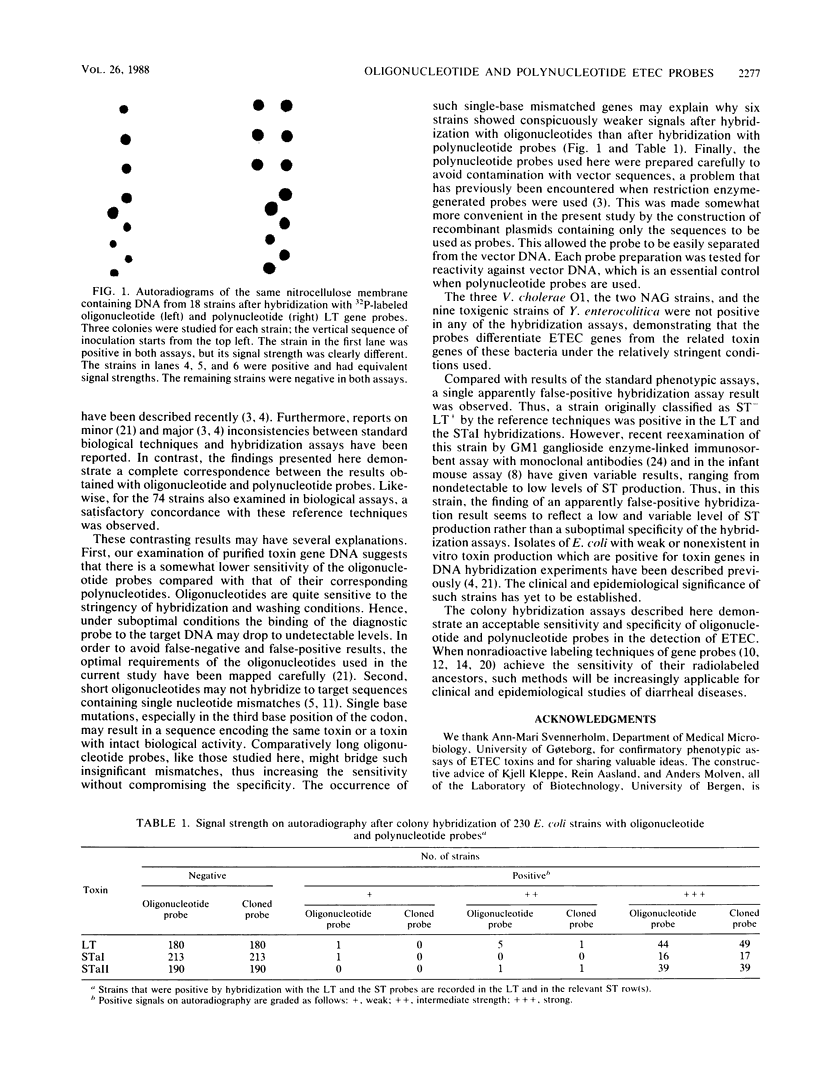
Abstract
Restriction endonuclease-generated polynucleotide and synthetically produced oligonucleotide gene probes used in colony hybridization assays proved to be efficient for the detection and differentiation of enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli. To compare their relative efficiencies, these two sets of probes were radiolabeled with 32P and were applied to 74 strains of E. coli with known enterotoxin profiles and to 156 previously unexamined E. coli isolates. The enterotoxigenic bacteria Vibrio cholerae O1, Vibrio cholerae non-O1 (NAG), Yersinia enterocolitica, and E. coli harboring the plasmid vectors of the polynucleotide gene probes were examined for further evaluation of probe specificity. The two classes of probes showed a perfect concordance in their specific detection and differentiation of enterotoxigenic E. coli. In the analysis of six strains, the signal strength on autoradiography after hybridization with oligonucleotides was weaker than that obtained after hybridization with polynucleotide probes. The probes did not hybridize with DNA from V. cholerae O1, V. cholerae non-O1 (NAG), or Y. enterocolitica. The strains of E. coli harboring the plasmid vectors of the polynucleotide gene probes were, likewise, negative in the hybridization assays.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Clements J. D., Finkelstein R. A. Immunological cross-reactivity between a heat-labile enterotoxin(s) of Escherichia coli and subunits of Vibrio cholerae enterotoxin. Infect Immun. 1978 Sep;21(3):1036–1039. doi: 10.1128/iai.21.3.1036-1039.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dallas W. S., Gill D. M., Falkow S. Cistrons encoding Escherichia coli heat-labile toxin. J Bacteriol. 1979 Sep;139(3):850–858. doi: 10.1128/jb.139.3.850-858.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Echeverria P., Taylor D. N., Seriwatana J., Chatkaeomorakot A., Khungvalert V., Sakuldaipeara T., Smith R. D. A comparative study of enterotoxin gene probes and tests for toxin production to detect enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli. J Infect Dis. 1986 Feb;153(2):255–260. doi: 10.1093/infdis/153.2.255. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Echeverria P., Taylor D. N., Seriwatana J., Moe C. Comparative study of synthetic oligonucleotide and cloned polynucleotide enterotoxin gene probes to identify enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli. J Clin Microbiol. 1987 Jan;25(1):106–109. doi: 10.1128/jcm.25.1.106-109.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisenstein B. I., Engleberg N. C. Applied molecular genetics: new tools for microbiologists and clinicians. J Infect Dis. 1986 Mar;153(3):416–430. doi: 10.1093/infdis/153.3.416. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. "A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity". Addendum. Anal Biochem. 1984 Feb;137(1):266–267. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(84)90381-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity. Anal Biochem. 1983 Jul 1;132(1):6–13. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90418-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giannella R. A. Suckling mouse model for detection of heat-stable Escherichia coli enterotoxin: characteristics of the model. Infect Immun. 1976 Jul;14(1):95–99. doi: 10.1128/iai.14.1.95-99.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guerrant R. L., Brunton L. L., Schnaitman T. C., Rebhun L. I., Gilman A. G. Cyclic adenosine monophosphate and alteration of Chinese hamster ovary cell morphology: a rapid, sensitive in vitro assay for the enterotoxins of Vibrio cholerae and Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1974 Aug;10(2):320–327. doi: 10.1128/iai.10.2.320-327.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haas M. J., Fleming D. J. Use of biotinylated DNA probes in colony hybridization. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 May 12;14(9):3976–3976. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.9.3976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ikuta S., Takagi K., Wallace R. B., Itakura K. Dissociation kinetics of 19 base paired oligonucleotide-DNA duplexes containing different single mismatched base pairs. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Jan 26;15(2):797–811. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.2.797. