Abstract
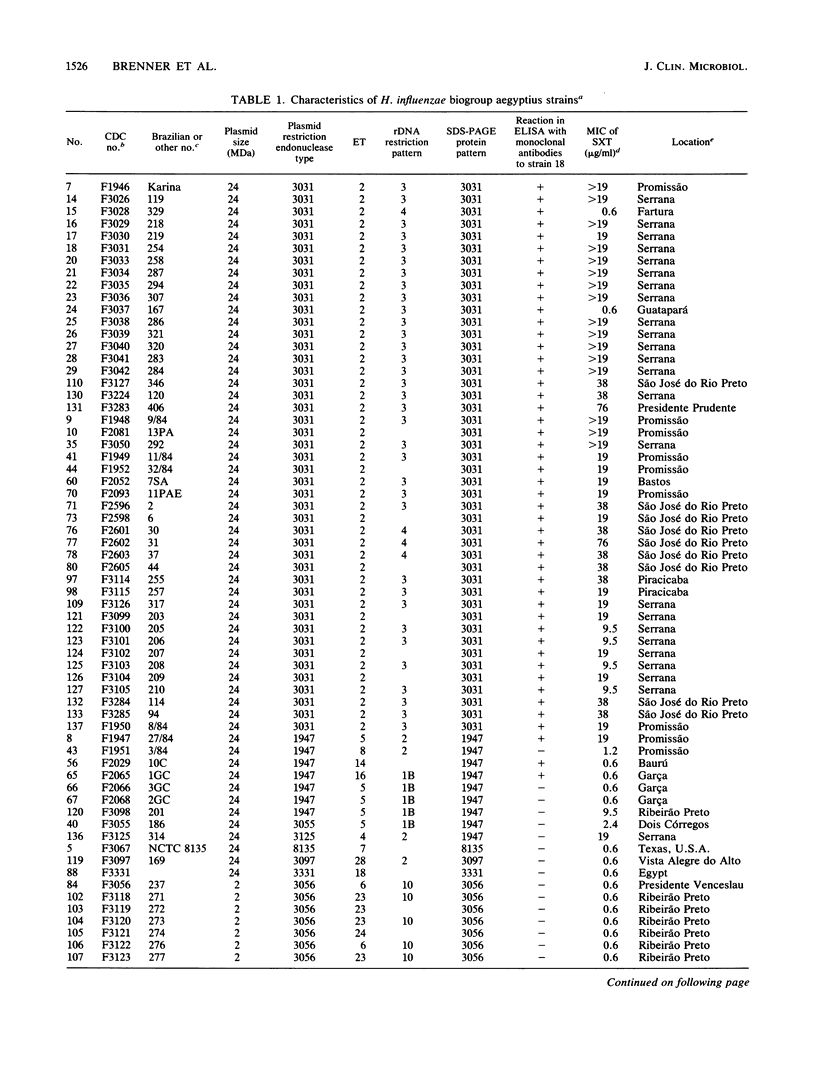
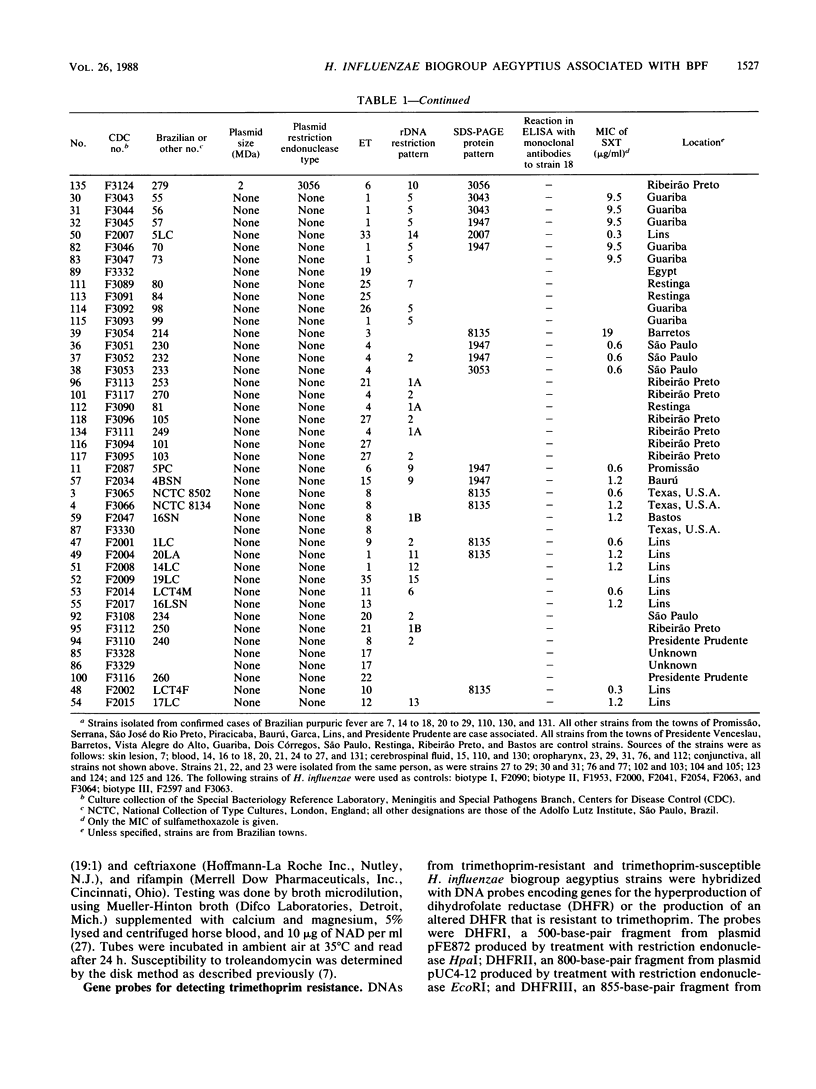
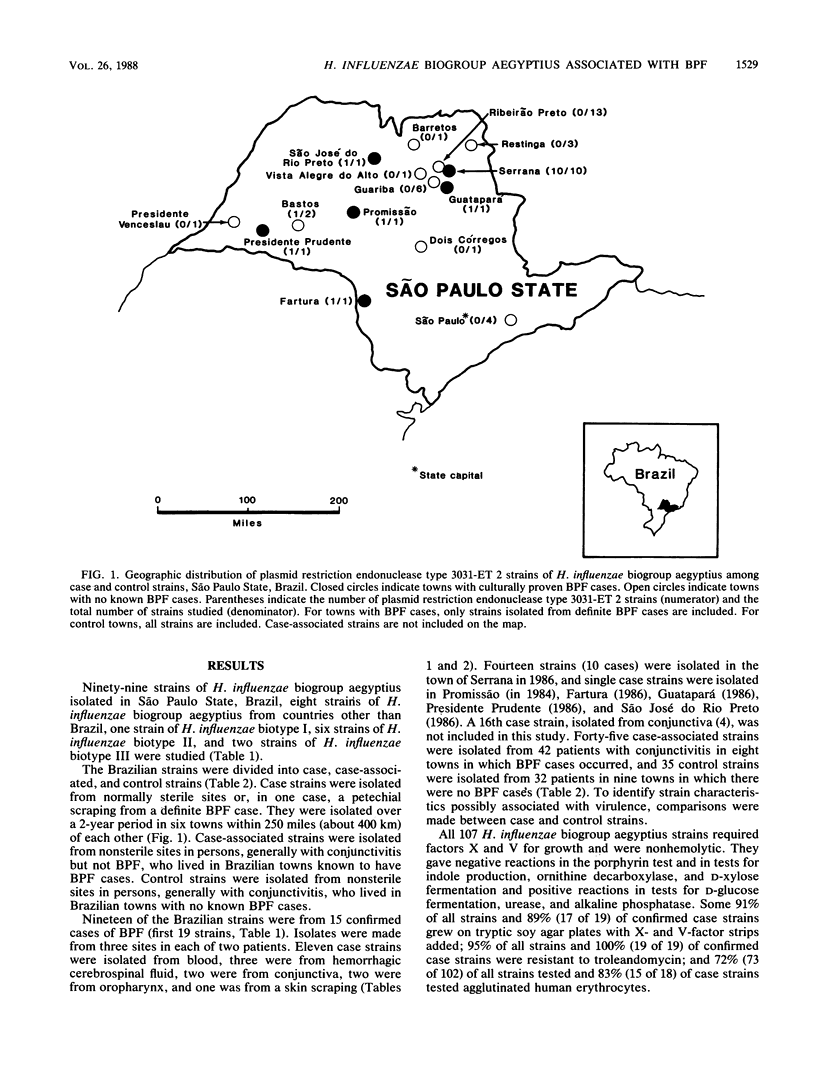
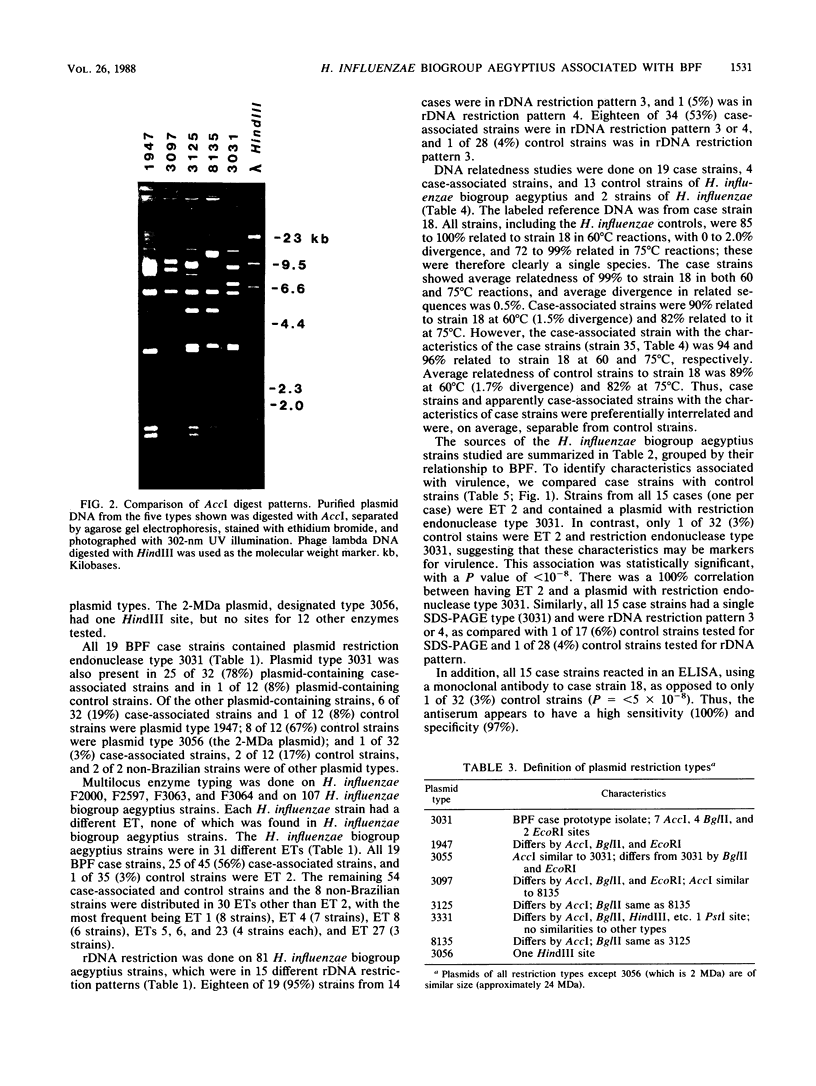
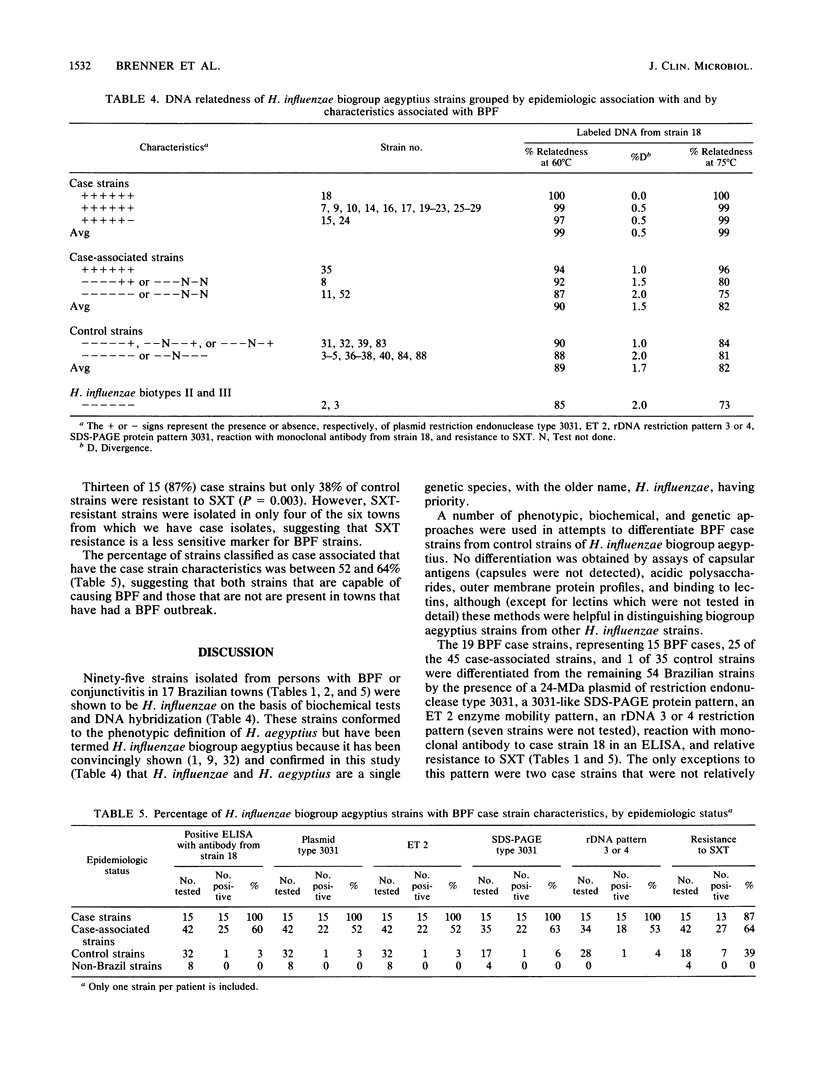
Brazilian purpuric fever (BPF) is a recently recognized fulminant pediatric disease characterized by fever, with rapid progression to purpura, hypotensive shock, and death. BPF is usually preceded by purulent conjunctivitis that has resolved before the onset of fever. Both the conjunctivitis and BPF are caused by Haemophilus influenzae biogroup aegyptius (formerly called H. aegyptius). Isolates from 15 BPF cases, mainly from blood or hemorrhagic cerebrospinal fluid, case-associated isolates from 42 persons in towns where BPF cases occurred, and control strains from 32 persons in towns without BPF cases were characterized biochemically, genetically, and epidemiologically. Results indicated that a single clone was responsible for all BPF cases identified in six Brazilian towns from 1984 through 1986. All of 15 (100%) case strains were the same clone as was 1 of 32 (3%) control strains (P = less than 10(-8). Isolates of the clone were preferentially intrarelated by DNA hybridization (99% relatedness, hydroxyapatite method at 60 and 75 degrees C) and were separable from other H. influenzae biogroup aegyptius strains (approximately 90% relatedness at 60 degrees C and 82% relatedness at 75 degrees C). All isolates of the BPF clone and no other strains contained a 24-megadalton plasmid of restriction endonuclease type 3031, were of a single multilocus enzyme mobility type, were of a single sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis type, and were in one of