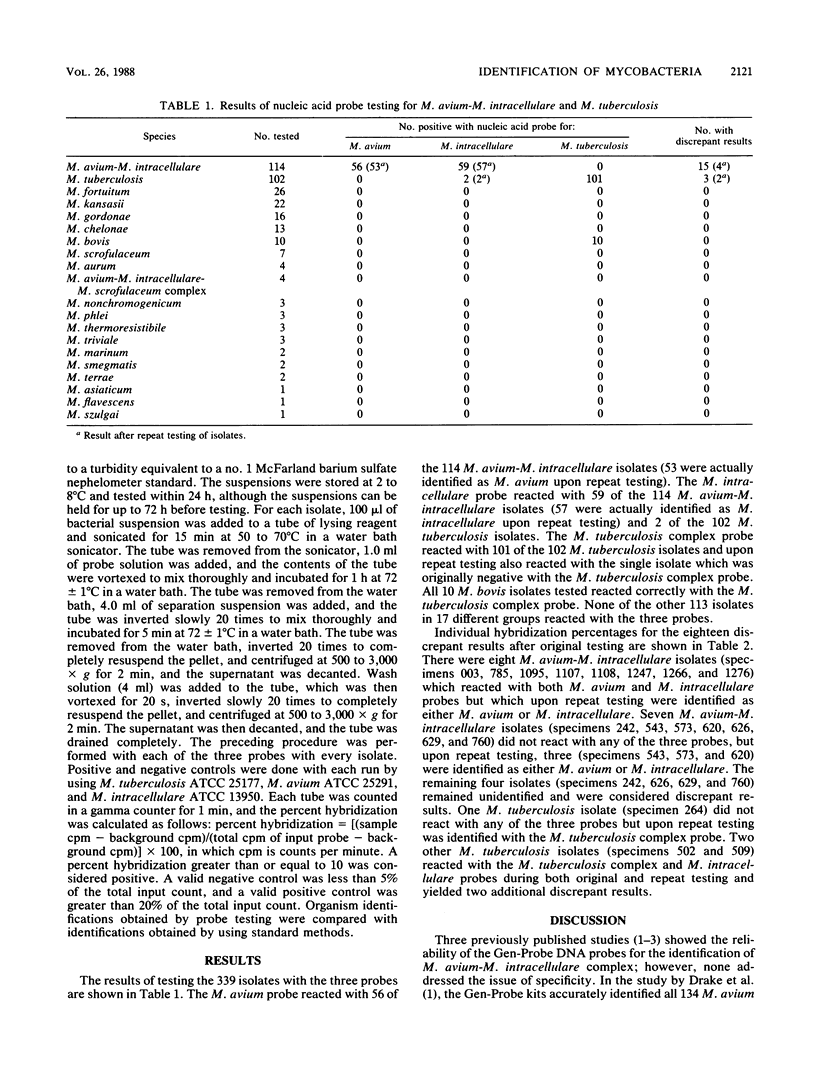
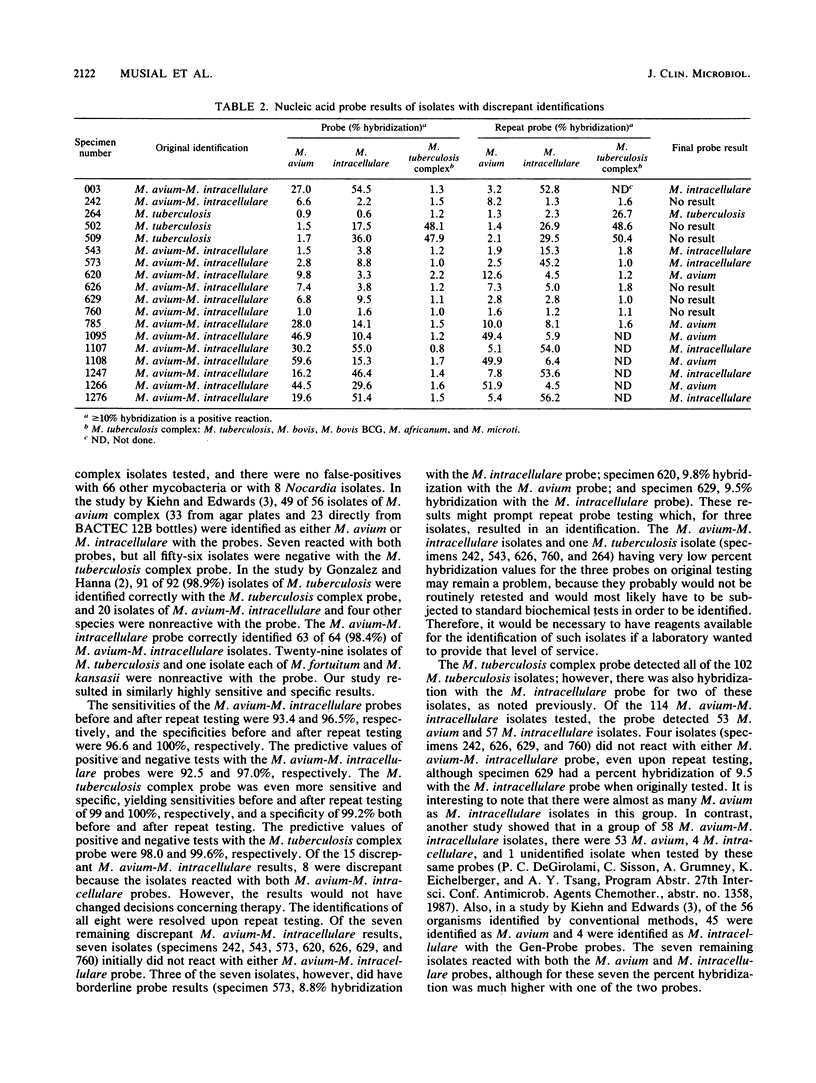
Abstract
Commercially available kits (Mycobacterium avium Complex Rapid Diagnostic System and Mycobacterium tuberculosis Complex Rapid Diagnostic System; Gen-Probe, Inc., San Diego, Calif.) utilizing nucleic acid hybridization for the rapid identification of members of the M. avium-M. intracellulare complex and M. tuberculosis complex were evaluated by using 339 clinical and American Type Culture Collection (Rockville, Md.) isolates. The tests, which can be performed in approximately 2 h, use specific [125I]DNA probes complementary to the rRNAs of M. avium, M. intracellulare, and M. tuberculosis complex, the latter of which includes M. tuberculosis, M. bovis, M. bovis BCG, M. africanum, and M. microti. The M. avium-M. intracellulare probes correctly identified 99 of 114 M. avium-M. intracellulare isolates, with 7 false-negatives and 8 false-positives, for a sensitivity of 93.4% and a specificity of 96.6%. After repeat testing, 110 of 114 were correctly identified, with 4 false-negatives and no false-positives, for a sensitivity of 96.5% and a specificity of 100%. The M. tuberculosis complex probe correctly identified 99 of 102 M. tuberculosis isolates, with 1 false-negative and 2 false-positives, for a sensitivity of 99% and a specificity of 99.2%. After repeat testing, 100 of 102 isolates were correctly identified, with no false-negatives and 2 false-positives, for