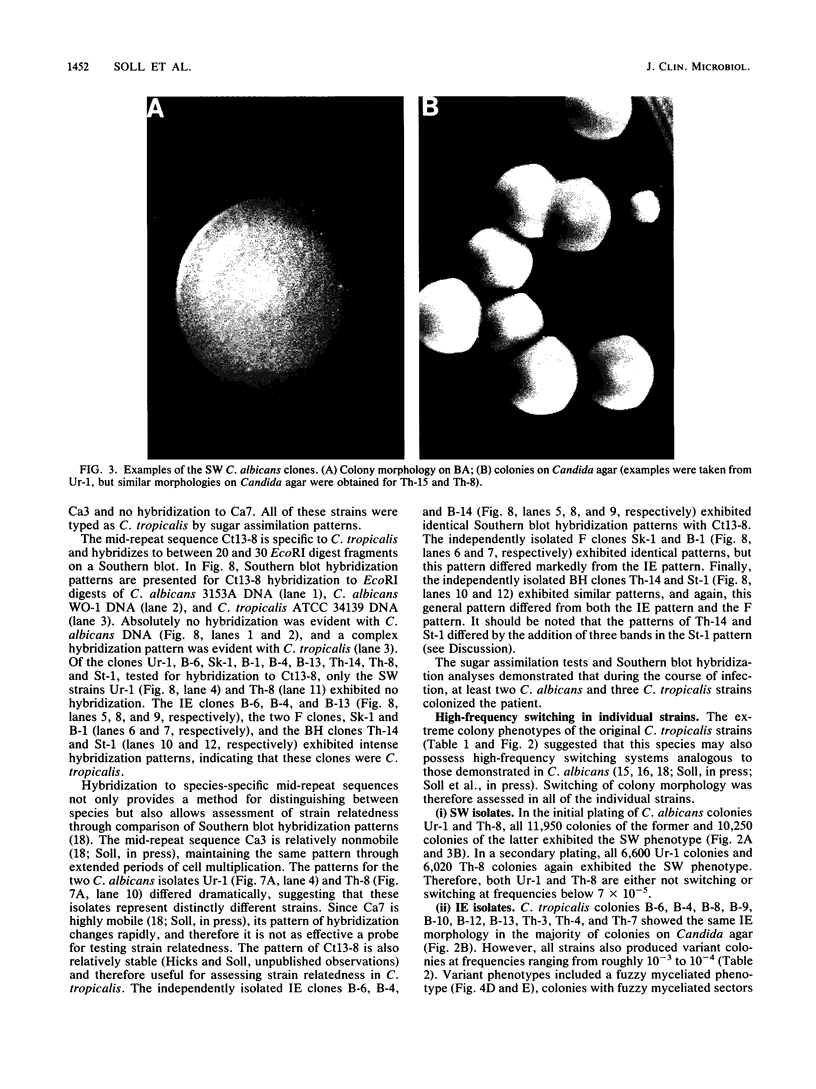
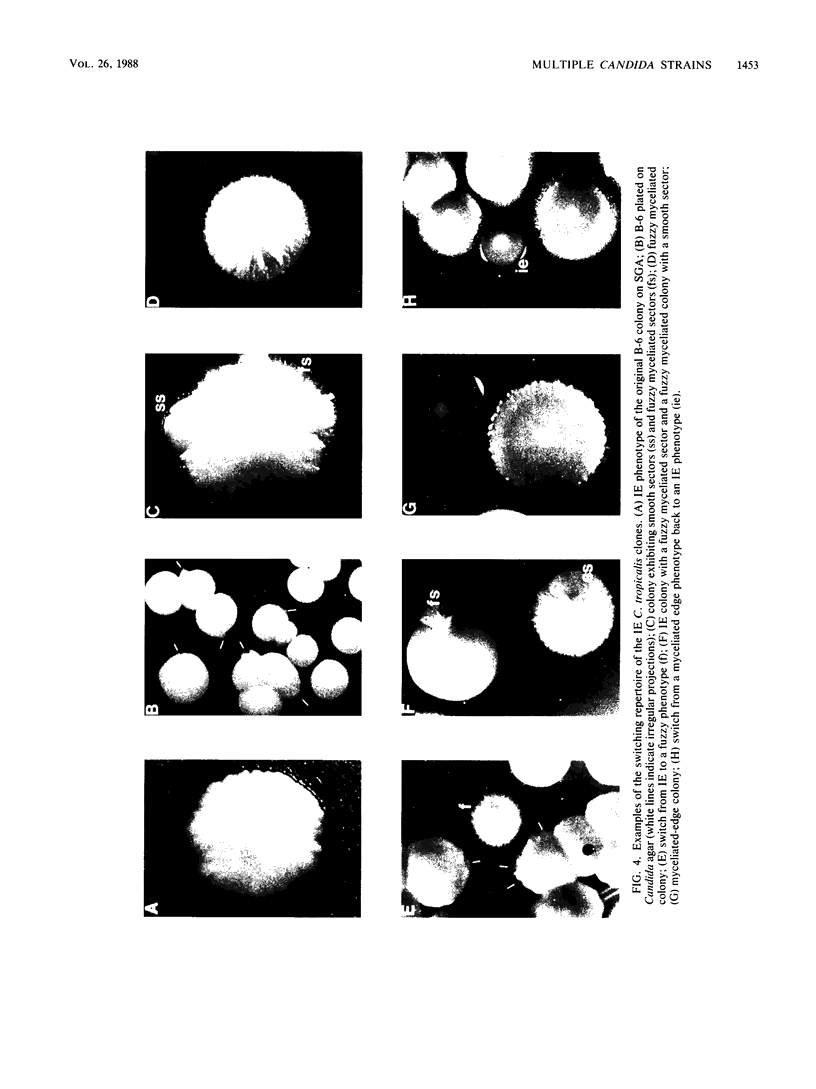
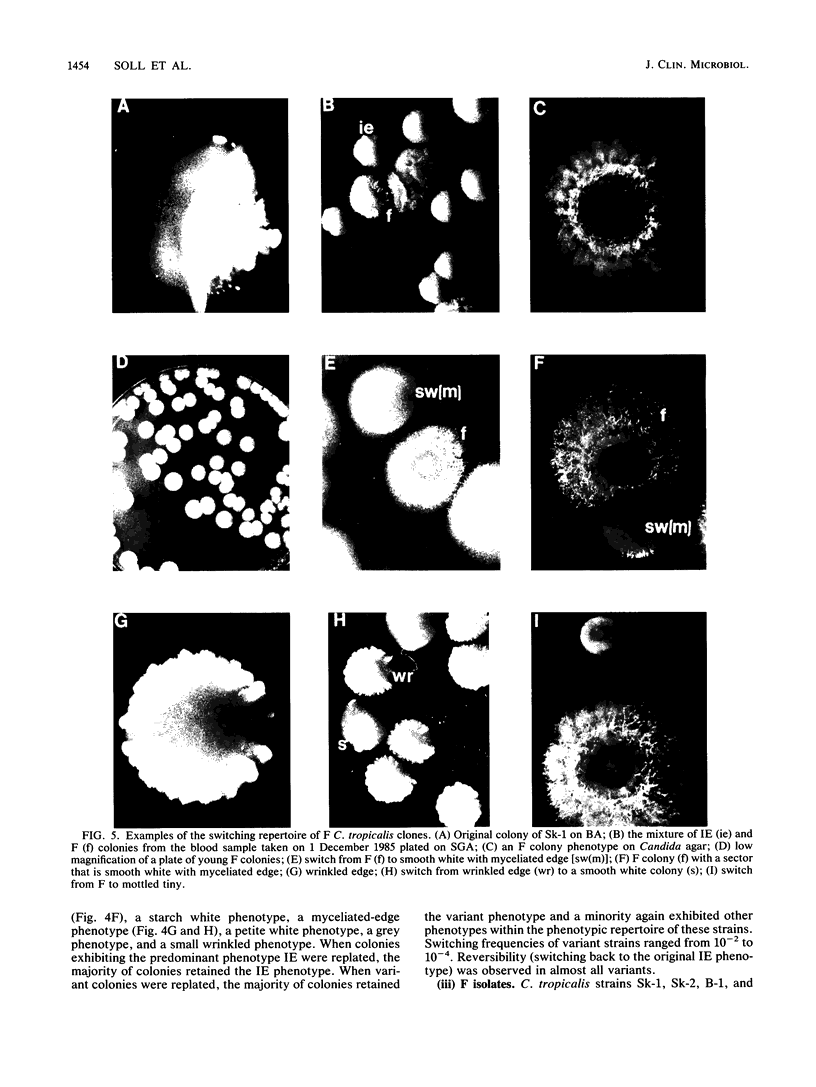
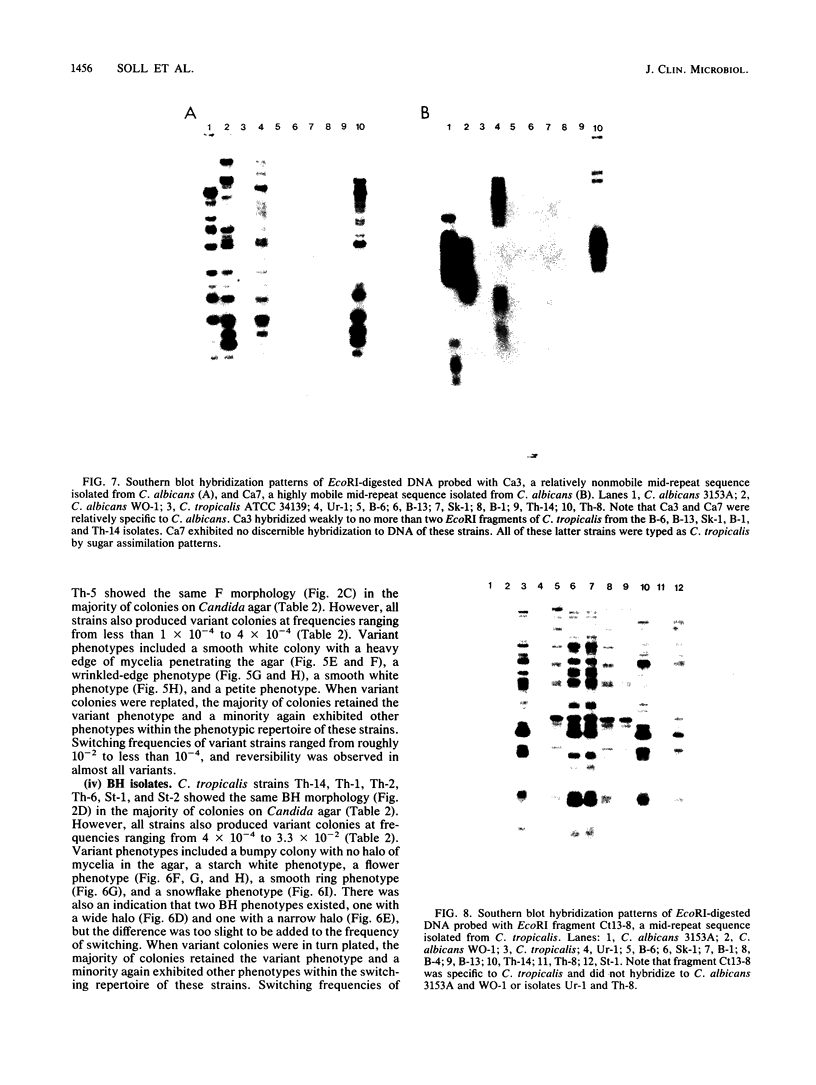
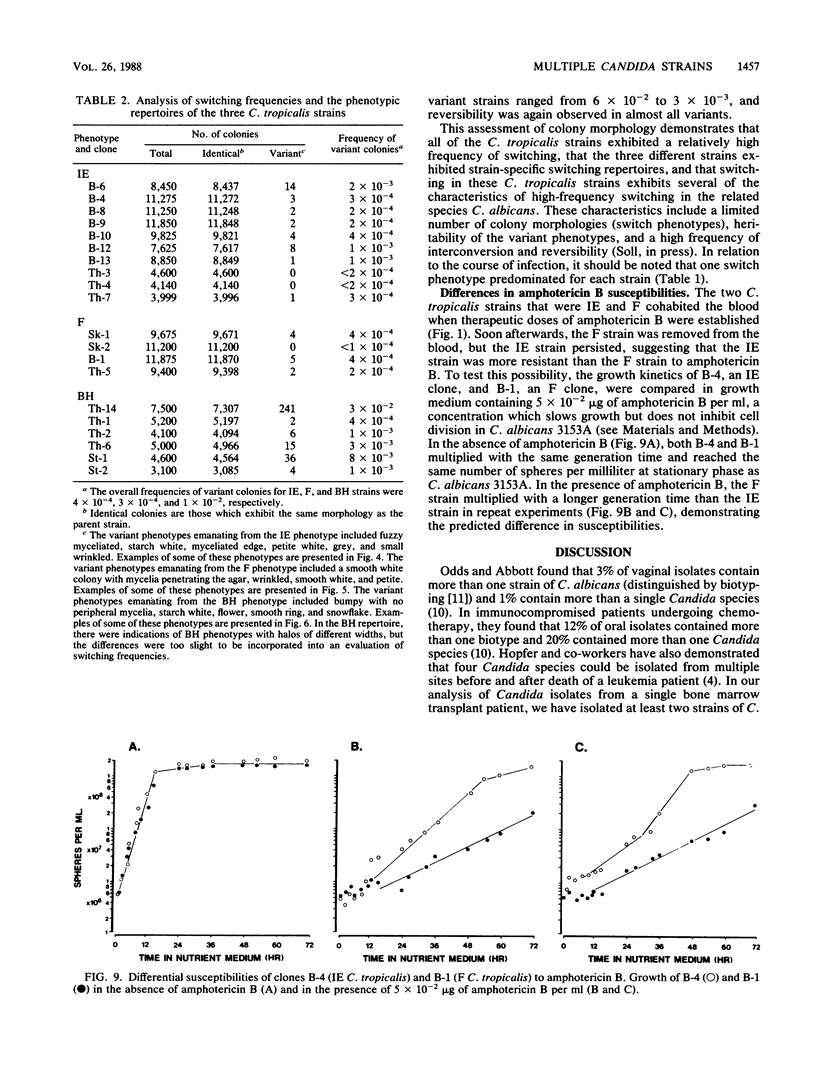
Species and strain variabilities have been monitored during the history of a prolonged Candida infection in a single compromised bone marrow transplant patient by analyzing sugar assimilation patterns, high-frequency switching repertoires, and Southern blot hybridization patterns with two cloned mid-repeat sequences (Ca3 and Ca7) which are species specific for Candida albicans and one cloned mid-repeat sequence (Ct13-8) which is species specific for Candida tropicalis. Evidence is presented that during the course of this infection (i) two strains of C. albicans and three strains of C. tropicalis were distinguished by their switching repertoires, Southern blot hybridization patterns, and sugar assimilation patterns; (ii) the three C. tropicalis strains were in a high-frequency mode of switching; (iii) two C. tropicalis strains coexisted in the blood and three C. tropicalis strains coexisted in the throat at different times during the history of the infection; (iv) amphotericin B treatment selectively removed one of two C. tropicalis strains coexisting in the blood and this strain exhibited greater