Abstract
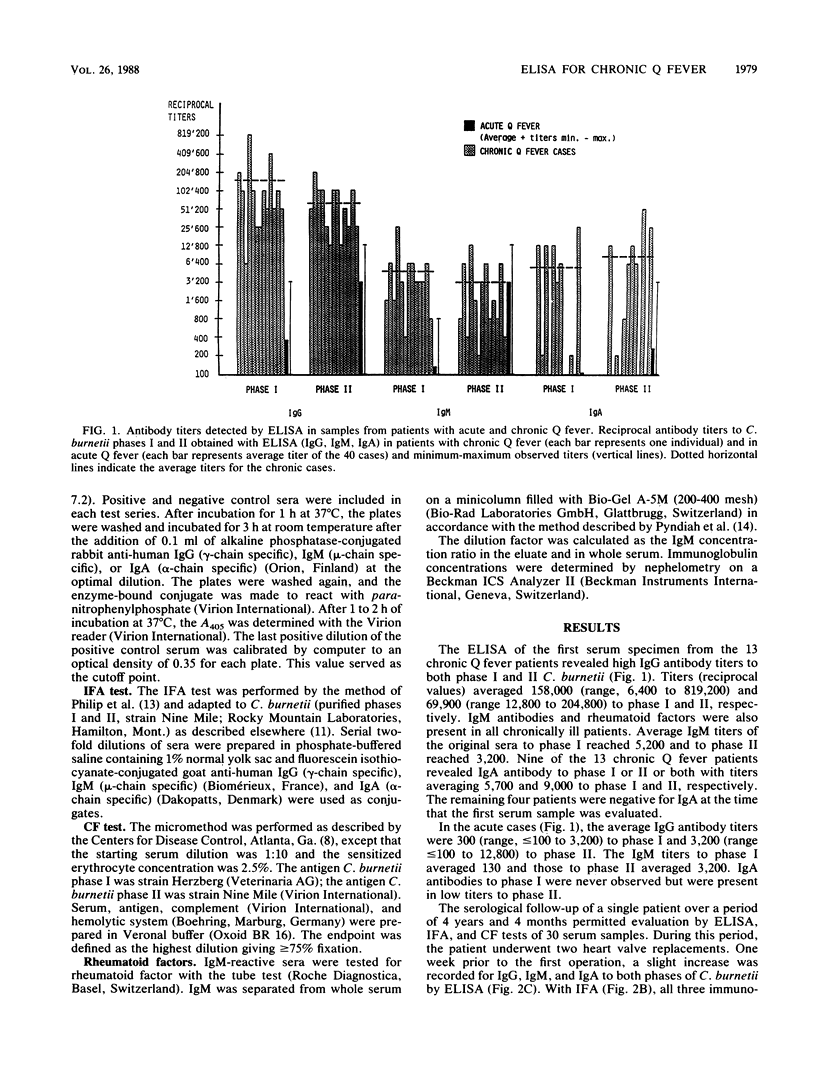
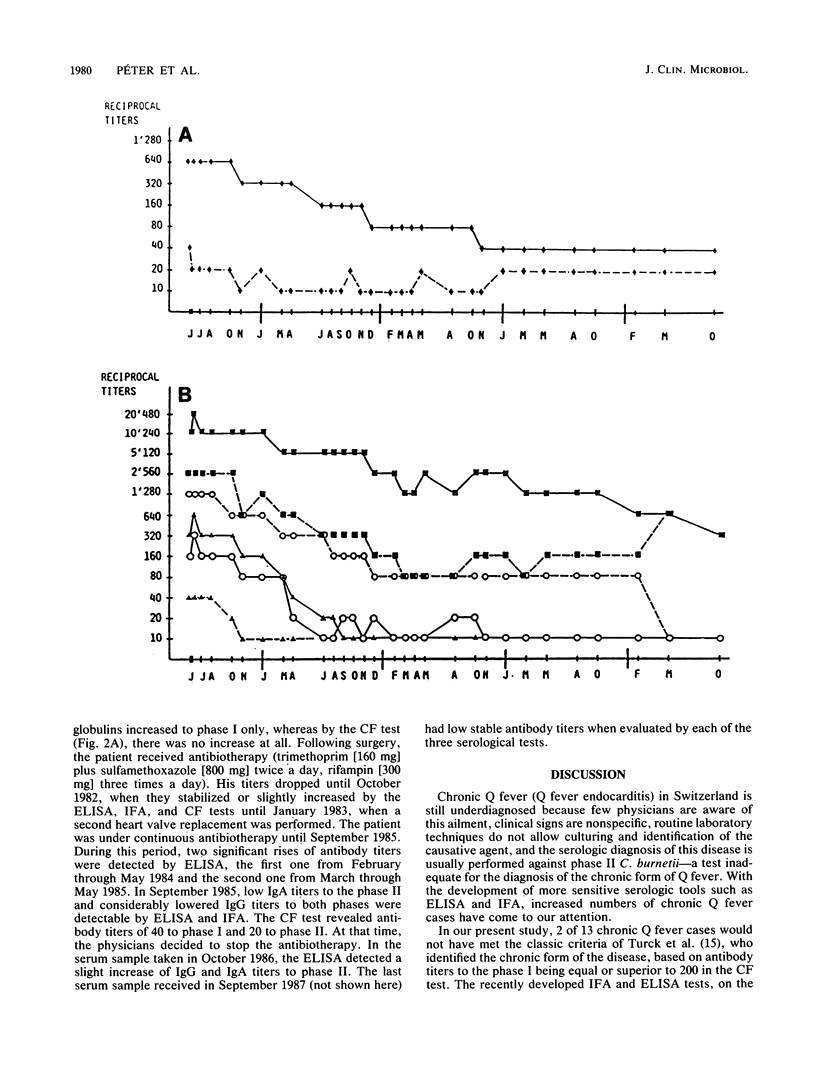
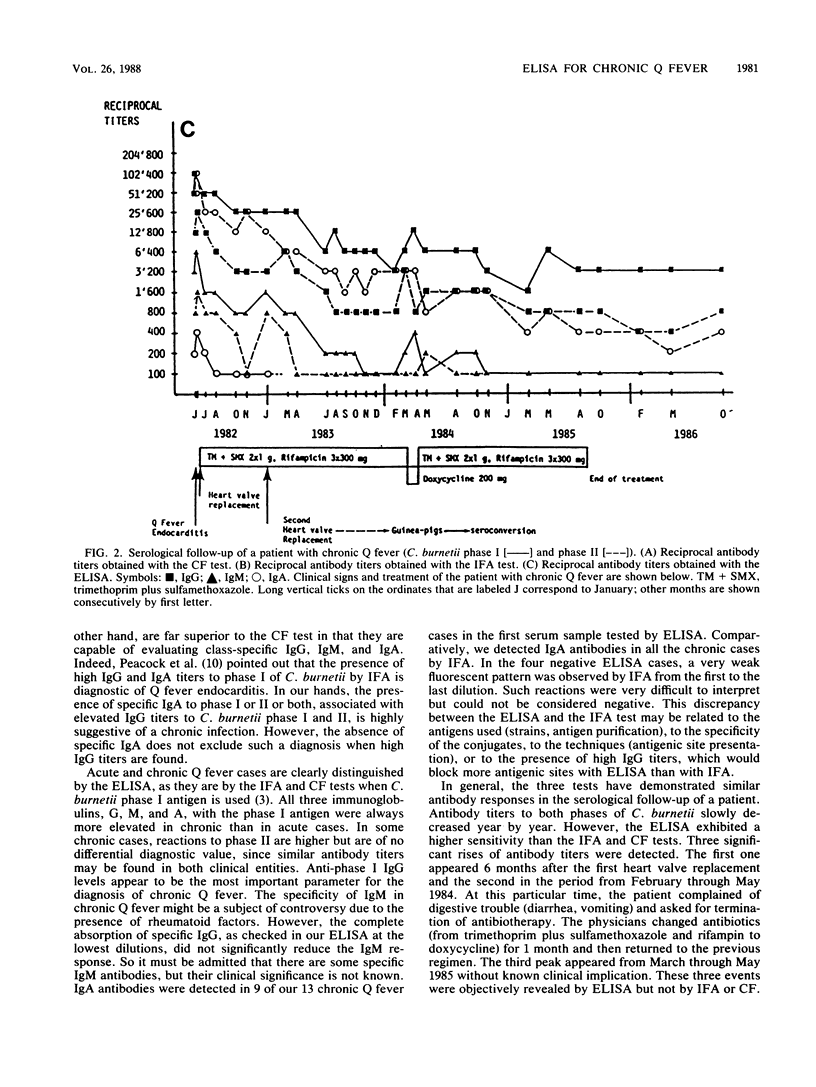
From 1982 through 1987 we diagnosed 13 chronic Q fever cases. Clinically these patients presented a culture-negative endocarditis, and all but two had high complement-fixing antibody titers to Coxiella burnetii phase I (reciprocal titer above 200). With the enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA), titers of immunoglobulin G (IgG) to phases I and II of C. burnetii averaged 158,000 and 69,900, respectively, whereas they reached 300 and 3,200 in acute Q fever cases. Similarly, IgA to both phases of C. burnetii and IgM to phase I were consistently higher during chronic than acute Q fever. The serological follow-up of one patient with chronic Q fever over a 4-year period showed a good correlation between the titers of IgG and IgM antibody titers detected by ELISA and indirect fluorescent-antibody test (IFA) to both phases of C. burnetii. Few discrepancies appeared with IgA. Shortly after initiation of antibiotic treatment, a slow and steady decrease of the antibody titers to C. burnetii phases I and II was observed. The complement fixation, IFA, and ELISA tests showed the same type of antibody response. The ELISA proved to be an excellent diagnostic test for chronic Q fever. It distinguished negative from positive reactions clearly, and results were highly reproducible. The reading is objective, and the test is simple to perform and more sensitive than the IFA and complement fixation tests. The ELISA is recommended for serologic evaluation of patients with chronic Q fever.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Amano K., Williams J. C. Chemical and immunological characterization of lipopolysaccharides from phase I and phase II Coxiella burnetii. J Bacteriol. 