Abstract
We determined the levels of group A common and neutralizing antibodies against human rotavirus in paired serum specimens obtained from 38 infants within 12 days of the onset of diarrhea. Thirty of the infants excreted rotavirus in stools, and eight did not. Nine patients (30%) with rotavirus diarrhea and seven patients (88%) with diarrhea due to other causes had detectable levels (greater than or equal to 1: 80) of immunoglobulin (IgG) common antibodies in acute-phase sera. All the patients with rotavirus diarrhea showed at least fourfold rises in titers of IgG or IgM common antibodies or both, while only two control patients showed significant rises in either IgG or IgM common antibodies in their convalescent-phase sera. Of the 19 patients excreting "short" electropherotypes of rotavirus, 18 showed at least fourfold rises in titers of neutralizing antibodies against serotype 2 human rotavirus but not against serotype 1, 3, or 4. Nine of the ten patients excreting "long" electropherotypes showed significant rises in neutralizing antibodies against serotype 3, and the other patient showed a significant rise in neutralizing antibodies against serotype 1. One patient excreted long and short electropherotypes simultaneously, and he also showed a significant rise in neutralizing antibodies against serotype 2 and 3 viruses. The control patients with diarrhea did not show significant changes in titers of antibodies against any of the serotypes. These results demonstrated that the neutralizing antibody response within 2 weeks after clinical onset is specific for the infecting serotype of rotavirus.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Beards G. M., Pilfold J. N., Thouless M. E., Flewett T. H. Rotavirus serotypes by serum neutralisation. J Med Virol. 1980;5(3):231–237. doi: 10.1002/jmv.1890050307. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bishop R. F., Cipriani E., Lund J. S., Barnes G. L., Hosking C. S. Estimation of rotavirus immunoglobulin G antibodies in human serum samples by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay: expression of results as units derived from a standard curve. J Clin Microbiol. 1984 Apr;19(4):447–452. doi: 10.1128/jcm.19.4.447-452.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chiba S., Yokoyama T., Nakata S., Morita Y., Urasawa T., Taniguchi K., Urasawa S., Nakao T. Protective effect of naturally acquired homotypic and heterotypic rotavirus antibodies. Lancet. 1986 Aug 23;2(8504):417–421. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(86)92133-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark H. F., Dolan K. T., Horton-Slight P., Palmer J., Plotkin S. A. Diverse serologic response to rotavirus infection of infants in a single epidemic. Pediatr Infect Dis. 1985 Nov-Dec;4(6):626–631. doi: 10.1097/00006454-198511000-00006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark H. F., Hoshino Y., Bell L. M., Groff J., Hess G., Bachman P., Offit P. A. Rotavirus isolate WI61 representing a presumptive new human serotype. J Clin Microbiol. 1987 Sep;25(9):1757–1762. doi: 10.1128/jcm.25.9.1757-1762.