Abstract
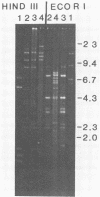
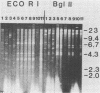
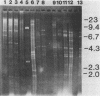
Fourteen strains of Naegleria fowleri, two strains of N. gruberi, and one strain each of N. australiensis, N. jadini, N. lovaniensis, Acanthamoeba sp., A. castellanii, A. polyphaga, and A. comandoni isolated from patients, soil, or water were characterized by restriction fragment length polymorphisms. Total cellular DNA (1 microgram) was digested with either HindIII, BglII, or EcoRI; separated on agarose gels; and stained with ethidium bromide. From 2 to 15 unusually prominent repetitive restriction fragment bands, totaling 15 to 50 kilobases in length and constituting probably more than 30% of the total DNA, were detected for all ameba strains. Each species displayed a characteristic pattern of repetitive restriction fragments. Digests of the four Acanthamoeba spp. displayed fewer, less intensely staining repetitive fragments than those of the Naegleria spp. All N. fowleri strains, whether isolated from the cerebrospinal fluid of patients from different parts of the world or from hot springs, had repetitive restriction fragment bands of similar total lengths (ca. 45 kilobases), and most repetitive bands displayed identical mobilities. However, polymorphic bands were useful in identifying particular isolates. Restriction fragment length polymorphism analysis generally was consistent with taxonomy based on studies of infectivity, morphology, isoenzyme patterns, and antibody reactivity and suggests that this technique may help classify amebae isolated from clinical specimens or from the environment.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bell G. I., Karam J. H., Rutter W. J. Polymorphic DNA region adjacent to the 5' end of the human insulin gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Sep;78(9):5759–5763. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.9.5759. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins F. H., Mendez M. A., Rasmussen M. O., Mehaffey P. C., Besansky N. J., Finnerty V. A ribosomal RNA gene probe differentiates member species of the Anopheles gambiae complex. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1987 Jul;37(1):37–41. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1987.37.37. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grillner L., Strangert K. Restriction endonuclease analysis of cytomegalovirus DNA from strains isolated in day care centers. Pediatr Infect Dis. 1986 Mar-Apr;5(2):184–187. doi: 10.1097/00006454-198603000-00004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hammer S. M., Buchman T. G., D'Angelo L. J., Karchmer A. W., Roizman B., Hirsch M. S. Temporal cluster of herpes simplex encephalitis: investigation by restriction endonuclease cleavage of viral DNA. J Infect Dis. 1980 Apr;141(4):436–440. doi: 10.1093/infdis/141.4.436. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khabbaz R. F., Kaper J. B., Moody M. R., Schimpff S. C., Tenney J. H. Molecular epidemiology of group JK Corynebacterium on a cancer ward: lack of evidence for patient-to-patient transmission. J Infect Dis. 1986 Jul;154(1):95–99. doi: 10.1093/infdis/154.1.95. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kristiansen B. E., Sørensen B., Bjorvatn B., Falk E. S., Fosse E., Bryn K., Frøholm L. O., Gaustad P., Bøvre K. An outbreak of group B meningococcal disease: tracing the causative strain of Neisseria meningitidis by DNA fingerprinting. J Clin Microbiol. 1986 Apr;23(4):764–767. doi: 10.1128/jcm.23.4.764-767.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Markowitz S. M., Veazey J. M., Jr, Macrina F. L., Mayhall C. G., Lamb V. A. Sequential outbreaks of infection due to Klebsiella pneumoniae in a neonatal intensive care unit: implication of a conjugative R plasmid. J Infect Dis. 1980 Jul;142(1):106–112. doi: 10.1093/infdis/142.1.106. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLaughlin G. L., Collins W. E., Campbell G. H. Comparison of genomic, plasmid, synthetic, and combined DNA probes for detecting Plasmodium falciparum DNA. J Clin Microbiol. 1987 May;25(5):791–795. doi: 10.1128/jcm.25.5.791-795.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLaughlin G. L., Ruth J. L., Jablonski E., Steketee R., Campbell G. H. Use of enzyme-linked synthetic DNA in diagnosis of falciparum malaria. Lancet. 1987 Mar 28;1(8535):714–716. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(87)90356-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mucenski C. M., Guerry P., Buesing M., Szarfman A., Trosper J., Walliker D., Watt G., Sangalang R., Ranoa C. P., Tuazon M. Evaluation of a synthetic oligonucleotide probe for diagnosis of Plasmodium falciparum infections. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1986 Sep;35(5):912–920. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1986.35.912. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nash T. E., McCutchan T., Keister D., Dame J. B., Conrad J. D., Gillin F. D. Restriction-endonuclease analysis of DNA from 15 Giardia isolates obtained from humans and animals. J Infect Dis. 1985 Jul;152(1):64–73. doi: 10.1093/infdis/152.1.64. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Visvesvara G. S., Peralta M. J., Brandt F. H., Wilson M., Aloisio C., Franko E. Production of monoclonal antibodies to Naegleria fowleri, agent of primary amebic meningoencephalitis. J Clin Microbiol. 1987 Sep;25(9):1629–1634. doi: 10.1128/jcm.25.9.1629-1634.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]