two ribosomal DNA restriction patterns. All BPF clone isolates reacted with monoclonal antibodies produced from a case strain; only 3 of 62 (5%) other strains reacted with this monoclonal antibody. Ninety percent of BPF clone strains and 27% of other strains were relatively resistant to sulfamethoxazole-trimethoprim.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Albritton W. L., Setlow J. K., Thomas M., Sottnek F., Steigerwalt A. G. Heterospecific transformation in the genus Haemophilus. Mol Gen Genet. 1984;193(2):358–363. doi: 10.1007/BF00330693. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birnboim H. C., Doly J. A rapid alkaline extraction procedure for screening recombinant plasmid DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Nov 24;7(6):1513–1523. doi: 10.1093/nar/7.6.1513. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brenner D. J., McWhorter A. C., Knutson J. K., Steigerwalt A. G. Escherichia vulneris: a new species of Enterobacteriaceae associated with human wounds. J Clin Microbiol. 1982 Jun;15(6):1133–1140. doi: 10.1128/jcm.15.6.1133-1140.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campos J., Garcia-Tornel S., Sanfeliu I. Susceptibility studies of multiply resistant Haemophilus influenzae isolated from pediatric patients and contacts. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1984 Jun;25(6):706–709. doi: 10.1128/aac.25.6.706. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carlone G. M., Sottnek F. O., Plikaytis B. D. Comparison of outer membrane protein and biochemical profiles of Haemophilus aegyptius and Haemophilus influenzae biotype III. J Clin Microbiol. 1985 Nov;22(5):708–713. doi: 10.1128/jcm.22.5.708-713.