Abstract
Latex beads (0.8-micron diameter; Difco Laboratories) were coated with fibronectin, fibrinogen, collagen type I, or denatured collagen (gelatin) and evaluated in a particle agglutination assay (PAA) for the rapid detection of fibronectin, fibrinogen, or collagen binding to Staphylococcus aureus. These assays were compared with a commercial test for detecting the binding of fibrinogen and immunoglobulin G (Staphaurex). Bacterial cells (approximately 10(10) cells per ml) suspended in 0.02 M potassium phosphate buffer (pH 6.8) caused the clumping of standard fibronectin, collagen, gelatin, and fibrinogen latex suspensions within 2 min on glass slides. The test results were scored semiquantitatively from strongly positive ( ) to weakly positive (+) and negative (-) reactions. The negative PAA reactions corresponded to a median value of 11.5% relative to the binding of 125I-labeled protein to strain Cowan 1, indicating the high sensitivity of the test. The reactions with fibronectin and fibrinogen latex suspensions and with Staphaurex were optimal for cells grown on tryptic soy and brain heart infusion broth media. Blood agar was optimal for reactions with collagen and gelatin latex suspensions. Media containing high salts (mannitol salt agar and staphylococcus medium 110) enhanced the tendency of cells to autoaggregate. These assays were also clinically evaluated on 187 S. aureus isolates. The PAA reagents were stable, and the assays were highly specific, sensitive, and reproducible, thus making PAA suitable for the rapid screening of the binding of various bacterial pathogens to serum and connective-tissue proteins.
Full text
PDF

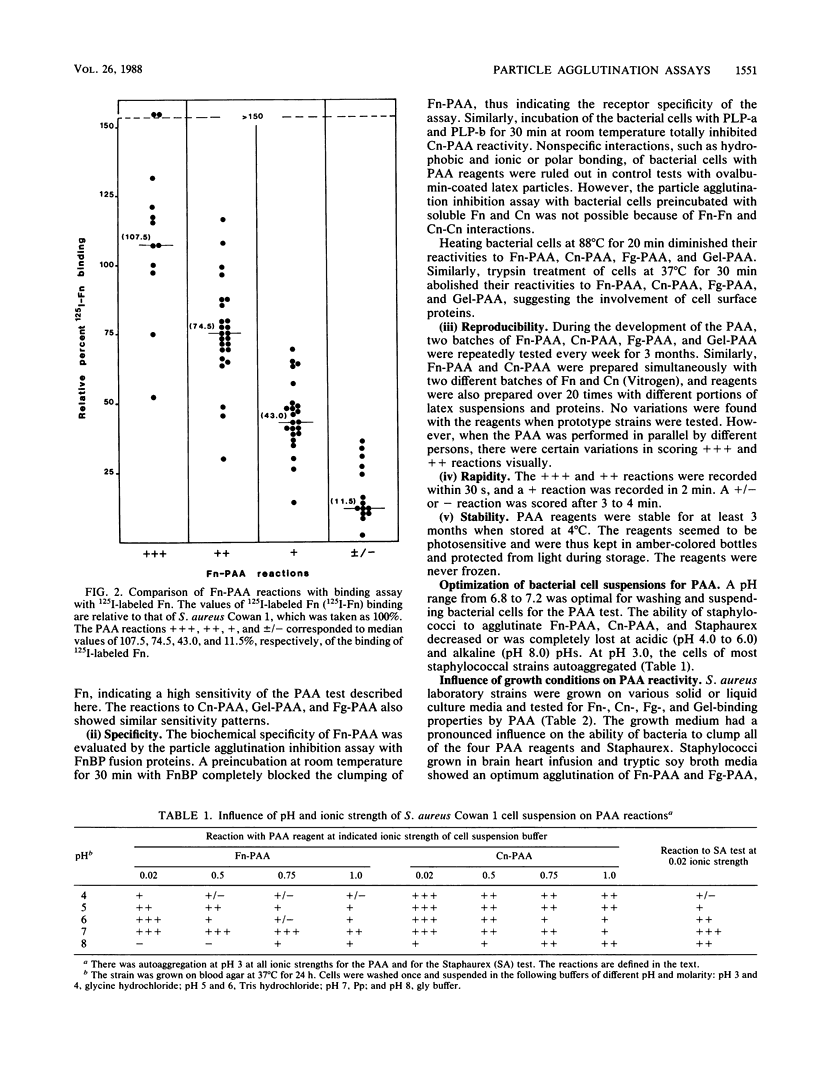
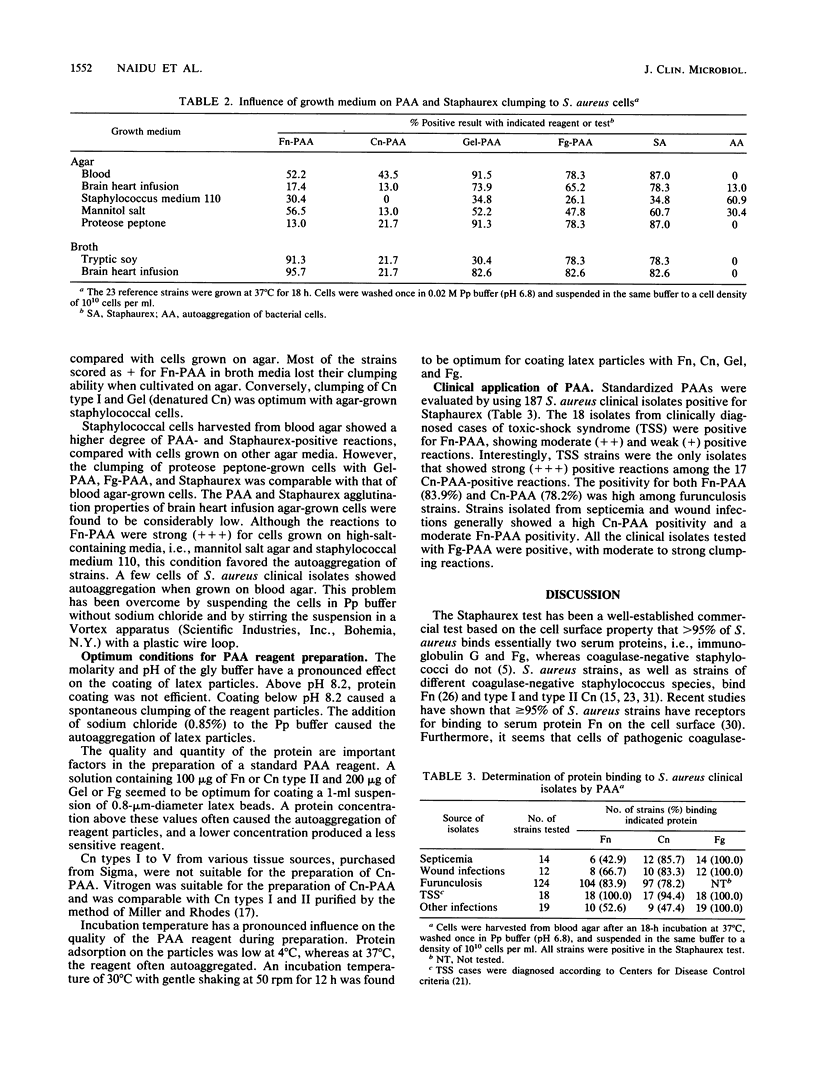


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Beachey E. H. Bacterial adherence: adhesin-receptor interactions mediating the attachment of bacteria to mucosal surface. J Infect Dis. 1981 Mar;143(3):325–345. doi: 10.1093/infdis/143.3.325. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carret G., Emonard H., Fardel G., Druguet M., Herbage D., Flandrois J. P. Gelatin and collagen binding to Staphylococcus aureus strains. Ann Inst Pasteur Microbiol. 1985 Mar-Apr;136A(2):241–245. doi: 10.1016/s0769-2609(85)80063-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Espersen F., Clemmensen I. Isolation of a fibronectin-binding protein from Staphylococcus aureus. Infect Immun. 1982 Aug;37(2):526–531. doi: 10.1128/iai.37.2.526-531.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Essers L., Radebold K. Rapid and reliable identification of Staphylococcus aureus by a latex agglutination test. J Clin Microbiol. 1980 Nov;12(5):641–643. doi: 10.1128/jcm.12.5.641-643.