Abstract
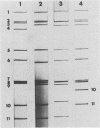
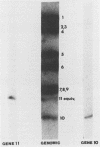
A rotavirus with a "super-short" RNA electropherotype was isolated from a calf with diarrhea and was designated VMRI strain. Segments 10 and 11 of this rotavirus migrated more slowly than did those of bovine rotavirus strains NCDV, B641, and B223. The electrophoretic pattern of the VMRI strain was similar to that reported for rotaviruses with super-short RNA electropherotypes from humans and rabbits. Northern (RNA) blot hybridization indicated that gene 11 of the VMRI strain was altered and migrated between gene segments 9 and 10. The subgroup of the VMRI strain was shown to be subgroup I. The VMRI strain of bovine rotavirus was neutralized by antisera containing polyclonal antibodies to rotavirus serotype 6 (bovine rotavirus serotype I) strains NCDV and B641 and by ascitic fluid containing monoclonal antibodies directed to VP7 of serotype 6 rotavirus. The VMRI strain was not neutralized by either polyclonal or monoclonal antibodies to strain B223 (bovine rotavirus serotype II). Collective data on the neutralization of the VMRI strain with monoclonal antibodies and polyclonal antibodies suggest that this virus is a member of the NCDV group (serotype 6) of rotaviruses (bovine rotavirus serotype I).
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Albert M. J., Unicomb L. E., Bishop R. F. Cultivation and characterization of human rotaviruses with "super short" RNA patterns. J Clin Microbiol. 1987 Jan;25(1):183–185. doi: 10.1128/jcm.25.1.183-185.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arias C. F., López S., Espejo R. T. Gene protein products of SA11 simian rotavirus genome. J Virol. 1982 Jan;41(1):42–50. doi: 10.1128/jvi.41.1.42-50.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bohl E. H., Saif L. J., Theil K. W., Agnes A. G., Cross R. F. Porcine pararotavirus: detection, differentiation from rotavirus, and pathogenesis in gnotobiotic pigs. J Clin Microbiol. 1982 Feb;15(2):312–319. doi: 10.1128/jcm.15.2.312-319.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bridger J. C., Brown J. F. Antigenic and pathogenic relationships of three bovine rotaviruses and a porcine rotavirus. J Gen Virol. 1984 Jul;65(Pt 7):1151–1158. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-65-7-1151. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bridger J. C. Detection by electron microscopy of caliciviruses, astroviruses and rotavirus-like particles in the faeces of piglets with diarrhoea. Vet Rec. 1980 Dec 6;107(23):532–533. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brüssow H., Marc-Martin S., Eichhorn W., Sidoti J., Fryder V. Characterization of a second bovine rotavirus serotype. Arch Virol. 1987;94(1-2):29–41. doi: 10.1007/BF01313723. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dimitrov D. H., Graham D. Y., Estes M. K. Detection of rotaviruses by nucleic acid hybridization with cloned DNA of simian rotavirus SA11 genes. J Infect Dis. 1985 Aug;152(2):293–300. doi: 10.1093/infdis/152.2.293. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eiden J., Vonderfecht S., Theil K., Torres-Medina A., Yolken R. H. Genetic and antigenic relatedness of human and animal strains of antigenically distinct rotaviruses. J Infect Dis. 1986 Dec;154(6):972–982. doi: 10.1093/infdis/154.6.972. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ericson B. L., Graham D. Y., Mason B. B., Estes M. K. Identification, synthesis, and modifications of simian rotavirus SA11 polypeptides in infected cells. J Virol. 1982 Jun;42(3):825–839. doi: 10.1128/jvi.42.3.825-839.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Estes M. K., Palmer E. L., Obijeski J. F. Rotaviruses: a review. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1983;105:123–184. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-69159-1_3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flewett T. H., Woode G. N. The rotaviruses. Arch Virol. 1978;57(1):1–23. doi: 10.1007/BF01315633. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fukusho A., Shimizu Y., Ito Y. Isolation of cytopathic porcine rotavirus in cell roller culture in the presence of trypsin. Arch Virol. 1981;69(1):49–60. doi: 10.1007/BF01315265. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaul S. K., Simpson T. F., Woode G. N., Fulton R. W. Antigenic relationships among some animal rotaviruses: virus neutralization in vitro and cross-protection in piglets. J Clin Microbiol. 1982 Sep;16(3):495–503. doi: 10.1128/jcm.16.3.495-503.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenberg H. B., Valdesuso J., van Wyke K., Midthun K., Walsh M., McAuliffe V., Wyatt R. G., Kalica A. R., Flores J., Hoshino Y. Production and preliminary characterization of monoclonal antibodies directed at two surface proteins of rhesus rotavirus. J Virol. 1983 Aug;47(2):267–275. doi: 10.1128/jvi.47.2.267-275.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenberg H., McAuliffe V., Valdesuso J., Wyatt R., Flores J., Kalica A., Hoshino Y., Singh N. Serological analysis of the subgroup protein of rotavirus, using monoclonal antibodies. Infect Immun. 1983 Jan;39(1):91–99. doi: 10.1128/iai.39.1.91-99.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hasegawa A., Inouye S., Matsuno S., Yamaoka K., Eko R., Suharyono W. Isolation of human rotaviruses with a distinct RNA electrophoretic pattern from Indonesia. Microbiol Immunol. 1984;28(6):719–722. doi: 10.1111/j.1348-0421.1984.tb00726.