1984 Dec;160(3):994–1002. doi: 10.1128/jb.160.3.994-1002.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baca O. G., Paretsky D. Q fever and Coxiella burnetii: a model for host-parasite interactions. Microbiol Rev. 1983 Jun;47(2):127–149. doi: 10.1128/mr.47.2.127-149.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dupuis G., Péter O., Lüthy R., Nicolet J., Peacock M., Burgdorfer W. Serological diagnosis of Q fever endocarditis. Eur Heart J. 1986 Dec;7(12):1062–1066. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.eurheartj.a062016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dupuis G., Péter O., Pedroni D., Petite J. Aspects cliniques observés lors d'une épidémie de 415 cas de fièvre Q. Schweiz Med Wochenschr. 1985 Jun 15;115(24):814–818. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Field P. R., Hunt J. G., Murphy A. M. Detection and persistence of specific IgM antibody to Coxiella burnetii by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay: a comparison with immunofluorescence and complement fixation tests. J Infect Dis. 1983 Sep;148(3):477–487. doi: 10.1093/infdis/148.3.477. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laufer D., Lew P. D., Oberhansli I., Cox J. N., Longson M. Chronic Q fever endocarditis with massive splenomegaly in childhood. J Pediatr. 1986 Apr;108(4):535–539. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(86)80828-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palmer S. R., Young S. E. Q-fever endocarditis in England and Wales, 1975-81. Lancet. 1982 Dec 25;2(8313):1448–1449. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(82)91341-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peacock M. G., Philip R. N., Williams J. C., Faulkner R. S. Serological evaluation of O fever in humans: enhanced phase I titers of immunoglobulins G and A are diagnostic for Q fever endocarditis. Infect Immun. 1983 Sep;41(3):1089–1098. doi: 10.1128/iai.41.3.1089-1098.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Philip R. N., Casper E. A., Ormsbee R. A., Peacock M. G., Burgdorfer W. Microimmunofluorescence test for the serological study of rocky mountain spotted fever and typhus. J Clin Microbiol. 1976 Jan;3(1):51–61. doi: 10.1128/jcm.3.1.51-61.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pyndiah N., Krech U., Price P., Wilhelm J. Simplified chromatographic separation of immunoglobulin M from G and its application to toxoplasma indirect immunofluorescence. J Clin Microbiol. 1979 Feb;9(2):170–174. doi: 10.1128/jcm.9.2.170-174.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Péter O., Dupuis G., Burgdorfer W., Peacock M. Evaluation of the complement fixation and indirect immunofluorescence tests in the early diagnosis of primary Q fever. Eur J Clin Microbiol. 1985 Aug;4(4):394–396. doi: 10.1007/BF02148690. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Péter O., Dupuis G., Peacock M. G., Burgdorfer W. Comparison of enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay and complement fixation and indirect fluorescent-antibody tests for detection of Coxiella burnetii antibody. J Clin Microbiol. 1987 Jun;25(6):1063–1067. doi: 10.1128/jcm.25.6.1063-1067.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turck W. P., Howitt G., Turnberg L. A., Fox H., Longson M., Matthews M. B., Das Gupta R. Chronic Q fever. Q J Med. 1976 Apr;45(178):193–217. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


