Abstract
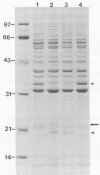
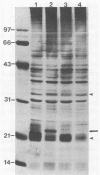
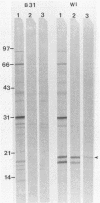
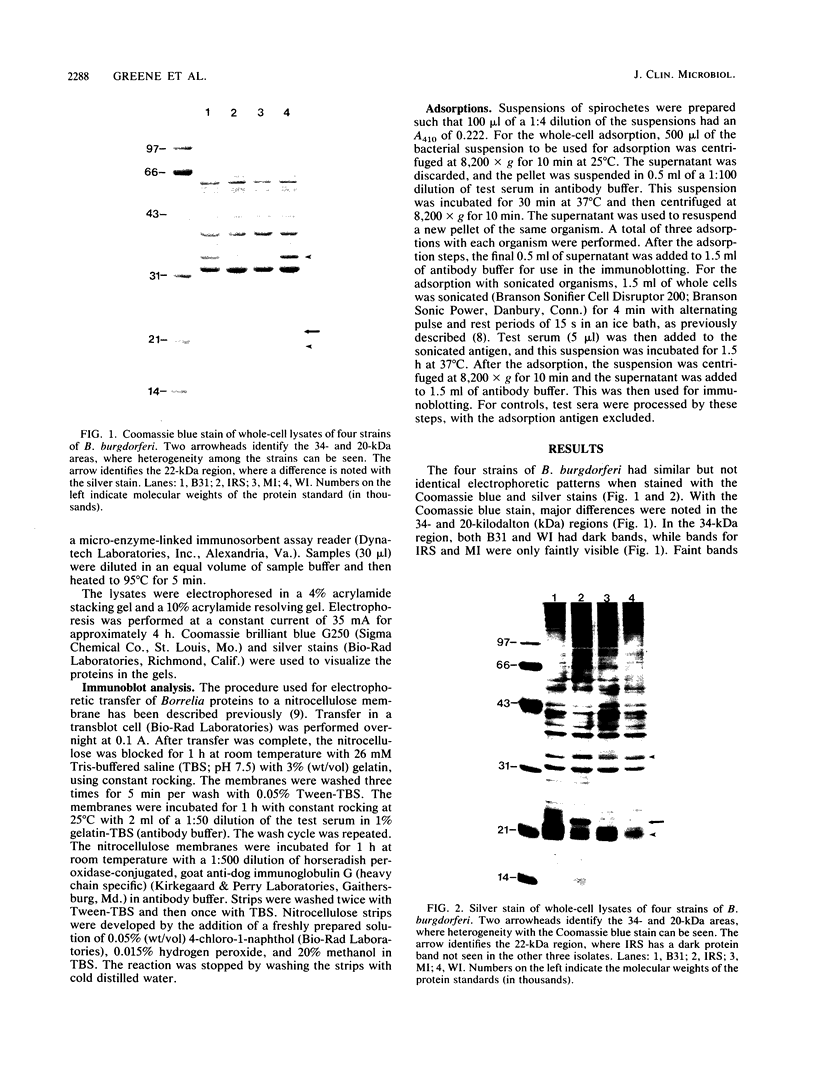
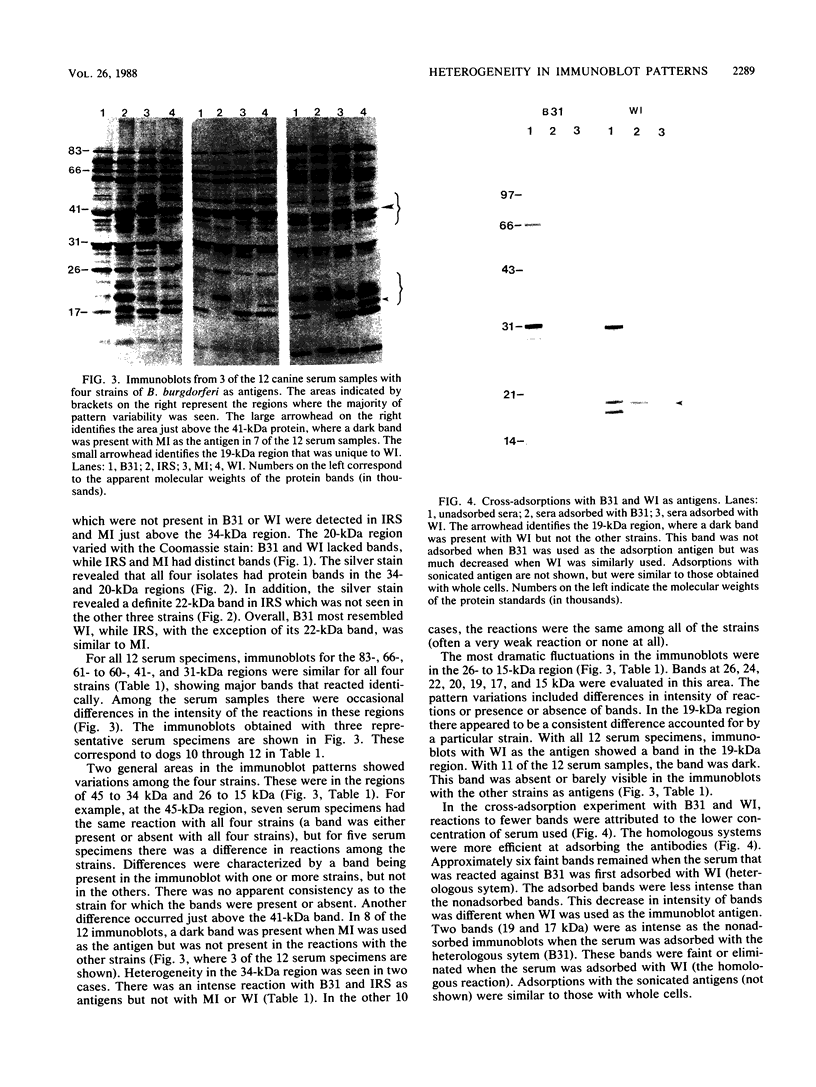
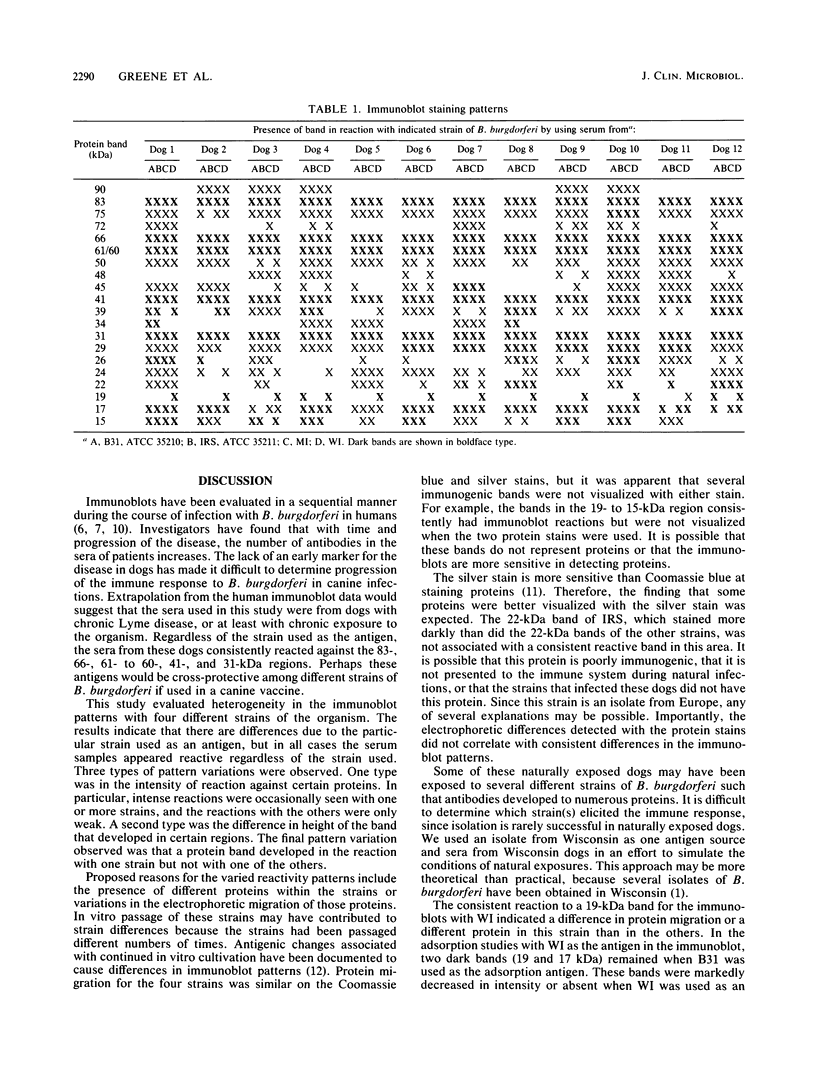
This study evaluated the differences in immunoblot patterns when serum specimens from seropositive dogs were reacted against four strains of Borrelia burgdorferi. Intense bands were consistently detected for the 83-, 66-, 61- to 60-, 41-, and 31-kilodalton regions for all four strains. Most variations were observed in the regions of 45 to 34 and 26 to 15 kilodaltons. Adsorption studies suggested that one reason for the observed variability was a difference in proteins among the organisms, rather than a difference in migration of proteins. Therefore, knowledge and consistency of the test antigen are essential when evaluating and comparing canine immunoblot patterns to B. burgdorferi, but for diagnostic purposes all of the serum samples would have been considered positive regardless of the strain used.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson J. F., Duray P. H., Magnarelli L. A. Prevalence of Borrelia burgdorferi in white-footed mice and Ixodes dammini at Fort McCoy, Wis. J Clin Microbiol. 1987 Aug;25(8):1495–1497. doi: 10.1128/jcm.25.8.1495-1497.