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flock J. I., Fröman G., Jönsson K., Guss B., Signäs C., Nilsson B., Raucci G., Hök M., Wadström T., Lindberg M. Cloning and expression of the gene for a fibronectin-binding protein from Staphylococcus aureus. EMBO J. 1987 Aug;6(8):2351–2357. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02511.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fröman G., Switalski L. M., Faris A., Wadström T., Hök M. Binding of Escherichia coli to fibronectin. A mechanism of tissue adherence. J Biol Chem. 1984 Dec 10;259(23):14899–14905. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuquay J. I., Loo D. T., Barnes D. W. Binding of Staphylococcus aureus by human serum spreading factor in an in vitro assay. Infect Immun. 1986 Jun;52(3):714–717. doi: 10.1128/iai.52.3.714-717.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GREENWOOD F. C., HUNTER W. M., GLOVER J. S. THE PREPARATION OF I-131-LABELLED HUMAN GROWTH HORMONE OF HIGH SPECIFIC RADIOACTIVITY. Biochem J. 1963 Oct;89:114–123. doi: 10.1042/bj0890114. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuusela P., Vartio T., Vuento M., Myhre E. B. Attachment of staphylococci and streptococci on fibronectin, fibronectin fragments, and fibrinogen bound to a solid phase. Infect Immun. 1985 Oct;50(1):77–81. doi: 10.1128/iai.50.1.77-81.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuusela P., Vartio T., Vuento M., Myhre E. B. Binding sites for streptococci and staphylococci in fibronectin. Infect Immun. 1984 Aug;45(2):433–436. doi: 10.1128/iai.45.2.433-436.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lopes J. D., dos Reis M., Brentani R. R. Presence of laminin receptors in Staphylococcus aureus. Science. 1985 Jul 19;229(4710):275–277. doi: 10.1126/science.3160113. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mamo W., Fröman G., Sundås A., Wadström T. Binding of fibronectin, fibrinogen and type II collagen to streptococci isolated from bovine mastitis. Microb Pathog. 1987 Jun;2(6):417–424. doi: 10.1016/0882-4010(87)90048-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxe I., Rydén C., Wadström T., Rubin K. Specific attachment of Staphylococcus aureus to immobilized fibronectin. Infect Immun. 1986 Dec;54(3):695–704. doi: 10.1128/iai.54.3.695-704.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller E. J., Rhodes R. K. Preparation and characterization of the different types of collagen. Methods Enzymol. 1982;82(Pt A):33–64. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(82)82059-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruoslahti E., Hayman E. G., Pierschbacher M., Engvall E. Fibronectin: purification, immunochemical properties, and biological activities. Methods Enzymol. 1982;82(Pt A):803–831. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(82)82103-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rydén C., Rubin K., Speziale P., Hök M., Lindberg M., Wadström T. Fibronectin receptors from Staphylococcus aureus. J Biol Chem. 1983 Mar 10;258(5):3396–3401. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shands K. N., Schmid G. P., Dan B. B., Blum D., Guidotti R. J., Hargrett N. T., Anderson R. L., Hill D. L., Broome C. V., Band J. D. Toxic-shock syndrome in menstruating women: association with tampon use and Staphylococcus aureus and clinical features in 52 cases. N Engl J Med. 1980 Dec 18;303(25):1436–1442. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198012183032502. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simpson W. A., Beachey E. H. Adherence of group A streptococci to fibronectin on oral epithelial cells. Infect Immun. 1983 Jan;39(1):275–279. doi: 10.1128/iai.39.1.275-279.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Speziale P., Hök M., Wadström T., Timpl R. Binding of the basement membrane protein laminin to Escherichia coli. FEBS Lett. 1982 Sep 6;146(1):55–58. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(82)80704-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Switalski L. M., Ljungh A., Rydén C., Rubin K., Hök M., Wadström T. Binding of fibronectin to the surface of group A, C, and G streptococci isolated from human infections. Eur J Clin Microbiol. 1982 Dec;1(6):381–387. doi: 10.1007/BF02019939. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Switalski L. M., Rydén C., Rubin K., Ljungh A., Hök M., Wadström T. Binding of fibronectin to Staphylococcus strains. Infect Immun. 1983 Nov;42(2):628–633. doi: 10.1128/iai.42.2.628-633.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas D. D., Baseman J. B., Alderete J. F. Enhanced levels of attachment of fibronectin-primed Treponema pallidum to extracellular matrix. Infect Immun. 1986 Jun;52(3):736–741. doi: 10.1128/iai.52.3.736-741.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vercellotti G. M., McCarthy J. B., Lindholm P., Peterson P. K., Jacob H. S., Furcht L. T. Extracellular matrix proteins (fibronectin, laminin, and type IV collagen) bind and aggregate bacteria. Am J Pathol. 1985 Jul;120(1):13–21. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vuento M., Vaheri A. Purification of fibronectin from human plasma by affinity chromatography under non-denaturing conditions. Biochem J. 1979 Nov 1;183(2):331–337. doi: 10.1042/bj1830331. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wadström T. Molecular aspects on pathogenesis of wound and foreign body infections due to staphylococci. Zentralbl Bakteriol Mikrobiol Hyg A. 1987 Aug;266(1-2):191–211. doi: 10.1016/s0176-6724(87)80032-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]