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carlone G. M., Thomas M. L., Rumschlag H. S., Sottnek F. O. Rapid microprocedure for isolating detergent-insoluble outer membrane proteins from Haemophilus species. J Clin Microbiol. 1986 Sep;24(3):330–332. doi: 10.1128/jcm.24.3.330-332.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Casin I., Grimont F., Grimont P. A. Deoxyribonucleic acid relatedness between Haemophilus aegyptius and Haemophilus influenzae. Ann Inst Pasteur Microbiol. 1986 Sep-Oct;137B(2):155–163. doi: 10.1016/s0769-2609(86)80104-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Claflin L., Williams K. Mouse myeloma--spleen cell hybrids: Enhanced hybridization frequencies and rapid screening procedures. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1978;81:107–109. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-67448-8_16. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grimont F., Grimont P. A. Ribosomal ribonucleic acid gene restriction patterns as potential taxonomic tools. Ann Inst Pasteur Microbiol. 1986 Sep-Oct;137B(2):165–175. doi: 10.1016/s0769-2609(86)80105-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEIDY G., JAFFEE I., ALEXANDER H. E. FURTHER EVIDENCE OF A HIGH DEGREE OF GENETIC HOMOLOGY BETWEEN H. INFLUENZAE AND H. AEGYPTIUS. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1965 Mar;118:671–679. doi: 10.3181/00379727-118-29935. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Markwell M. A., Haas S. M., Bieber L. L., Tolbert N. E. A modification of the Lowry procedure to simplify protein determination in membrane and lipoprotein samples. Anal Biochem. 1978 Jun 15;87(1):206–210. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(78)90586-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mazloum H. A., Kilian M., Mohamed Z. M., Said M. D. Differentiation of Haemophilus aegyptius and Haemophilus influenzae. Acta Pathol Microbiol Immunol Scand B. 1982 Apr;90(2):109–112. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1982.tb00090.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyers J. A., Sanchez D., Elwell L. P., Falkow S. Simple agarose gel electrophoretic method for the identification and characterization of plasmid deoxyribonucleic acid. J Bacteriol. 1976 Sep;127(3):1529–1537. doi: 10.1128/jb.127.3.1529-1537.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morozumi T., Nicolet J. Morphological variations of Haemophilus parasuis strains. J Clin Microbiol. 1986 Jan;23(1):138–142. doi: 10.1128/jcm.23.1.138-142.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morozumi T., Nicolet J. Some antigenic properties of Haemophilus parasuis and a proposal for serological classification. J Clin Microbiol. 1986 Jun;23(6):1022–1025. doi: 10.1128/jcm.23.6.1022-1025.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrissey J. H. Silver stain for proteins in polyacrylamide gels: a modified procedure with enhanced uniform sensitivity. Anal Biochem. 1981 Nov 1;117(2):307–310. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90783-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Musser J. M., Barenkamp S. J., Granoff D. M., Selander R. K. Genetic relationships of serologically nontypable and serotype b strains of Haemophilus influenzae. Infect Immun. 1986 Apr;52(1):183–191. doi: 10.1128/iai.52.1.183-191.