Abstract
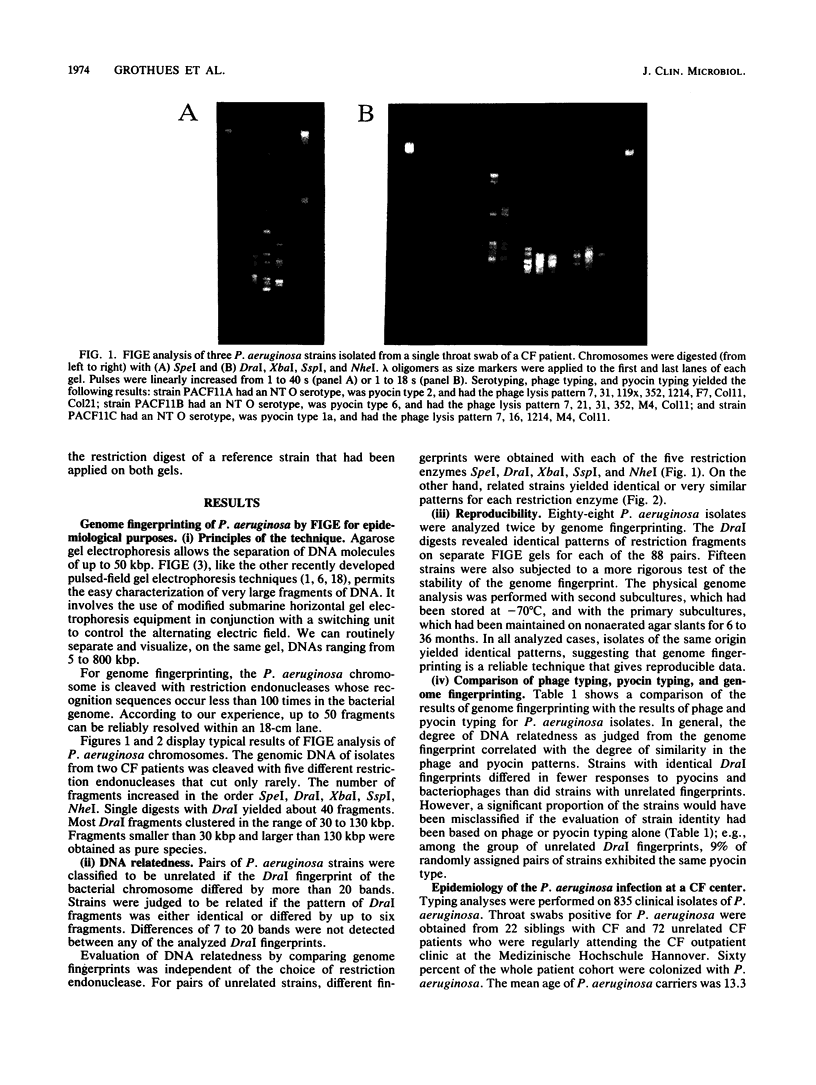
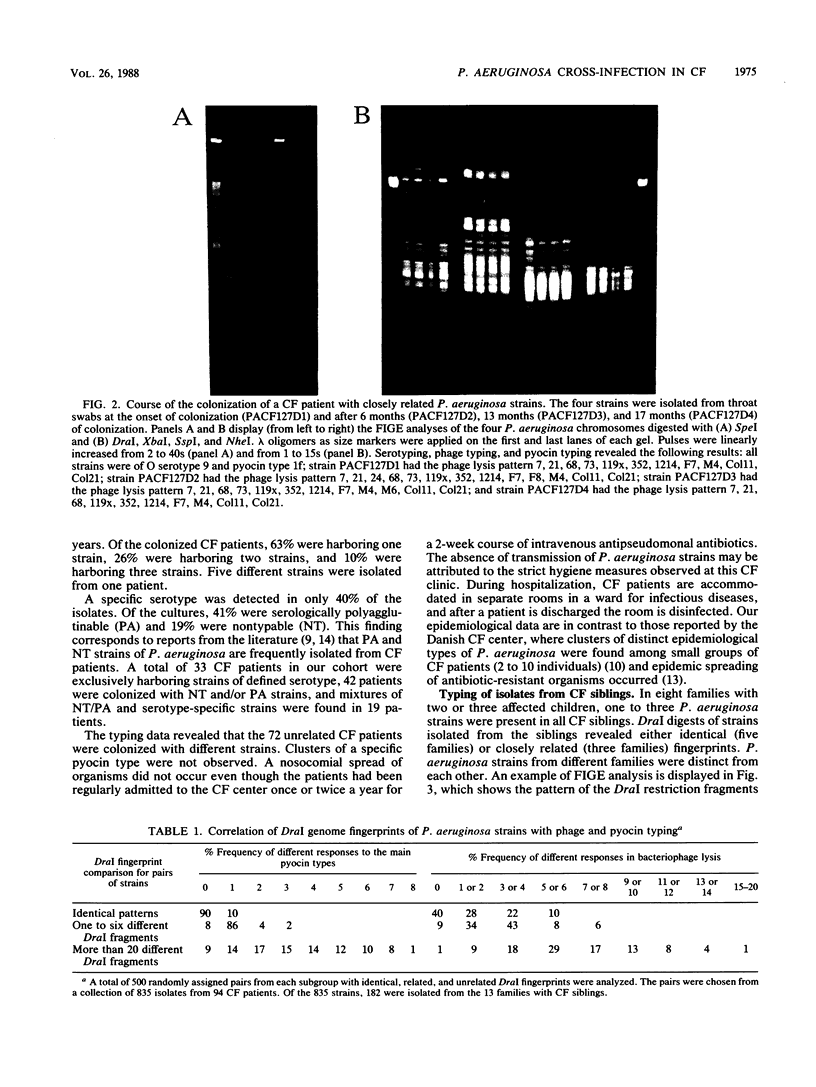
The epidemiology of Pseudomonas aeruginosa infection at a cystic fibrosis (CF) center was monitored over a 3-year period. A total of 835 isolates from 72 unrelated patients and 22 siblings with CF were analyzed by genome fingerprinting and serotyping, bacteriophage typing, and pyocin typing. For genome fingerprinting, bacterial chromosomes were digested with one of the restriction endonucleases SpeI, DraI, XbaI, SspI, and NheI, which cut only rarely, and subsequently separated by field inversion gel electrophoresis. The physical genome analysis allowed us to classify P. aeruginosa strains in terms of DNA relatedness. Related strains differed by fewer than six DraI bands in the fingerprint, whereas unrelated strains differed by more than 20 DraI bands. All unrelated CF patients were colonized with different strains. The absence of a nosocomial spread of organisms at the CF center was attributed to the strict hygiene measures observed at the hospital. CF siblings were harboring either identical or closely related strains; transmission within the family is thought to be the most likely cause.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Carle G. F., Frank M., Olson M. V. Electrophoretic separations of large DNA molecules by periodic inversion of the electric field. Science. 1986 Apr 4;232(4746):65–68. doi: 10.1126/science.3952500. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diaz E., Mosovich L. L., Neter E. Serogroups of Pseudomonas aeruginosa and the immune response of patients with cystic fibrosis. J Infect Dis. 1970 Mar;121(3):269–274. doi: 10.1093/infdis/121.3.269. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fyfe J. A., Harris G., Govan J. R. Revised pyocin typing method for Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Clin Microbiol. 1984 Jul;20(1):47–50. doi: 10.1128/jcm.20.1.47-50.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gardiner K., Laas W., Patterson D. Fractionation of large mammalian DNA restriction fragments using vertical pulsed-field gradient gel electrophoresis. Somat Cell Mol Genet. 1986 Mar;12(2):185–195. doi: 10.1007/BF01560665. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hancock R. E., Mutharia L. M., Chan L., Darveau R. P., Speert D. P., Pier G. B. Pseudomonas aeruginosa isolates from patients with cystic fibrosis: a class of serum-sensitive, nontypable strains deficient in lipopolysaccharide O side chains. Infect Immun. 1983 Oct;42(1):170–177. doi: 10.1128/iai.42.1.170-177.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Høiby N., Rosendal K. Epidemiology of Pseudomonas aeruginosa infection in patients treated at a cystic fibrosis centre. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand B. 1980 Jun;88(3):125–131. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1980.tb02617.