susceptibility to amphotericin B in vitro (the remaining strain was subsequently removed from the blood by flucytosine treatment); and (v) both the strain removed from the blood by amphotericin B and the strain removed from the blood by flucytosine reappeared several days later at another site of infection. It is demonstrated for the first time that C. tropicalis is capable of high-frequency switching of colony morphology just as C. albicans is, that there is more than one strain-specific switching repertoire in C. tropicalis, and that a C. tropicalis mid-repeat sequence can be used for discriminating species and assessing strain relatedness, as previously demonstrated for C. albicans mid-repeat sequences.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson J. M., Soll D. R. Unique phenotype of opaque cells in the white-opaque transition of Candida albicans. J Bacteriol. 1987 Dec;169(12):5579–5588. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.12.5579-5588.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cryer D. R., Eccleshall R., Marmur J. Isolation of yeast DNA. Methods Cell Biol. 1975;12:39–44. doi: 10.1016/s0091-679x(08)60950-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hopfer R. L., Fainstein V., Luna M. P., Bodey G. P. Disseminated candidiasis caused by four different Candida species. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 1981 Sep;105(9):454–455. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Land G. A., Harrison B. A., Hulme K. L., Cooper B. H., Byrd J. C. Evaluation of the new API 20C strip for yeast identification against a conventional method. J Clin Microbiol. 1979 Sep;10(3):357–364. doi: 10.1128/jcm.10.3.357-364.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Land G., Stotler R., Land K., Staneck J. Update and evaluation of the AutoMicrobic yeast identification system. J Clin Microbiol. 1984 Oct;20(4):649–652. doi: 10.1128/jcm.20.4.649-652.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee K. L., Buckley H. R., Campbell C. C. An amino acid liquid synthetic medium for the development of mycelial and yeast forms of Candida Albicans. Sabouraudia. 1975 Jul;13(2):148–153. doi: 10.1080/00362177585190271. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCreight M. C., Warnock D. W., Martin M. V. Resistogram typing of Candida albicans isolates from oral and cutaneous sites in irradiated patients. Sabouraudia. 1985 Dec;23(6):403–406. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Odds F. C., Abbott A. B. A simple system for the presumptive identification of Candida albicans and differentiation of strains within the species. Sabouraudia. 