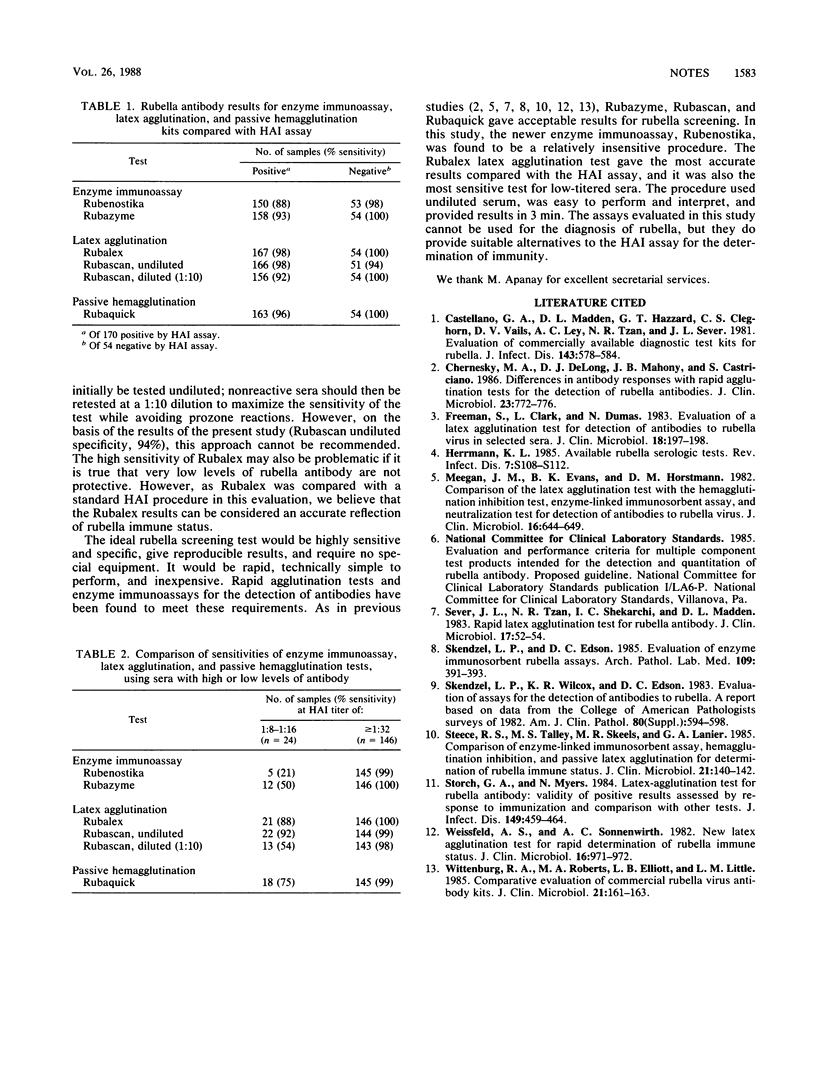
Abstract
A new enzyme immunoassay (Rubenostika; Organon Teknika, Turnhout, Belgium), a new latex agglutination test (Rubalex; Orion Diagnostica, Espoo, Finland), and three other accepted methods for the determination of rubella immunity were compared with a standard hemagglutination inhibition assay. Of 224 serum samples tested, 54 (24%) were nonreactive and 24 (11%) were low titered. All procedures were very specific (94 to 100%). Rubenostika was the least sensitive method (88%), and Rubalex was the most sensitive (98%).
Full text
PDF
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Castellano G. A., Madden D. L., Hazzard G. T., Cleghorn C. S., Vails D. V., Ley A. C., Tzan N. R., Sever J. L. Evaluation of commercially available diagnostic test kits for rubella. J Infect Dis. 1981 Apr;143(4):578–584. doi: 10.1093/infdis/143.4.578. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chernesky M. A., DeLong D. J., Mahony J. B., Castriciano S. Differences in antibody responses with rapid agglutination tests for the detection of rubella antibodies. J Clin Microbiol. 1986 Apr;23(4):772–776. doi: 10.1128/jcm.23.4.772-776.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freeman S., Clark L., Dumas N. Evaluation of a latex agglutination test for detection of antibodies to rubella virus in selected sera. J Clin Microbiol. 1983 Jul;18(1):197–198. doi: 10.1128/jcm.18.1.197-198.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herrmann K. L. Available rubella serologic tests. Rev Infect Dis. 1985 Mar-Apr;7 (Suppl 1):S108–S112. doi: 10.1093/clinids/7.supplement_1.s108. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meegan J. M., Evans B. K., Horstmann D. M. Comparison of the latex agglutination test with the hemagglutination inhibition test, enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay, and neutralization test for detection of antibodies to rubella virus. J Clin Microbiol. 1982 Oct;16(4):644–649. doi: 10.1128/jcm.16.4.644-649.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sever J. L., Tzan N. R., Shekarchi I. C., Madden D. L. Rapid latex agglutination test for rubella antibody. J Clin Microbiol. 1983 Jan;17(1):52–54. doi: 10.1128/jcm.17.1.52-54.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skendzel L. P., Edson D. C. Evaluation of enzyme immunosorbent rubella assays. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 1985 May;109(5):391–393. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skendzel L. P., Wilcox K. R., Edson D. C. Evaluation of assays for the detection of antibodies to rubella. A report based on data from the College of American Pathologists Surveys of 1982. Am J Clin Pathol. 1983 Oct;80(4 Suppl):594–598. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steece R. S., Talley M. S., Skeels M. R., Lanier G. A. Comparison of enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay, hemagglutination inhibition, and passive latex agglutination for determination of rubella immune status. J Clin Microbiol. 1985 Jan;21(1):140–142. doi: 10.1128/jcm.21.1.140-142.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Storch G. A., Myers N. Latex-agglutination test for rubella antibody: validity of positive results assessed by response to immunization and comparison with other tests. J Infect Dis. 1984 Mar;149(3):459–464. doi: 10.1093/infdis/149.3.459. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weissfeld A. S., Sonnenwirth A. C. New latex agglutination test for rapid determination of rubella immune status. J Clin Microbiol. 1982 Nov;16(5):971–972. doi: 10.1128/jcm.16.5.971-972.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wittenburg R. A., Roberts M. A., Elliott L. B., Little L. M. Comparative evaluation of commercial rubella virus antibody kits. J Clin Microbiol. 1985 Feb;21(2):161–163. doi: 10.1128/jcm.21.2.161-163.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


