Abstract
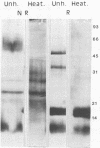
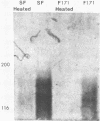
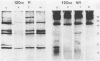
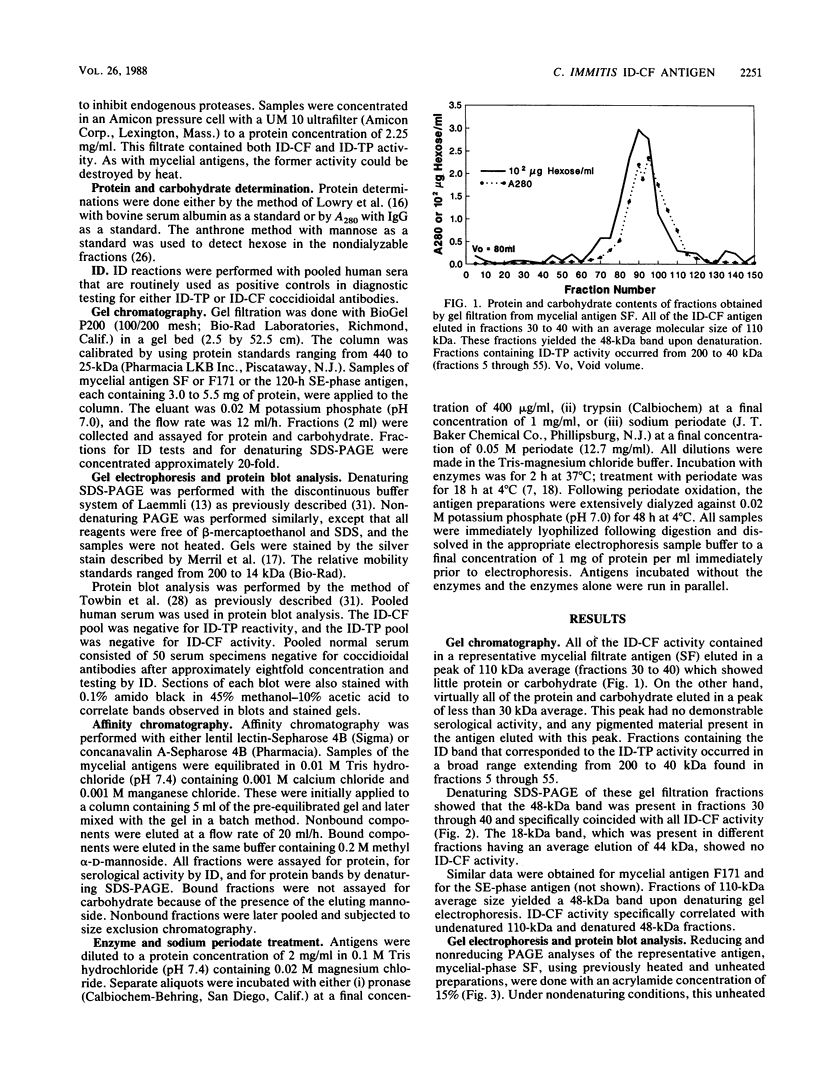
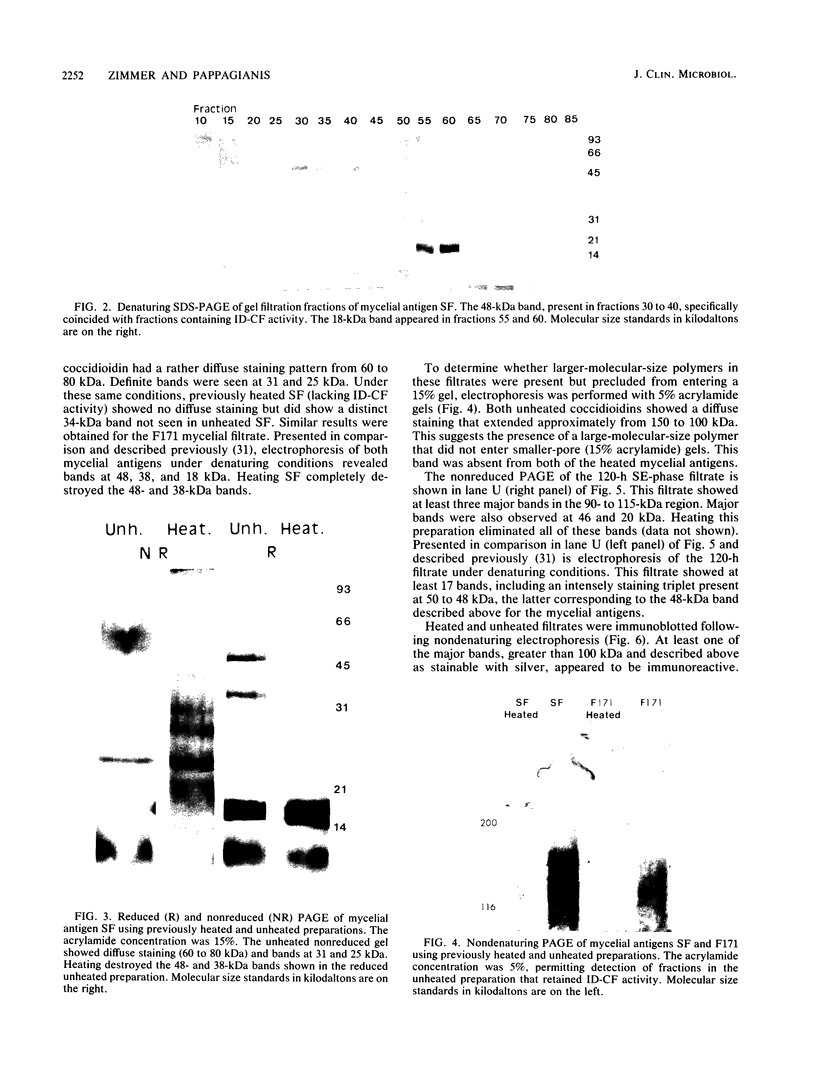
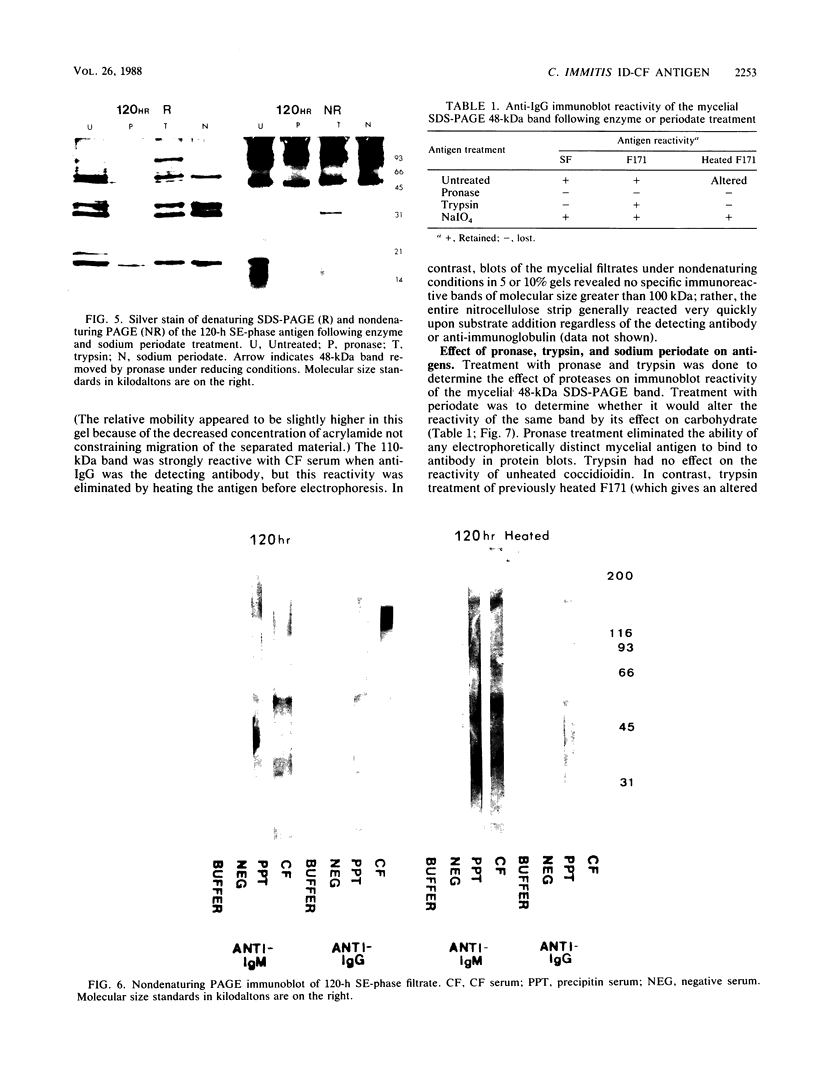
A 48-kilodalton (kDa) electrophoretically distinct antigen from Coccidioides immitis mycelial- and spherule-endospore-phase filtrates was previously associated by immunoblotting with the immunodiffusion band that corresponds to complement-fixing activity (ID-CF). To characterize this antigen and its precursor, both mycelial- and spherule-endospore-phase filtrates were fractionated by size exclusion chromatography, lectin affinity chromatography, and nondenaturing electrophoresis. By size exclusion chromatography, most of the protein and carbohydrate of the crude filtrates eluted in a peak of average molecular size less than 30 kDa, although other components were detected. ID-CF activity was associated with the component at a relative mobility of 110 kDa. Fractions containing the ID band that corresponded to tube precipitin activity occurred from 200 to 40 kDa. The appearance of the 48-kDa band in denaturing sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (PAGE) specifically coincided with the fractions containing ID-CF activity. Nondenaturing PAGE of filtrates showed silver-stainable and immunoblot-reactive bands in the region of 110 kDa. Prior treatment with pronase destroyed this electrophoretically separable antigen, whereas periodate had no effect. Trypsin did not affect the 110-kDa band in unheated or unreduced antigen. Mycelial filtrates were chromatographed on lentil lectin or concanavalin A-Sepharose 4B to deplete them of glucose- or mannose-containing carbohydrate. The effluent fraction contained ID-CF activity and, upon denaturing electrophoresis, the 48-kDa antigen. The 110-kDa protein represents the ID-CF antigen which is heat labile and denatured to a 48-kDa band by sodium dodecyl sulfate-PAGE.