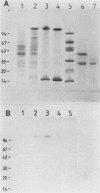
Abstract
The gene for Escherichia coli heat-stable enterotoxin type II (STII) was fused to the genes for protein A from Staphylococcus aureus and beta-galactosidase in two different expression systems. Antibodies raised in rabbits against the protein A-STII fusion protein recognized the beta-galactosidase-STII fusion protein. The latter fusion protein was used as the immobilized antigen in an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) for detection of STII. The correlation between the results of the ELISA and the intestinal loop test in piglets was 95%, suggesting that the ELISA can be used to reliably detect STII.
Full text
PDF
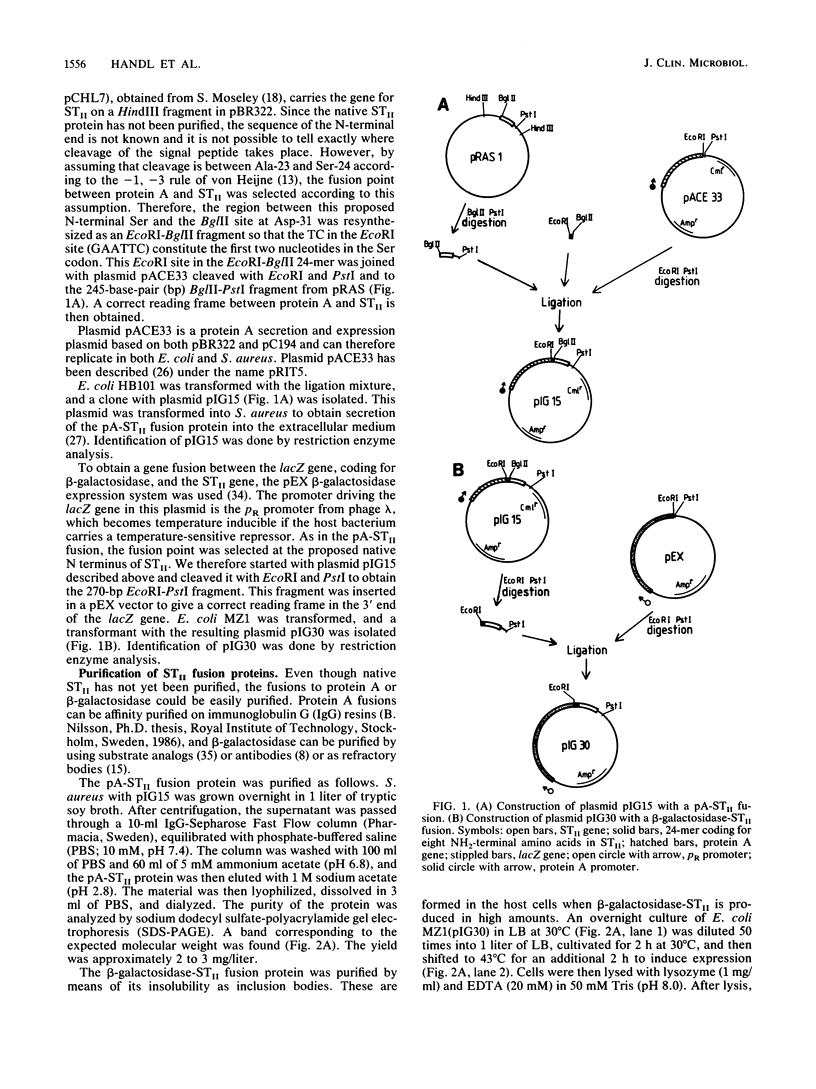

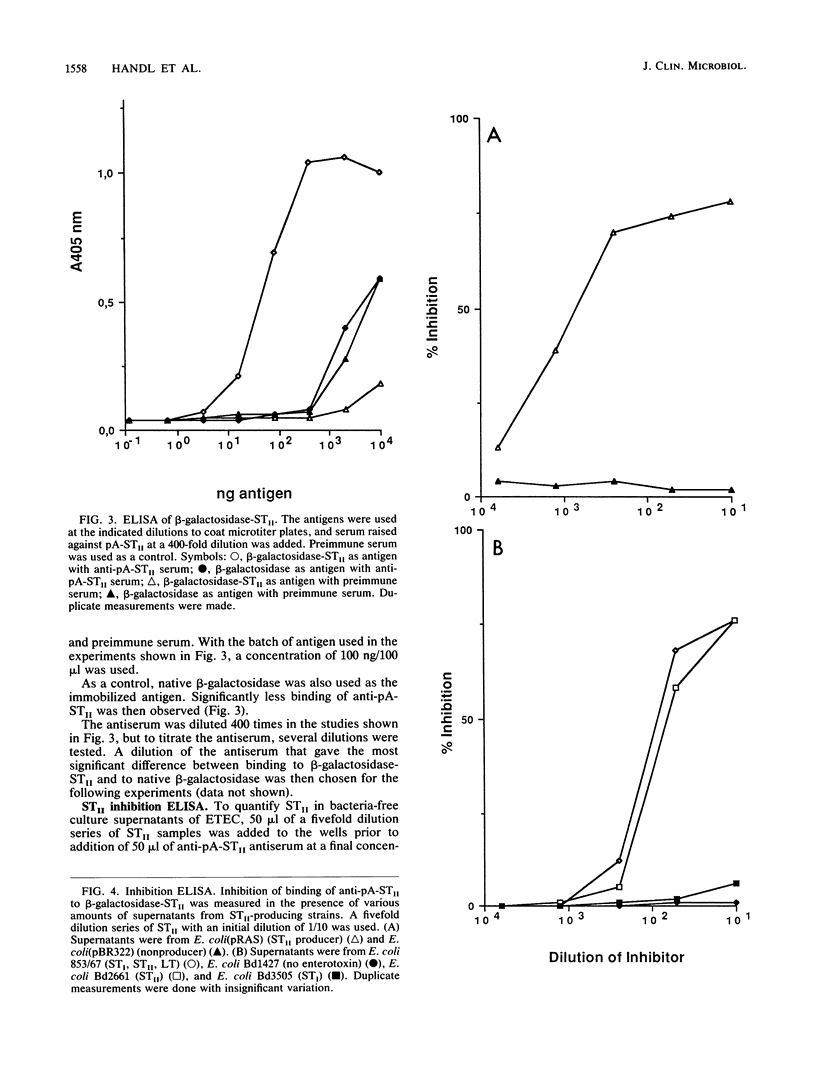


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aimoto S., Takao T., Shimonishi Y., Hara S., Takeda T., Takeda Y., Miwatani T. Amino-acid sequence of a heat-stable enterotoxin produced by human enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli. Eur J Biochem. 1982 Dec 15;129(2):257–263. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1982.tb07047.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birnboim H. C., Doly J. A rapid alkaline extraction procedure for screening recombinant plasmid DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Nov 24;7(6):1513–1523. doi: 10.1093/nar/7.6.1513. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burgess M. N., Bywater R. J., Cowley C. M., Mullan N. A., Newsome P. M. Biological evaluation of a methanol-soluble, heat-stable Escherichia coli enterotoxin in infant mice, pigs, rabbits, and calves. Infect Immun. 1978 Aug;21(2):526–531. doi: 10.1128/iai.21.2.526-531.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dallas W. S., Falkow S. Amino acid sequence homology between cholera toxin and Escherichia coli heat-labile toxin. Nature. 1980 Dec 4;288(5790):499–501. doi: 10.1038/288499a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans D. G., Evans D. J., Jr, Pierce N. F. Differences in the response of rabbit small intestine to heat-labile and heat-stable enterotoxins of Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1973 Jun;7(6):873–880. doi: 10.1128/iai.7.6.873-880.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans D. J., Jr, Chen L. C., Curlin G. T., Evans D. G. Stimulation of adenyl cyclase by Escherichia coli enterotoxin. Nat New Biol. 1972 Apr 5;236(66):137–138. doi: 10.1038/newbio236137a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frantz J. C., Robertson D. C. Immunological properties of Escherichia coli heat-stable enterotoxins: development of a radioimmunoassay specific for heat-stable enterotoxins with suckling mouse activity. Infect Immun. 1981 Jul;33(1):193–198. doi: 10.1128/iai.33.1.193-198.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Germino J., Bastia D. Rapid purification of a cloned gene product by genetic fusion and site-specific proteolysis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Aug;81(15):4692–4696. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.15.4692. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giannella R. A., Drake K. W., Luttrell M. Development of a radioimmunoassay for Escherichia coli heat-stable enterotoxin: comparison with the suckling mouse bioassay. Infect Immun. 1981 Jul;33(1):186–192. doi: 10.1128/iai.33.1.186-192.