a sensitivity of 100% and a specificity of 99.2%. Overall, there were 15 discrepant M. avium-M. intracellulare results, with 4 such results after repeat testing, and 3 discrepant M. tuberculosis complex results, with 2 such results after repeat testing. The Gen-Probe kits are highly sensitive and specific for use in identifying M. avium-M. intracellulare complex and M. tuberculosis complex isolates and will be useful in the clinical laboratory which can use the present radionuclide-containing kits cost effectively.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Drake T. A., Hindler J. A., Berlin O. G., Bruckner D. A. Rapid identification of Mycobacterium avium complex in culture using DNA probes. J Clin Microbiol. 1987 Aug;25(8):1442–1445. doi: 10.1128/jcm.25.8.1442-1445.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gonzalez R., Hanna B. A. Evaluation of Gen-Probe DNA hybridization systems for the identification of Mycobacterium tuberculosis and Mycobacterium avium-intracellulare. Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis. 1987 Oct;8(2):69–77. doi: 10.1016/0732-8893(87)90152-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kiehn T. E., Edwards F. F. Rapid identification using a specific DNA probe of Mycobacterium avium complex from patients with acquired immunodeficiency syndrome. J Clin Microbiol. 1987 Aug;25(8):1551–1552. doi: 10.1128/jcm.25.8.1551-1552.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


