Abstract
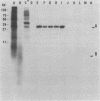
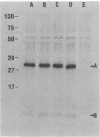
The major obstacle in large-scale epidemiological investigations of the incidence of Shiga-like toxin (SLT)-producing Escherichia coli in diarrheal stools is the lack of a rapid, specific test to detect toxin. Enterohemorrhagic E. coli produces elevated levels of SLT-I, SLT-II, or both cytotoxins (also called Verotoxins). SLT-I but not SLT-II can be neutralized by antiserum to purified Shiga toxin and by monoclonal antibodies to the B subunit of SLT-I. In this study, monoclonal antibodies were generated against a crude preparation of SLT-II produced by an E. coli K-12 strain lysogenized with the 933W toxin-converting phage of enterohemorrhagic E. coli 933. Hybridoma culture supernatants were screened for anti-SLT-II antibodies by a cytotoxicity neutralization assay and by an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA). Of 53 ELISA-positive lines, 5 were capable of neutralizing the cytotoxicity of SLT-II but not of SLT-I, Shiga toxin, or a variant of SLT-II produced by E. coli that causes edema disease of swine. All five monoclonal antibodies immunoprecipitated the isolated A subunit of SLT-II but not the B subunit. Of these five neutralizing monoclonal antibodies, four were of the immunoglobulin M class and one belonged to the immunoglobulin G1 subclass. All five lines had kappa light chains. These neutralizing monoclonal antibodies have been used as probes in a colony ELISA to detect SLT-II-positive bacterial colonies. The colony ELISA with these monoclonal antibodies is a specific, sensitive test with potential diagnostic value.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brown J. E., Griffin D. E., Rothman S. W., Doctor B. P. Purification and biological characterization of shiga toxin from Shigella dysenteriae 1. Infect Immun. 1982 Jun;36(3):996–1005. doi: 10.1128/iai.36.3.996-1005.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burnette W. N. "Western blotting": electrophoretic transfer of proteins from sodium dodecyl sulfate--polyacrylamide gels to unmodified nitrocellulose and radiographic detection with antibody and radioiodinated protein A. Anal Biochem. 1981 Apr;112(2):195–203. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90281-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donohue-Rolfe A., Keusch G. T., Edson C., Thorley-Lawson D., Jacewicz M. Pathogenesis of Shigella diarrhea. IX. Simplified high yield purification of Shigella toxin and characterization of subunit composition and function by the use of subunit-specific monoclonal and polyclonal antibodies. J Exp Med. 1984 Dec 1;160(6):1767–1781. doi: 10.1084/jem.160.6.1767. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmes R. K., Twiddy E. M. Characterization of monoclonal antibodies that react with unique and cross-reacting determinants of cholera enterotoxin and its subunits. Infect Immun. 1983 Dec;42(3):914–923. doi: 10.1128/iai.42.3.914-923.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackson M. P., Newland J. W., Holmes R. K., O'Brien A. D. Nucleotide sequence analysis of the structural genes for Shiga-like toxin I encoded by bacteriophage 933J from Escherichia coli. Microb Pathog. 1987 Feb;2(2):147–153. doi: 10.1016/0882-4010(87)90106-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karch H., Heesemann J., Laufs R. Phage-associated cytotoxin production by and enteroadhesiveness of enteropathogenic Escherichia coli isolated from infants with diarrhea in West Germany. J Infect Dis. 1987 Apr;155(4):707–715. doi: 10.1093/infdis/155.4.707. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karmali M. A., Petric M., Lim C., Cheung R., Arbus G. S. Sensitive method for detecting low numbers of verotoxin-producing Escherichia coli in mixed cultures by use of colony sweeps and polymyxin extraction of verotoxin. J Clin Microbiol. 1985 Oct;22(4):614–619. doi: 10.1128/jcm.22.4.614-619.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karmali M. A., Petric M., Lim C., Fleming P. C., Arbus G. S., Lior H. The association between idiopathic hemolytic uremic syndrome and infection by verotoxin-producing Escherichia coli. J Infect Dis. 1985 May;151(5):775–782. doi: 10.1093/infdis/151.5.775. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kashiwazaki M., Ogawa T., Isayama Y., Akaike Y., Tamura K., Sakazaki R. Detection of Vero cytotoxic strains of Escherichia coli isolated from diseased animals. Natl Inst Anim Health Q (Tokyo) 1980 Fall;20(3):116–117. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kessler S. W. Cell membrane antigen isolation with the staphylococcal protein A-antibody adsorbent. J Immunol. 1976 Nov;117(5 Pt 1):1482–1490. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kessler S. W. Rapid isolation of antigens from cells with a staphylococcal protein A-antibody adsorbent: parameters of the interaction of antibody-antigen complexes with protein A. J Immunol. 1975 Dec;115(6):1617–1624. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levine M. M. Escherichia coli that cause diarrhea: enterotoxigenic, enteropathogenic, enteroinvasive, enterohemorrhagic, and enteroadherent. J Infect Dis. 1987 Mar;155(3):377–389. doi: 10.1093/infdis/155.3.377. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marques L. R., Moore M. A., Wells J. G., Wachsmuth I. K., O'Brien A. D. Production of Shiga-like toxin by Escherichia coli. J Infect Dis. 1986 Aug;154(2):338–341. doi: 10.1093/infdis/154.2.338. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Brien A. D., Holmes R. K. Shiga and Shiga-like toxins. Microbiol Rev. 1987 Jun;51(2):206–220. doi: 10.1128/mr.51.2.206-220.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Brien A. D., LaVeck G. D., Griffin D. E., Thompson M. R. Characterization of Shigella dysenteriae 1 (Shiga) toxin purified by anti-Shiga toxin affinity chromatography. Infect Immun. 1980 Oct;30(1):170–179. doi: 10.1128/iai.30.1.170-179.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Brien A. D., LaVeck G. D. Purification and characterization of a Shigella dysenteriae 1-like toxin produced by Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1983 May;40(2):675–683. doi: 10.1128/iai.40.2.675-683.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olsnes S., Reisbig R., Eiklid K. Subunit structure of Shigella cytotoxin. J Biol Chem. 1981 Aug 25;256(16):8732–8738. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sherwood D., Snodgrass D. R., O'Brien A. D. Shiga-like toxin production from Escherichia coli associated with calf diarrhoea. Vet Rec. 1985 Feb 23;116(8):217–218. doi: 10.1136/vr.116.8.217. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strockbine N. A., Jackson M. P., Sung L. M., Holmes R. K., O'Brien A. D. Cloning and sequencing of the genes for Shiga toxin from Shigella dysenteriae type 1. J Bacteriol. 1988 Mar;170(3):1116–1122. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.3.1116-1122.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strockbine N. A., Marques L. R., Holmes R. K., O'Brien A. D. Characterization of monoclonal antibodies against Shiga-like toxin from Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1985 Dec;50(3):695–700. doi: 10.1128/iai.50.3.695-700.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strockbine N. A., Marques L. R., Newland J. W., Smith H. W., Holmes R. K., O'Brien A. D. Two toxin-converting phages from Escherichia coli O157:H7 strain 933 encode antigenically distinct toxins with similar biologic activities. Infect Immun. 1986 Jul;53(1):135–140. doi: 10.1128/iai.53.1.135-140.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinstein D. L., Jackson M. P., Samuel J. E., Holmes R. K., O'Brien A. D. Cloning and sequencing of a Shiga-like toxin type II variant from Escherichia coli strain responsible for edema disease of swine. J Bacteriol. 1988 Sep;170(9):4223–4230. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.9.4223-4230.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yutsudo T., Nakabayashi N., Hirayama T., Takeda Y. Purification and some properties of a Vero toxin from Escherichia coli O157:H7 that is immunologically unrelated to Shiga toxin. Microb Pathog. 1987 Jul;3(1):21–30. doi: 10.1016/0882-4010(87)90034-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]