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gill D. M., Richardson S. H. Adenosine diphosphate-ribosylation of adenylate cyclase catalyzed by heat-labile enterotoxin of Escherichia coli: comparison with cholera toxin. J Infect Dis. 1980 Jan;141(1):64–70. doi: 10.1093/infdis/141.1.64. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guerrant R. L., Hughes J. M., Chang B., Robertson D. C., Murad F. Activation of intestinal guanylate cyclase by heat-stable enterotoxin of Escherichia coli: studies of tissue specificity, potential receptors, and intermediates. J Infect Dis. 1980 Aug;142(2):220–228. doi: 10.1093/infdis/142.2.220. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Götz F., Ahrné S., Lindberg M. Plasmid transfer and genetic recombination by protoplast fusion in staphylococci. J Bacteriol. 1981 Jan;145(1):74–81. doi: 10.1128/jb.145.1.74-81.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iordănescu S. Recombinant plasmid obtained from two different, compatible staphylococcal plasmids. J Bacteriol. 1975 Nov;124(2):597–601. doi: 10.1128/jb.124.2.597-601.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Itakura K., Hirose T., Crea R., Riggs A. D., Heyneker H. L., Bolivar F., Boyer H. W. Expression in Escherichia coli of a chemically synthesized gene for the hormone somatostatin. Science. 1977 Dec 9;198(4321):1056–1063. doi: 10.1126/science.412251. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Langone J. J. Protein A of Staphylococcus aureus and related immunoglobulin receptors produced by streptococci and pneumonococci. Adv Immunol. 1982;32:157–252. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee C. H., Moseley S. L., Moon H. W., Whipp S. C., Gyles C. L., So M. Characterization of the gene encoding heat-stable toxin II and preliminary molecular epidemiological studies of enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli heat-stable toxin II producers. Infect Immun. 1983 Oct;42(1):264–268. doi: 10.1128/iai.42.1.264-268.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Löwenadler B., Nilsson B., Abrahmsén L., Moks T., Ljungqvist L., Holmgren E., Paleus S., Josephson S., Philipson L., Uhlén M. Production of specific antibodies against protein A fusion proteins. EMBO J. 1986 Sep;5(9):2393–2398. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04509.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mainil J. G., Moseley S. L., Schneider R. A., Sutch K., Casey T. A., Moon H. W. Hybridization of bovine Escherichia coli isolates with gene probes for four enterotoxins (STaP, STaH, STb, LT) and one adhesion factor (K99). Am J Vet Res. 1986 May;47(5):1145–1148. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moon H. W., Schneider R. A., Moseley S. L. Comparative prevalence of four enterotoxin genes among Escherichia coli isolated from swine. Am J Vet Res. 1986 Feb;47(2):210–212. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moseley S. L., Hardy J. W., Hug M. I., Echeverria P., Falkow S. Isolation and nucleotide sequence determination of a gene encoding a heat-stable enterotoxin of Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1983 Mar;39(3):1167–1174. doi: 10.1128/iai.39.3.1167-1174.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moseley S. L., Samadpour-Motalebi M., Falkow S. Plasmid association and nucleotide sequence relationships of two genes encoding heat-stable enterotoxin production in Escherichia coli H-10407. J Bacteriol. 1983 Oct;156(1):441–443. doi: 10.1128/jb.156.1.441-443.