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herring A. J., Inglis N. F., Ojeh C. K., Snodgrass D. R., Menzies J. D. Rapid diagnosis of rotavirus infection by direct detection of viral nucleic acid in silver-stained polyacrylamide gels. J Clin Microbiol. 1982 Sep;16(3):473–477. doi: 10.1128/jcm.16.3.473-477.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoshino Y., Wyatt R. G., Greenberg H. B., Flores J., Kapikian A. Z. Serotypic similarity and diversity of rotaviruses of mammalian and avian origin as studied by plaque-reduction neutralization. J Infect Dis. 1984 May;149(5):694–702. doi: 10.1093/infdis/149.5.694. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ihara T., Samejima T., Kuwahara H., Tajima M. Isolation of new serotypes of bovine rotavirus. Brief report. Arch Virol. 1983;78(1-2):145–150. doi: 10.1007/BF01310870. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kalica A. R., Greenberg H. B., Wyatt R. G., Flores J., Sereno M. M., Kapikian A. Z., Chanock R. M. Genes of human (strain Wa) and bovine (strain UK) rotaviruses that code for neutralization and subgroup antigens. Virology. 1981 Jul 30;112(2):385–390. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(81)90285-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kalica A. R., Wyatt R. G., Kapikian A. Z. Detection of differences among human and animal rotaviruses, using analysis of viral RNA. J Am Vet Med Assoc. 1978 Sep 1;173(5 Pt 2):531–537. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsuno S., Hasegawa A., Kalica A. R., Kono R. Isolation of a recombinant between simian and bovine rotaviruses. J Gen Virol. 1980 May;48(1):253–256. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-48-1-253. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsuno S., Hasegawa A., Mukoyama A., Inouye S. A candidate for a new serotype of human rotavirus. J Virol. 1985 May;54(2):623–624. doi: 10.1128/jvi.54.2.623-624.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murakami Y., Nishioka N., Hashiguchi Y., Kuniyasu C. Serotypes of bovine rotaviruses distinguished by serum neutralization. Infect Immun. 1983 Jun;40(3):851–855. doi: 10.1128/iai.40.3.851-855.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Offit P. A., Blavat G. Identification of the two rotavirus genes determining neutralization specificities. J Virol. 1986 Jan;57(1):376–378. doi: 10.1128/jvi.57.1.376-378.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ojeh C. K., Snodgrass D. R., Herring A. J. Evidence for serotypic variation among bovine rotaviruses. Arch Virol. 1984;79(3-4):161–171. doi: 10.1007/BF01310809. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pedley S., Bridger J. C., Brown J. F., McCrae M. A. Molecular characterization of rotaviruses with distinct group antigens. J Gen Virol. 1983 Oct;64(Pt 10):2093–2101. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-64-10-2093. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pedley S., Bridger J. C., Chasey D., McCrae M. A. Definition of two new groups of atypical rotaviruses. J Gen Virol. 1986 Jan;67(Pt 1):131–137. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-67-1-131. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saif L. J., Bohl E. H., Theil K. W., Cross R. F., House J. A. Rotavirus-like, calicivirus-like, and 23-nm virus-like particles associated with diarrhea in young pigs. J Clin Microbiol. 1980 Jul;12(1):105–111. doi: 10.1128/jcm.12.1.105-111.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snodgrass D. R., Ojeh C. K., Campbell I., Herring A. J. Bovine rotavirus serotypes and their significance for immunization. J Clin Microbiol. 1984 Sep;20(3):342–346. doi: 10.1128/jcm.20.3.342-346.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Theil K. W., McCloskey C. M. Partial characterization of a bovine group A rotavirus with a short genome electropherotype. J Clin Microbiol. 1988 Jun;26(6):1094–1099. doi: 10.1128/jcm.26.6.1094-1099.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thouless M. E., DiGiacomo R. F., Neuman D. S. Isolation of two lapine rotaviruses: characterization of their subgroup, serotype and RNA electropherotypes. Arch Virol. 1986;89(1-4):161–170. doi: 10.1007/BF01309886. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woode G. N., Bridger J. C., Hall G., Dennis M. J. The isolation of a reovirus-like agent associated with diarrhoea in colostrum-deprived calves in Great Britain. Res Vet Sci. 1974 Jan;16(1):102–105. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woode G. N., Bridger J. C., Jones J. M., Flewett T. H., Davies H. A., Davis H. A., White G. B. Morphological and antigenic relationships between viruses (rotaviruses) from acute gastroenteritis of children, calves, piglets, mice, and foals. Infect Immun. 1976 Sep;14(3):804–810. doi: 10.1128/iai.14.3.804-810.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woode G. N., Kelso N. E., Simpson T. F., Gaul S. K., Evans L. E., Babiuk L. Antigenic relationships among some bovine rotaviruses: serum neutralization and cross-protection in gnotobiotic calves. J Clin Microbiol. 1983 Aug;18(2):358–364. doi: 10.1128/jcm.18.2.358-364.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woode G. N., Zheng S. L., Rosen B. I., Knight N., Gourley N. E., Ramig R. F. Protection between different serotypes of bovine rotavirus in gnotobiotic calves: specificity of serum antibody and coproantibody responses. J Clin Microbiol. 1987 Jun;25(6):1052–1058. doi: 10.1128/jcm.25.6.1052-1058.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]