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelly N. M., Fitzgerald M. X., Tempany E., O'Boyle C., Falkiner F. R., Keane C. T. Does pseudomonas cross-infection occur between cystic-fibrosis patients. Lancet. 1982 Sep 25;2(8300):688–690. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(82)90714-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ogle J. W., Janda J. M., Woods D. E., Vasil M. L. Characterization and use of a DNA probe as an epidemiological marker for Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Infect Dis. 1987 Jan;155(1):119–126. doi: 10.1093/infdis/155.1.119. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pedersen S. S., Koch C., Høiby N., Rosendal K. An epidemic spread of multiresistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa in a cystic fibrosis centre. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1986 Apr;17(4):505–516. doi: 10.1093/jac/17.4.505. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Penketh A., Pitt T., Roberts D., Hodson M. E., Batten J. C. The relationship of phenotype changes in Pseudomonas aeruginosa to the clinical condition of patients with cystic fibrosis. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1983 May;127(5):605–608. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1983.127.5.605. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pier G. B. Pulmonary disease associated with Pseudomonas aeruginosa in cystic fibrosis: current status of the host-bacterium interaction. J Infect Dis. 1985 Apr;151(4):575–580. doi: 10.1093/infdis/151.4.575. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pitt T. L., Erdman Y. J. The specificity of agglutination reactions of Pseudomonas aeruginosa with O antisera. J Med Microbiol. 1978 Feb;11(1):15–23. doi: 10.1099/00222615-11-1-15. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seale T. W., Thirkill H., Tarpay M., Flux M., Rennert O. M. Serotypes and antibiotic susceptibilities of Pseudomonas aeruginosa isolates from single sputa of cystic fibrosis patients. J Clin Microbiol. 1979 Jan;9(1):72–78. doi: 10.1128/jcm.9.1.72-78.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tenover F. C. Plasmid fingerprinting. A tool for bacterial strain identification and surveillance of nosocomial and community-acquired infections. Clin Lab Med. 1985 Sep;5(3):413–436. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomassen M. J., Demko C. A., Boxerbaum B., Stern R. C., Kuchenbrod P. J. Multiple of isolates of Pseudomonas aeruginosa with differing antimicrobial susceptibility patterns from patients with cystic fibrosis. J Infect Dis. 1979 Dec;140(6):873–880. doi: 10.1093/infdis/140.6.873. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vasil M. L., Chamberlain C., Grant C. C. Molecular studies of Pseudomonas exotoxin A gene. Infect Immun. 1986 May;52(2):538–548. doi: 10.1128/iai.52.2.538-548.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]