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barbour A. G., Burgdorfer W., Grunwaldt E., Steere A. C. Antibodies of patients with Lyme disease to components of the Ixodes dammini spirochete. J Clin Invest. 1983 Aug;72(2):504–515. doi: 10.1172/JCI110998. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barbour A. G., Tessier S. L., Hayes S. F. Variation in a major surface protein of Lyme disease spirochetes. Infect Immun. 1984 Jul;45(1):94–100. doi: 10.1128/iai.45.1.94-100.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burgdorfer W., Barbour A. G., Hayes S. F., Benach J. L., Grunwaldt E., Davis J. P. Lyme disease-a tick-borne spirochetosis? Science. 1982 Jun 18;216(4552):1317–1319. doi: 10.1126/science.7043737. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coleman J. L., Benach J. L. Isolation of antigenic components from the Lyme disease spirochete: their role in early diagnosis. J Infect Dis. 1987 Apr;155(4):756–765. doi: 10.1093/infdis/155.4.756. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Craft J. E., Fischer D. K., Shimamoto G. T., Steere A. C. Antigens of Borrelia burgdorferi recognized during Lyme disease. Appearance of a new immunoglobulin M response and expansion of the immunoglobulin G response late in the illness. J Clin Invest. 1986 Oct;78(4):934–939. doi: 10.1172/JCI112683. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greene R. T., Levine J. F., Breitschwerdt E. B., Walker R. L., Berkhoff H. A., Cullen J., Nicholson W. L. Clinical and serologic evaluations of induced Borrelia burgdorferi infection in dogs. Am J Vet Res. 1988 Jun;49(6):752–757. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greene R. T., Walker R. L., Nicholson W. L., Heidner H. W., Levine J. F., Burgess E. C., Wyand M., Breitschwerdt E. B., Berkhoff H. A. Immunoblot analysis of immunoglobulin G response to the Lyme disease agent (Borrelia burgdorferi) in experimentally and naturally exposed dogs. J Clin Microbiol. 1988 Apr;26(4):648–653. doi: 10.1128/jcm.26.4.648-653.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grodzicki R. L., Steere A. C. Comparison of immunoblotting and indirect enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay using different antigen preparations for diagnosing early Lyme disease. J Infect Dis. 1988 Apr;157(4):790–797. doi: 10.1093/infdis/157.4.790. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merril C. R., Goldman D., Sedman S. A., Ebert M. H. Ultrasensitive stain for proteins in polyacrylamide gels shows regional variation in cerebrospinal fluid proteins. Science. 1981 Mar 27;211(4489):1437–1438. doi: 10.1126/science.6162199. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwan T. G., Burgdorfer W. Antigenic changes of Borrelia burgdorferi as a result of in vitro cultivation. J Infect Dis. 1987 Nov;156(5):852–853. doi: 10.1093/infdis/156.5.852-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]