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson K. L., Wheat R. W., Conant N. F. Fractionation and composition studies of skin test-active components of sensitins from Coccidioides immitis. Appl Microbiol. 1971 Sep;22(3):294–299. doi: 10.1128/am.22.3.294-299.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BERMAN R. J., FRIEDMAN L., ROESSLER W. G., SMITH C. E. The virulence and infectivity of twenty-seven strains of Coccidioides immitis. Am J Hyg. 1956 Sep;64(2):198–210. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a119834. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CANFIELD R. E., LIU A. K. THE DISULFIDE BONDS OF EGG WHITE LYSOZYME (MURAMIDASE). J Biol Chem. 1965 May;240:1997–2002. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calhoun D. L., Osir E. O., Dugger K. O., Galgiani J. N., Law J. H. Humoral antibody responses to specific antigens of Coccidioides immitis. J Infect Dis. 1986 Aug;154(2):265–272. doi: 10.1093/infdis/154.2.265. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cox R. A., Britt L. A. Antigenic identity of biologically active antigens in coccidioidin and spherulin. Infect Immun. 1987 Nov;55(11):2590–2596. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.11.2590-2596.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cox R. A., Britt L. A., Michael R. A. Isolation of Coccidioides immitis F antigen by immunoaffinity chromatography with monospecific antiserum. Infect Immun. 1987 Jan;55(1):227–232. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.1.227-232.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huppert M., Spratt N. S., Vukovich K. R., Sun S. H., Rice E. H. Antigenic analysis of coccidioidin and spherulin determined by two-dimensional immunoelectrophoresis. Infect Immun. 