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagai K., Thøgersen H. C. Generation of beta-globin by sequence-specific proteolysis of a hybrid protein produced in Escherichia coli. 1984 Jun 28-Jul 4Nature. 309(5971):810–812. doi: 10.1038/309810a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nilsson B., Abrahmsén L., Uhlén M. Immobilization and purification of enzymes with staphylococcal protein A gene fusion vectors. EMBO J. 1985 Apr;4(4):1075–1080. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03741.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nilsson B., Holmgren E., Josephson S., Gatenbeck S., Philipson L., Uhlen M. Efficient secretion and purification of human insulin-like growth factor I with a gene fusion vector in Staphylococci. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Feb 25;13(4):1151–1162. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.4.1151. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olsson E., Söderlind O. Comparison of different assays for definition of heat-stable enterotoxigenicity of Escherichia coli porcine strains. J Clin Microbiol. 1980 Jan;11(1):6–15. doi: 10.1128/jcm.11.1.6-15.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Picken R. N., Mazaitis A. J., Maas W. K., Rey M., Heyneker H. Nucleotide sequence of the gene for heat-stable enterotoxin II of Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1983 Oct;42(1):269–275. doi: 10.1128/iai.42.1.269-275.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rao M. C., Guandalini S., Smith P. L., Field M. Mode of action of heat-stable Escherichia coli enterotoxin. Tissue and subcellular specificities and role of cyclic GMP. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1980 Sep 17;632(1):35–46. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(80)90247-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sekizaki T., Akashi H., Terakado N. Nucleotide sequences of the genes for Escherichia coli heat-stable enterotoxin I of bovine, avian, and porcine origins. Am J Vet Res. 1985 Apr;46(4):909–912. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanley K. K., Luzio J. P. Construction of a new family of high efficiency bacterial expression vectors: identification of cDNA clones coding for human liver proteins. EMBO J. 1984 Jun;3(6):1429–1434. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb01988.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Söderlind O. Studies on Escherichia coli in pigs. IV. Reactions of Escherichia coli strains in the ligated intestine test. Zentralbl Veterinarmed B. 1973 Sep;20(7):558–571. doi: 10.1111/j.1439-0450.1973.tb01492.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ullmann A. One-step purification of hybrid proteins which have beta-galactosidase activity. Gene. 1984 Jul-Aug;29(1-2):27–31. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(84)90162-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weikel C. S., Guerrant R. L. STb enterotoxin of Escherichia coli: cyclic nucleotide-independent secretion. Ciba Found Symp. 1985;112:94–115. doi: 10.1002/9780470720936.ch6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Heijne G. A new method for predicting signal sequence cleavage sites. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Jun 11;14(11):4683–4690. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.11.4683. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]