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Musser J. M., Granoff D. M., Pattison P. E., Selander R. K. A population genetic framework for the study of invasive diseases caused by serotype b strains of Haemophilus influenzae. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Aug;82(15):5078–5082. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.15.5078. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olsvik O., Sørum H., Birkness K., Wachsmuth K., Fjølstad M., Lassen J., Fossum K., Feeley J. C. Plasmid characterization of Salmonella typhimurium transmitted from animals to humans. J Clin Microbiol. 1985 Sep;22(3):336–338. doi: 10.1128/jcm.22.3.336-338.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orskov F. Agarose electrophoresis combined with second dimensional Cetavlon precipitation. A new method for demonstration of acidic polysaccharide K antigens. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand B. 1976 Oct;84B(5):319–320. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plikaytis B. D., Carlone G. M., Edmonds P., Mayer L. W. Robust estimation of standard curves for protein molecular weight and linear-duplex DNA base-pair number after gel electrophoresis. Anal Biochem. 1986 Feb 1;152(2):346–364. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(86)90420-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plikaytis B. D., Carlone G. M., Plikaytis B. B. Numerical analysis of normalized whole-cell protein profiles after sodium dodecyl sulphate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. J Gen Microbiol. 1986 Sep;132(9):2653–2660. doi: 10.1099/00221287-132-9-2653. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Porras O., Caugant D. A., Gray B., Lagergård T., Levin B. R., Svanborg-Edén C. Difference in structure between type b and nontypable Haemophilus influenzae populations. Infect Immun. 