1978 May;20(2):541–551. doi: 10.1128/iai.20.2.541-551.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ibrahim A. B., Pappagianis D. Experimental induction of anergy to coccidioidin by antigens of Coccidioides immitis. Infect Immun. 1973 May;7(5):786–794. doi: 10.1128/iai.7.5.786-794.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEVINE H. B., COBB J. M., SMITH C. E. Immunity to coccidioi-domycosis induced in mice by purified spherule, arthrospore, and mycelial vaccines. Trans N Y Acad Sci. 1960 Apr;22:436–449. doi: 10.1111/j.2164-0947.1960.tb00711.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levine H. B., Pappagianis D., Cobb J. M. Development of vaccines for coccidioidomycosis. Mycopathol Mycol Appl. 1970;41(1):177–185. doi: 10.1007/BF02051493. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merril C. R., Goldman D., Sedman S. A., Ebert M. H. Ultrasensitive stain for proteins in polyacrylamide gels shows regional variation in cerebrospinal fluid proteins. Science. 1981 Mar 27;211(4489):1437–1438. doi: 10.1126/science.6162199. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Naot Y., Guptill D. R., Mullenax J., Remington J. S. Characterization of Toxoplasma gondii antigens that react with human immunoglobulin M and immunoglobulin G antibodies. Infect Immun. 1983 Jul;41(1):331–338. doi: 10.1128/iai.41.1.331-338.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osawa T., Tsuji T. Fractionation and structural assessment of oligosaccharides and glycopeptides by use of immobilized lectins. Annu Rev Biochem. 1987;56:21–42. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.56.070187.000321. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PAPPAGIANIS D., LINDSEY N. J., SMITH C. E., SAITO M. T. ANTIBODIES IN HUMAN COCCIDIOIDOMYCOSIS: IMMUNOELECTROPHORETIC PROPERTIES. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1965 Jan;118:118–122. doi: 10.3181/00379727-118-29773. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PAPPAGIANIS D., PUTMAN E. W., KOBAYASHI G. S. Polysaccharide of Coccidioides immitis. J Bacteriol. 1961 Nov;82:714–723. doi: 10.1128/jb.82.5.714-723.1961. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Resnick S., Pappagianis D., McKerrow J. H. Proteinase production by the parasitic cycle of the pathogenic fungus Coccidioides immitis. Infect Immun. 1987 Nov;55(11):2807–2815. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.11.2807-2815.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SMITH C. E., SAITO M. T., SIMONS S. A. Pattern of 39,500 serologic tests in coccidioidomycosis. J Am Med Assoc. 1956 Feb 18;160(7):546–552. doi: 10.1001/jama.1956.02960420026008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sawaki Y., Huppert M., Bailey J. W., Yagi Y. Patterns of human antibody reactions in coccidioidomycosis. J Bacteriol. 1966 Jan;91(1):422–427. doi: 10.1128/jb.91.1.422-427.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scheer E., Terai T., Kulkarni S., Conant N. F., Wheat R. W., Lowe E. P. Unusual reducing sugar from Coccidioides immitis. J Bacteriol. 1970 Aug;103(2):525–526. doi: 10.1128/jb.103.2.525-526.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yuan L., Cole G. T. Isolation and characterization of an extracellular proteinase of Coccidioides immitis. Infect Immun. 1987 Sep;55(9):1970–1978. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.9.1970-1978.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zimmer B. L., Pappagianis D. Comparison of immunoblot analyses of spherule-endospore-phase extracellular protein and mycelial-phase antigen of Coccidioides immitis. Infect Immun. 1986 Jul;53(1):64–70. doi: 10.1128/iai.53.1.64-70.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]