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cukor G., Blacklow N. R. Human viral gastroenteritis. Microbiol Rev. 1984 Jun;48(2):157–179. doi: 10.1128/mr.48.2.157-179.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dimitrov D. H., Estes M. K., Rangelova S. M., Shindarov L. M., Melnick J. L., Graham D. Y. Detection of antigenically distinct rotaviruses from infants. Infect Immun. 1983 Aug;41(2):523–526. doi: 10.1128/iai.41.2.523-526.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Estes M. K., Palmer E. L., Obijeski J. F. Rotaviruses: a review. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1983;105:123–184. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-69159-1_3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerna G., Battaglia M., Milenesi G., Passarani N., Percivalle E., Cattaneo E. Serotyping of cell culture-adapted subgroup 2 human rotavirus strains by neutralization. Infect Immun. 1984 Feb;43(2):722–729. doi: 10.1128/iai.43.2.722-729.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herring A. J., Inglis N. F., Ojeh C. K., Snodgrass D. R., Menzies J. D. Rapid diagnosis of rotavirus infection by direct detection of viral nucleic acid in silver-stained polyacrylamide gels. J Clin Microbiol. 1982 Sep;16(3):473–477. doi: 10.1128/jcm.16.3.473-477.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoshino Y., Sereno M. M., Midthun K., Flores J., Kapikian A. Z., Chanock R. M. Independent segregation of two antigenic specificities (VP3 and VP7) involved in neutralization of rotavirus infectivity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Dec;82(24):8701–8704. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.24.8701. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kapikian A. Z., Kim H. W., Wyatt R. G., Cline W. L., Arrobio J. O., Brandt C. D., Rodriguez W. J., Sack D. A., Chanock R. M., Parrott R. H. Human reovirus-like agent as the major pathogen associated with "winter" gastroenteritis in hospitalized infants and young children. N Engl J Med. 1976 Apr 29;294(18):965–972. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197604292941801. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kapikian A. Z., Kim H. W., Wyatt R. G., Rodriguez W. J., Ross S., Cline W. L., Parrott R. H., Chanock R. M. Reoviruslike agent in stools: association with infantile diarrhea and development of serologic tests. Science. 1974 Sep 20;185(4156):1049–1053. doi: 10.1126/science.185.4156.1049. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kapikian A. Z., Wyatt R. G., Levine M. M., Yolken R. H., VanKirk D. H., Dolin R., Greenberg H. B., Chanock R. M. Oral administration of human rotavirus to volunteers: induction of illness and correlates of resistance. J Infect Dis. 1983 Jan;147(1):95–106. doi: 10.1093/infdis/147.1.95. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- López S., Arias C. F., Bell J. R., Strauss J. H., Espejo R. T. Primary structure of the cleavage site associated with trypsin enhancement of rotavirus SA11 infectivity. Virology. 1985 Jul 15;144(1):11–19. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(85)90300-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsuno S., Hasegawa A., Mukoyama A., Inouye S. A candidate for a new serotype of human rotavirus. J Virol. 