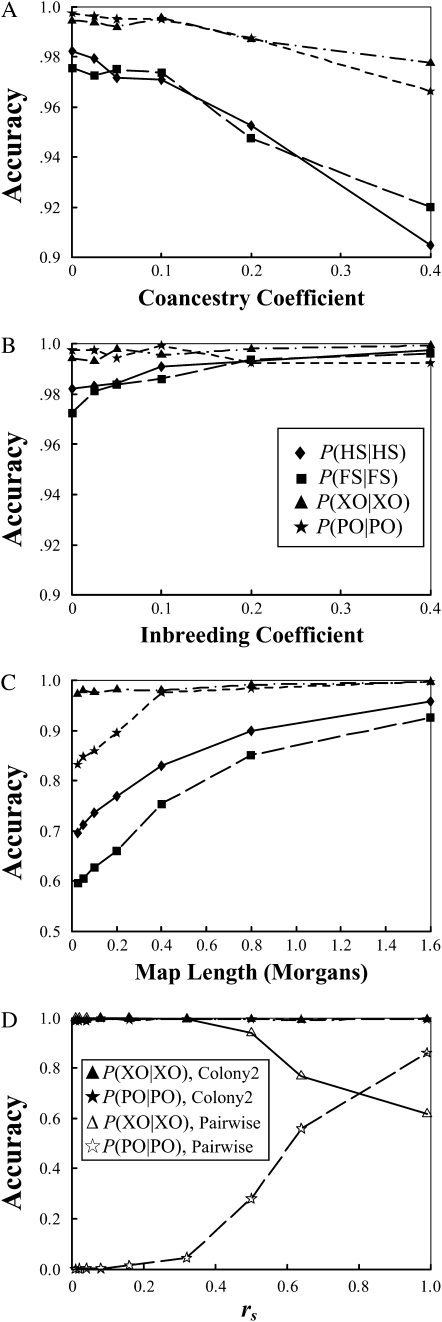
Figure 3.—
Robustness of the method with inbreeding in offspring, inbreeding in parents, linkage among loci, and the sampling errors of rs. Accuracy is measured by the frequencies that simulated full-sib (FS) and half-sib (HS) offspring are identified as such, P(FS | FS), P(HS | HS). It is also measured by the frequencies that parentage is correctly assigned, P(PO | PO), and correctly unassigned, P(XO | XO), for the offspring whose actual parents are included in and excluded from the candidates, respectively. Details about how simulated data sets were generated are described in the text. (A) Accuracy is plotted against the coancestry coefficients among the parents in a family cluster; (B) accuracy is plotted against the inbreeding coefficients of the parents; (C) accuracy is plotted against the map length (in morgans) of the chromosomal fragment on which all five SSRs are assumed to be equally spaced; (D) accuracy is plotted against the value of rs assumed in both our likelihood (denoted as Colony2) and the pairwise (denoted as Pairwise) methods.