1986 Jul;53(1):79–89. doi: 10.1128/iai.53.1.79-89.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Porras O., Caugant D. A., Lagergård T., Svanborg-Edén C. Application of multilocus enzyme gel electrophoresis to Haemophilus influenzae. Infect Immun. 1986 Jul;53(1):71–78. doi: 10.1128/iai.53.1.71-78.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selander R. K., Caugant D. A., Ochman H., Musser J. M., Gilmour M. N., Whittam T. S. Methods of multilocus enzyme electrophoresis for bacterial population genetics and systematics. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1986 May;51(5):873–884. doi: 10.1128/aem.51.5.873-884.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swanson J. Colony opacity and protein II compositions of gonococci. Infect Immun. 1982 Jul;37(1):359–368. doi: 10.1128/iai.37.1.359-368.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swanson J. Studies on gonococcus infection. XVIII. 125I-labeled peptide mapping of the major protein of the gonococcal cell wall outer membrane. Infect Immun. 1979 Mar;23(3):799–810. doi: 10.1128/iai.23.3.799-810.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takahashi S., Nagano Y. Rapid procedure for isolation of plasmid DNA and application to epidemiological analysis. J Clin Microbiol. 1984 Oct;20(4):608–613. doi: 10.1128/jcm.20.4.608-613.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson R., Hughes S. G., Broda P. Plasmid identification using specific endonucleases. Mol Gen Genet. 1974;133(2):141–149. doi: 10.1007/BF00264835. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