1985 May;54(2):623–624. doi: 10.1128/jvi.54.2.623-624.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McNulty M. S., McFerran J. B., Bryson D. G., Logan E. F., Curran W. L. Studies on rotavirus infection and diarrhoea in young calves. Vet Rec. 1976 Sep 18;99(12):229–230. doi: 10.1136/vr.99.12.229. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Offit P. A., Blavat G. Identification of the two rotavirus genes determining neutralization specificities. J Virol. 1986 Jan;57(1):376–378. doi: 10.1128/jvi.57.1.376-378.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Puerto F. I., Padilla-Noriega L., Zamora-Chávez A., Briceño A., Puerto M., Arias C. F. Prevalent patterns of serotype-specific seroconversion in Mexican children infected with rotavirus. J Clin Microbiol. 1987 May;25(5):960–963. doi: 10.1128/jcm.25.5.960-963.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodger S. M., Schnagl R. D., Holmes I. H. Biochemical and biophysical characteristics of diarrhea viruses of human and calf origin. J Virol. 1975 Nov;16(5):1229–1235. doi: 10.1128/jvi.16.5.1229-1235.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sato K., Inaba Y., Shinozaki T., Fujii R., Matumoto M. Isolation of human rotavirus in cell cultures: brief report. Arch Virol. 1981;69(2):155–160. doi: 10.1007/BF01315159. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simhon A., Chrystie I. L., Totterdell B. M., Banatvala J. E., Rice S. J., Walker-Smith J. A. Sequential rotavirus diarrhoea caused by virus of same subgroup. Lancet. 1981 Nov 21;2(8256):1174–1174. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(81)90627-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snodgrass D. R., Wells P. W. The immunoprophylaxis of of rotavirus infections in lambs. Vet Rec. 1978 Feb 18;102(7):146–148. doi: 10.1136/vr.102.7.146. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
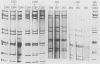
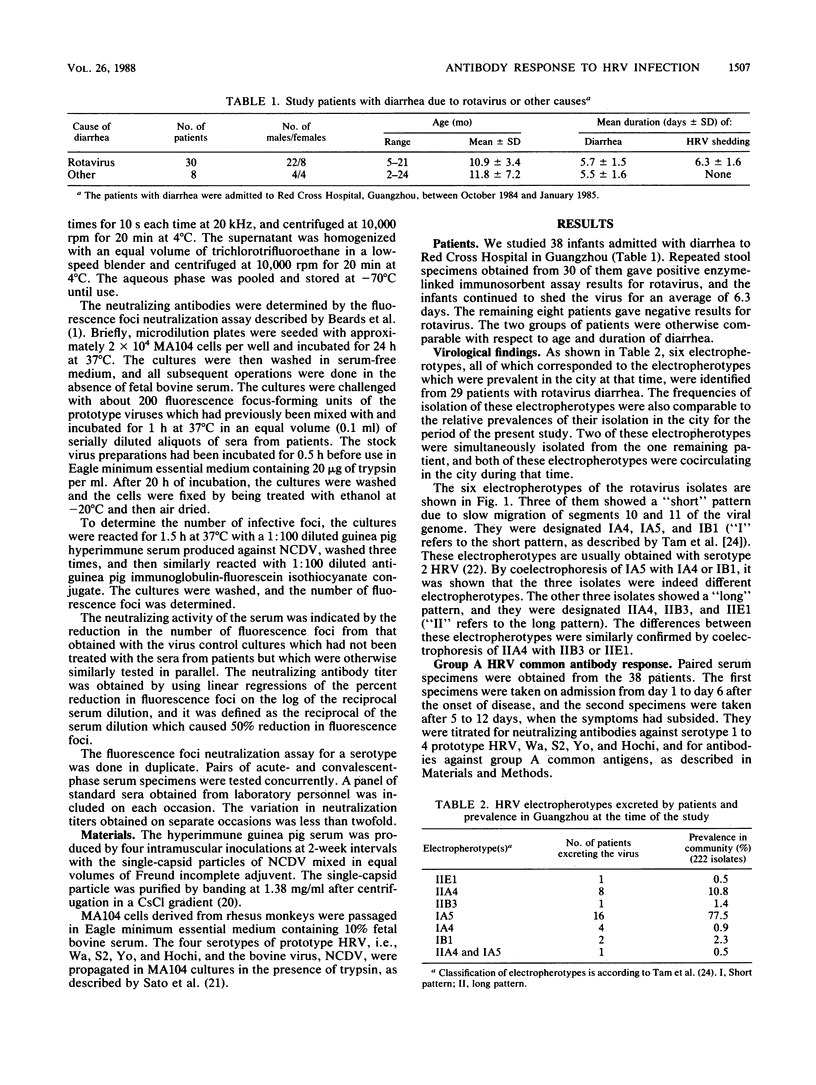
- Tam J. S., Kum W. W., Lam B., Yeung C. Y., Ng M. H. Molecular epidemiology of human rotavirus infection in children in Hong Kong. J Clin Microbiol. 1986 Mar;23(3):660–664. doi: 10.1128/jcm.23.3.660-664.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thouless M. E., Beards G. M., Flewett T. H. Serotyping and subgrouping of rotavirus strains by the ELISA test. Arch Virol. 1982;73(3-4):219–230. doi: 10.1007/BF01318076. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vesikari T., Isolauri E., D'Hondt E., Delem A., André F. E., Zissis G. Protection of infants against rotavirus diarrhoea by RIT 4237 attenuated bovine rotavirus strain vaccine. Lancet. 1984 May 5;1(8384):977–981. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(84)92323-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wyatt R. G., Kapikian A. Z., Mebus C. A. Induction of cross-reactive serum neutralizing antibody to human rotavirus in calves after in utero administration of bovine rotavirus. J Clin Microbiol. 1983 Sep;18(3):505–508. doi: 10.1128/jcm.18.3.505-508.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]