Abstract
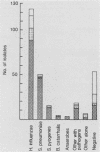
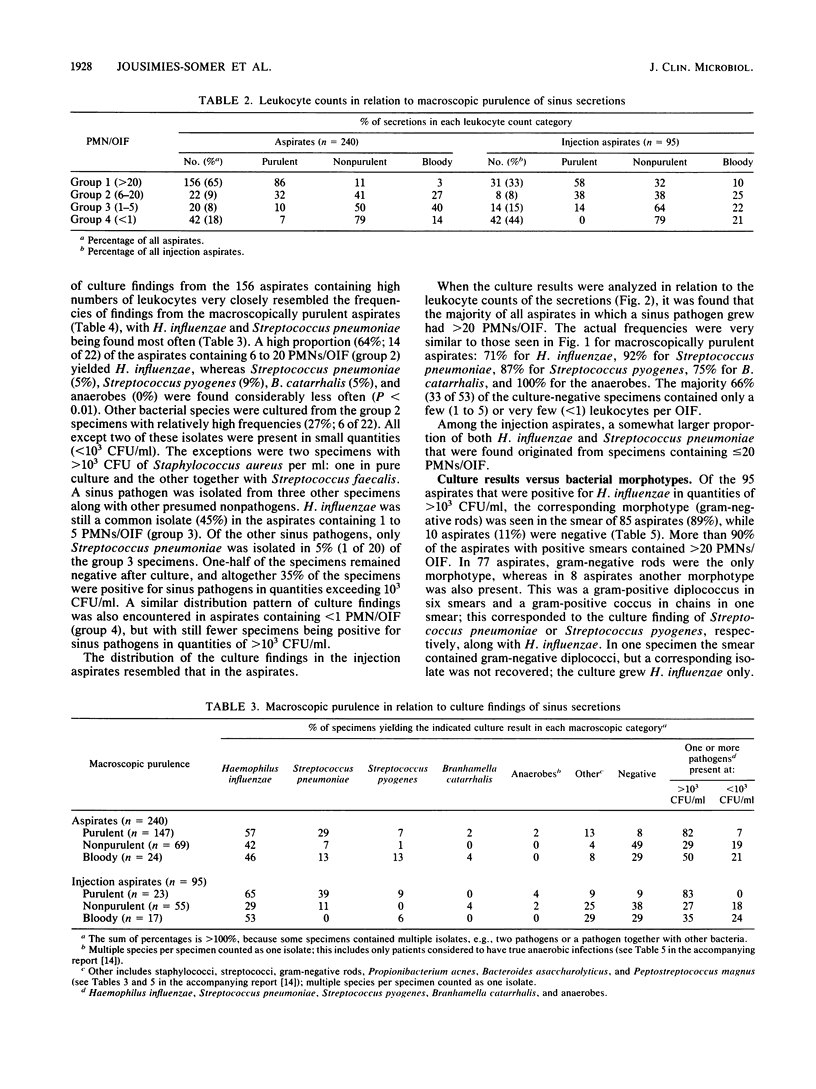
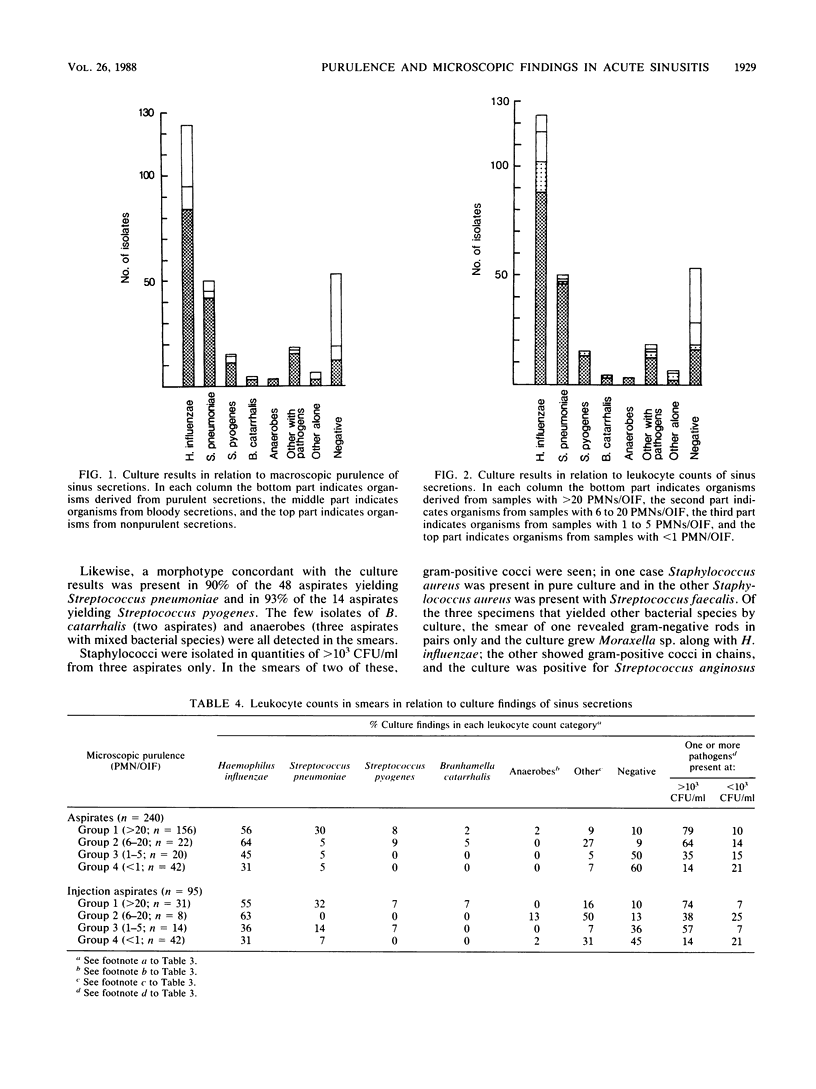
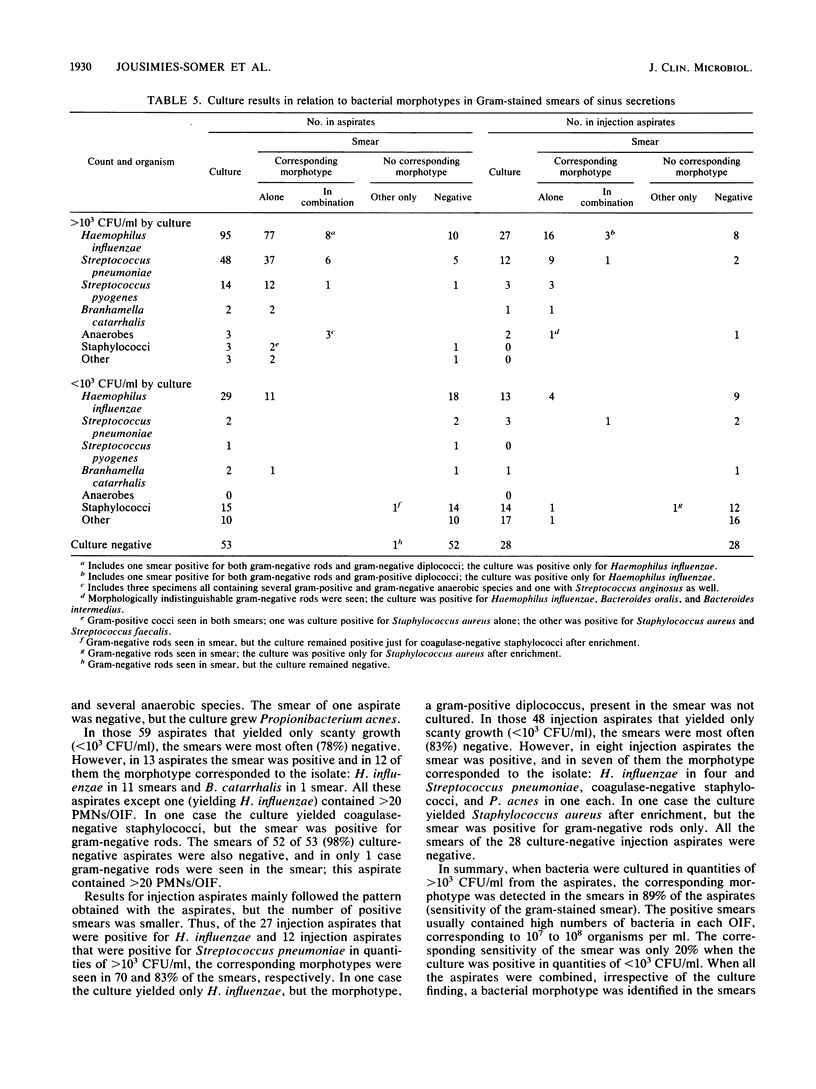
Macroscopic purulence, leukocyte counts, and bacterial morphotypes in Gram-stained smears were investigated in 335 sinus secretions (240 aspirates and 95 injection aspirates) obtained by puncture in 234 young patients with acute maxillary sinusitis. Over 90% of the 147 aspirates macroscopically classified as purulent also contained high numbers of leukocytes (greater than 20 per oil immersion field). A total of 82% of the 147 macroscopically purulent aspirates and 79% of the 156 aspirates containing high numbers of leukocytes yielded presumed sinus pathogens by culture in quantities of greater than 10(3) CFU/ml. Streptococcus pneumoniae or Streptococcus pyogenes was associated relatively more often (92 or 87%, respectively) with high numbers of leukocytes than Haemophilus influenzae, which was not infrequently (29%) recovered from the less purulent aspirates. When a bacterial morphotype was seen in the Gram-stained smear, a corresponding sinus pathogen was isolated in quantities of greater than 10(3) CFU/ml in 92% of aspirates. Other bacterial species (most often staphylococci) were usually isolated in low numbers and were almost never seen in the smear, suggesting nasal contamination. The 95 injection aspirates behaved, to a large extent, like diluted aspirates, with the exception that there was a higher frequency of probable nasal contamination. Macroscopic purulence, high leukocyte counts, and bacterial morphotypes seen in Gram-stained smears each predicted well the isolation of a presumed sinus pathogen and in some cases supported the significance of an otherwise doubtful culture finding. However, the macroscopic appearance of the secretion should not be used to screen samples for culture, because in several cases H. influenzae grew from nonpurulent samples as well.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Axelsson A., Brorson J. E. The correlation between bacteriological findings in the nose and maxillary sinus in acute maxillary sinusitis. Laryngoscope. 1973 Dec;83(12):2003–2011. doi: 10.1288/00005537-197312000-00011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bridger R. C. Sinusitis: an improved regime of investigation for the clinical laboratory. J Clin Pathol. 