Abstract
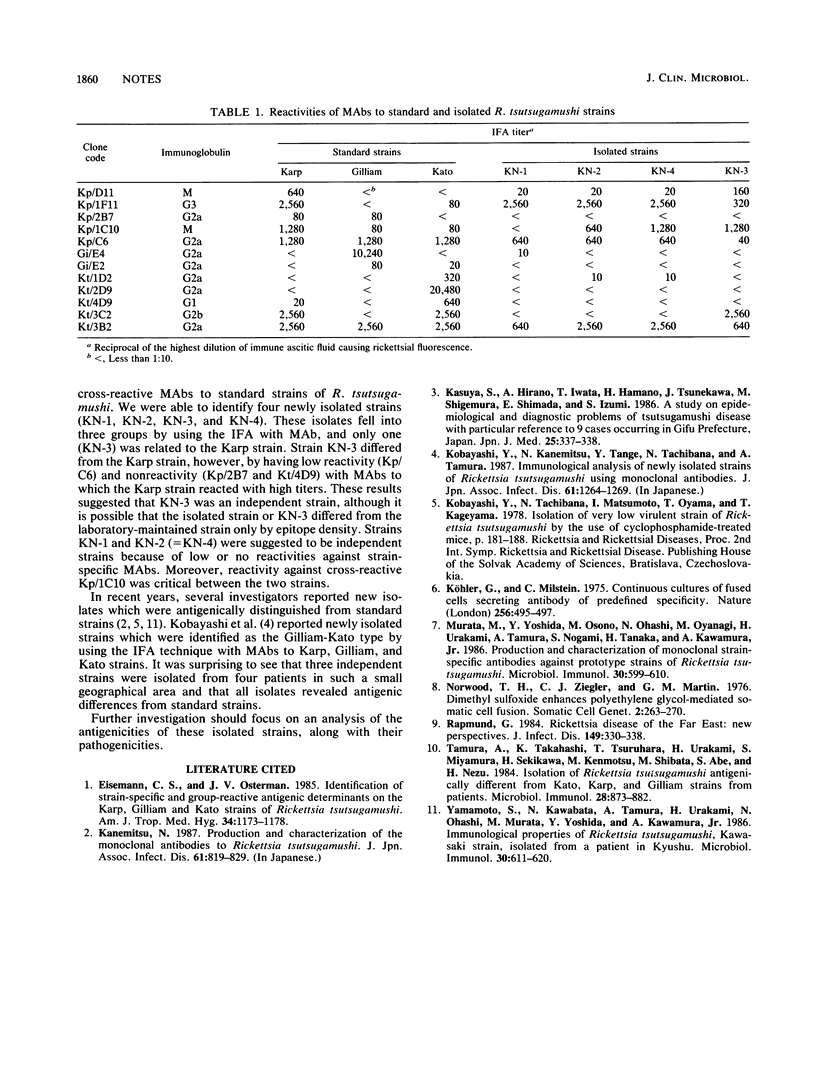
Four isolated strains of Rickettsia tsutsugamushi from patients in a new endemic area of Japan were tested for antigenicities by using 12 monoclonal antibodies to Karp, Gilliam, and Kato strains. It was suggested that one isolate was Karp related and that the others were two independent strains.
Full text
PDF
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Eisemann C. S., Osterman J. V. Identification of strain-specific and group-reactive antigenic determinants on the Karp, Gilliam and Kato strains of Rickettsia tsutsugamushi. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1985 Nov;34(6):1173–1178. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1985.34.1173. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kanemitsu N. [Production and characterization of the monoclonal antibodies to Rickettsia tsutsugamushi]. Kansenshogaku Zasshi. 1987 Jul;61(7):819–829. doi: 10.11150/kansenshogakuzasshi1970.61.819. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kobayashi Y., Kanemitsu N., Tange Y., Tachibana N., Tamura A. [Immunological analysis of newly isolated strains of Rickettsia tsutsugamushi using monoclonal antibodies]. Kansenshogaku Zasshi. 1987 Nov;61(11):1264–1269. doi: 10.11150/kansenshogakuzasshi1970.61.1264. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Köhler G., Milstein C. Continuous cultures of fused cells secreting antibody of predefined specificity. Nature. 1975 Aug 7;256(5517):495–497. doi: 10.1038/256495a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murata M., Yoshida Y., Osono M., Ohashi N., Oyanagi M., Urakami H., Tamura A., Nogami S., Tanaka H., Kawamura A., Jr Production and characterization of monoclonal strain-specific antibodies against prototype strains of Rickettsia tsutsugamushi. Microbiol Immunol. 1986;30(7):599–610. doi: 10.1111/j.1348-0421.1986.tb02987.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norwood T. H., Zeigler C. J., Martin G. M. Dimethyl sulfoxide enhances polyethylene glycol-mediated somatic cell fusion. Somatic Cell Genet. 1976 May;2(3):263–270. doi: 10.1007/BF01538964. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rapmund G. Rickettsial diseases of the Far East: new perspectives. J Infect Dis. 1984 Mar;149(3):330–338. doi: 10.1093/infdis/149.3.330. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tamura A., Takahashi K., Tsuruhara T., Urakami H., Miyamura S., Sekikawa H., Kenmotsu M., Shibata M., Abe S., Nezu H. Isolation of Rickettsia tsutsugamushi antigenically different from Kato, Karp, and Gilliam strains from patients. Microbiol Immunol. 1984;28(8):873–882. doi: 10.1111/j.1348-0421.1984.tb00743.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto S., Kawabata N., Tamura A., Urakami H., Ohashi N., Murata M., Yoshida Y., Kawamura A., Jr Immunological properties of Rickettsia tsutsugamushi, Kawasaki strain, isolated from a patient in Kyushu. Microbiol Immunol. 1986;30(7):611–620. doi: 10.1111/j.1348-0421.1986.tb02988.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