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jablonski E., Moomaw E. W., Tullis R. H., Ruth J. L. Preparation of oligodeoxynucleotide-alkaline phosphatase conjugates and their use as hybridization probes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Aug 11;14(15):6115–6128. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.15.6115. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lathe R., Hirth P., DeWilde M., Harford N., Lecocq J. P. Cell-free synthesis of enterotoxin of E. coli from a cloned gene. Nature. 1980 Apr 3;284(5755):473–474. doi: 10.1038/284473a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li P., Medon P. P., Skingle D. C., Lanser J. A., Symons R. H. Enzyme-linked synthetic oligonucleotide probes: non-radioactive detection of enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli in faecal specimens. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Jul 10;15(13):5275–5287. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.13.5275. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moseley S. L., Echeverria P., Seriwatana J., Tirapat C., Chaicumpa W., Sakuldaipeara T., Falkow S. Identification of enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli by colony hybridization using three enterotoxin gene probes. J Infect Dis. 1982 Jun;145(6):863–869. doi: 10.1093/infdis/145.6.863. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moseley S. L., Hardy J. W., Hug M. I., Echeverria P., Falkow S. Isolation and nucleotide sequence determination of a gene encoding a heat-stable enterotoxin of Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1983 Mar;39(3):1167–1174. doi: 10.1128/iai.39.3.1167-1174.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moseley S. L., Huq I., Alim A. R., So M., Samadpour-Motalebi M., Falkow S. Detection of enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli by DNA colony hybridization. J Infect Dis. 1980 Dec;142(6):892–898. doi: 10.1093/infdis/142.6.892. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray B. E., Mathewson J. J., DuPont H. L., Hill W. E. Utility of oligodeoxyribonucleotide probes for detecting enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli. J Infect Dis. 1987 Apr;155(4):809–811. doi: 10.1093/infdis/155.4.809. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seriwatana J., Echeverria P., Taylor D. N., Sakuldaipeara T., Changchawalit S., Chivoratanond O. Identification of enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli with synthetic alkaline phosphatase-conjugated oligonucleotide DNA probes. J Clin Microbiol. 1987 Aug;25(8):1438–1441. doi: 10.1128/jcm.25.8.1438-1441.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sommerfelt H., Svennerholm A. M., Kalland K. H., Haukanes B. I., Bjorvatn B. Comparative study of colony hybridization with synthetic oligonucleotide probes and enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for identification of enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli. J Clin Microbiol. 1988 Mar;26(3):530–534. doi: 10.1128/jcm.26.3.530-534.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Svennerholm A. M., Wiklund G. Rapid GM1-enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay with visual reading for identification of Escherichia coli heat-labile enterotoxin. J Clin Microbiol. 1983 Apr;17(4):596–600. doi: 10.1128/jcm.17.4.596-600.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Svennerholm A. M., Wikström M., Lindblad M., Holmgren J. Monoclonal antibodies against Escherichia coli heat-stable toxin (STa) and their use in a diagnostic ST ganglioside GM1-enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. J Clin Microbiol. 1986 Oct;24(4):585–590. doi: 10.1128/jcm.24.4.585-590.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takao T., Shimonishi Y., Kobayashi M., Nishimura O., Arita M., Takeda T., Honda T., Miwatani T. Amino acid sequence of heat-stable enterotoxin produced by Vibrio cholerae non-01. FEBS Lett. 1985 Dec 2;193(2):250–254. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(85)80163-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takao T., Tominaga N., Shimonishi Y., Hara S., Inoue T., Miyama A. Primary structure of heat-stable enterotoxin produced by Yersinia enterocolitica. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1984 Dec 28;125(3):845–851. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(84)91360-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto T., Tamura T., Yokota T. Primary structure of heat-labile enterotoxin produced by Escherichia coli pathogenic for humans. J Biol Chem. 1984 Apr 25;259(8):5037–5044. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