1980 Dec;18(4):301–317. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Odds F. C. Candida infections: an overview. Crit Rev Microbiol. 1987;15(1):1–5. doi: 10.3109/10408418709104444. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Odds F. C. Genital candidosis. Clin Exp Dermatol. 1982 Jul;7(4):345–354. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2230.1982.tb02441.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Polonelli L., Archibusacci C., Sestito M., Morace G. Killer system: a simple method for differentiating Candida albicans strains. J Clin Microbiol. 1983 May;17(5):774–780. doi: 10.1128/jcm.17.5.774-780.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rigby P. W., Dieckmann M., Rhodes C., Berg P. Labeling deoxyribonucleic acid to high specific activity in vitro by nick translation with DNA polymerase I. J Mol Biol. 1977 Jun 15;113(1):237–251. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90052-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scherer S., Stevens D. A. Application of DNA typing methods to epidemiology and taxonomy of Candida species. J Clin Microbiol. 1987 Apr;25(4):675–679. doi: 10.1128/jcm.25.4.675-679.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slutsky B., Buffo J., Soll D. R. High-frequency switching of colony morphology in Candida albicans. Science. 1985 Nov 8;230(4726):666–669. doi: 10.1126/science.3901258. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slutsky B., Staebell M., Anderson J., Risen L., Pfaller M., Soll D. R. "White-opaque transition": a second high-frequency switching system in Candida albicans. J Bacteriol. 1987 Jan;169(1):189–197. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.1.189-197.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soll D. R., Bedell G. W., Brummel M. Zinc and regulation of growth and phenotype in the infectious yeast Candida albicans. Infect Immun. 1981 Jun;32(3):1139–1147. doi: 10.1128/iai.32.3.1139-1147.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soll D. R., Langtimm C. J., McDowell J., Hicks J., Galask R. High-frequency switching in Candida strains isolated from vaginitis patients. J Clin Microbiol. 1987 Sep;25(9):1611–1622. doi: 10.1128/jcm.25.9.1611-1622.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warnock D. W., Speller C. D., Milne J. D., Hilton A. L., Kershaw P. I. Epidemiological investigation of patients with vulvovaginal candidosis. Application of a resistogram method for strain differentiation of Candida albicans. Br J Vener Dis. 1979 Oct;55(5):357–361. doi: 10.1136/sti.55.5.357. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]