1980 Mar;33(3):276–281. doi: 10.1136/jcp.33.3.276. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carenfelt C., Lundberg C., Nord C. E., Wretlind B. Bacteriology of maxillary sinusitis in relation to quality of the retained secretion. Acta Otolaryngol. 1978 Sep-Oct;86(3-4):298–302. doi: 10.3109/00016487809124750. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carenfelt C., Lundberg C. Purulent and non-purulent maxillary sinus secretions with respect to pO2, pCO2 and pH. Acta Otolaryngol. 1977 Jul-Aug;84(1-2):138–144. doi: 10.3109/00016487709123952. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carenfelt C., Lundberg C. The role of local gas composition in pathogenesis of maxillary sinus empyema. Acta Otolaryngol. 1978 Jan-Feb;85(1-2):116–121. doi: 10.3109/00016487809121431. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carenfelt C. Pathogenesis of sinus empyema. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol. 1979 Jan-Feb;88(1 Pt 1):16–20. doi: 10.1177/000348947908800104. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engquist S., Lundberg C. Akut sinuit--när, hur och av vem bör den behandlas? Lakartidningen. 1986 Sep 17;83(38):3112–3114. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engquist S., Lundberg C. Bacteria and inflammatory cells in maxillary sinusitis. Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 1984;239(2):173–180. doi: 10.1007/BF00463558. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans F. O., Jr, Sydnor J. B., Moore W. E., Moore G. R., Manwaring J. L., Brill A. H., Jackson R. T., Hanna S., Skaar J. S., Holdeman L. V. Sinusitis of the maxillary antrum. N Engl J Med. 1975 Oct 9;293(15):735–739. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197510092931502. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gwaltney J. M., Jr, Sydnor A., Jr, Sande M. A. Etiology and antimicrobial treatment of acute sinusitis. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol Suppl. 1981 May-Jun;90(3 Pt 3):68–71. doi: 10.1177/00034894810903s216. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamory B. H., Sande M. A., Sydnor A., Jr, Seale D. L., Gwaltney J. M., Jr Etiology and antimicrobial therapy of acute maxillary sinusitis. J Infect Dis. 1979 Feb;139(2):197–202. doi: 10.1093/infdis/139.2.197. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jousimies-Somer H. R., Savolainen S., Ylikoski J. S. Bacteriological findings of acute maxillary sinusitis in young adults. J Clin Microbiol. 1988 Oct;26(10):1919–1925. doi: 10.1128/jcm.26.10.1919-1925.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KORTEKANGAS A. E. ANTIBIOTICS IN THE TREATMENT OF MAXILLARY SINUSITIS. Acta Otolaryngol Suppl. 1964;188:SUPPL 188–188:379+. doi: 10.3109/00016486409134591. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LYSTAD A., BERDAL P., LUND-IVERSEN L. THE BACTERIAL FLORA OF SINUSITIS WITH AN IN VITRO STUDY OF THE BACTERIAL RESISTANCE TO ANTIBIOTICS. Acta Otolaryngol Suppl. 1964;188:SUPPL 188–188:390+. doi: 10.3109/00016486409134592. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ludman H. Paranasal sinus diseases. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed) 1981 Mar 28;282(6269):1054–1057. doi: 10.1136/bmj.282.6269.1054. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lundberg C., Carenfelt C., Engquist S., Nord C. E. Anaerobic bacteria in maxillary sinusitis. Scand J Infect Dis Suppl. 1979;(19):74–76. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Cauwenberge P., Verschraegen G., Van Renterghem L. Bacteriological findings in sinusitis (1963-1975). Scand J Infect Dis Suppl. 1976;(9):72–77. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vecchio T. J. Predictive value of a single diagnostic test in unselected populations. N Engl J Med. 1966 May 26;274(21):1171–1173. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196605262742104. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wald E. R., Milmoe G. J., Bowen A., Ledesma-Medina J., Salamon N., Bluestone C. D. Acute maxillary sinusitis in children. N Engl J Med. 1981 Mar 26;304(13):749–754. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198103263041302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wald E. R., Reilly J. S., Casselbrant M., Ledesma-Medina J., Milmoe G. J., Bluestone C. D., Chiponis D. Treatment of acute maxillary sinusitis in childhood: a comparative study of amoxicillin and cefaclor. J Pediatr. 1984 Feb;104(2):297–302. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(84)81018-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Cauwenberge P., Kluyskens P., van Renterghem L. The importance of the anaerobic bacteria in paranasal sinusitis. Rhinology. 1975 Nov;13(3):141–145. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]