Abstract
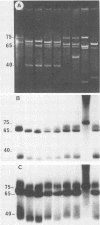
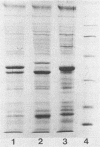
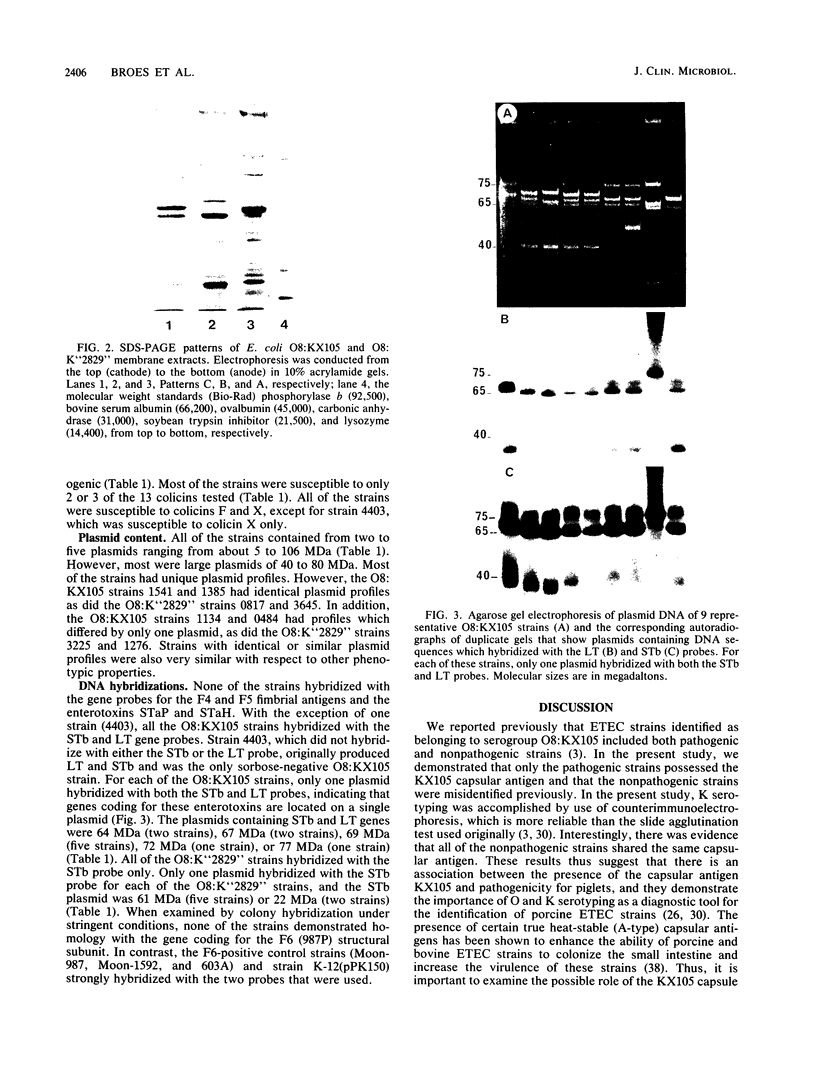
Twelve pathogenic and seven nonpathogenic enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli strains which were previously identified as belonging to serogroup O8:KX105 (A. Broes, J. M. Fairbrother, S. Larivière, M. Jacques, and W. M. Johnson, Infect. Immun. 56:241-246, 1988) were further examined for their phenotypic and genotypic properties. Only the 12 pathogenic strains were confirmed to possess the capsular antigen KX105. The seven nonpathogenic strains did not possess this antigen and thus were incorrectly assigned to have capsular antigen KX105. All seven nonpathogenic strains apparently possessed a previously unrecognized capsular antigen which has been designated K"2829". Studies with antisera prepared against F1 (type 1) fimbriae from three E. coli strains suggested that at least three antigenic subtypes of F1 fimbriae were represented among the O8:KX105 strains examined. By using serotyping, biotyping, and outer membrane protein profile analyses, the O8:KX105 strains were divided into at least two distinct clusters, whereas the O8:K"2829" strains were grouped into a single unique cluster. Most of the strains of the same cluster were further differentiated by testing for antibiotic resistance and colicin production and resistance and by analysis of plasmid content. With the exception of one strain which lost its enterotoxicity during storage, all of the O8:KX105 strains hybridized with the gene probes for the heat-labile (LT) and heat-stable (STb) enterotoxins. For each O8:KX105 strain, a single plasmid ranging in size from 61 to 77 megadaltons carried the LT and STb genes.All of the enterotoxigenic O8: KX105 strains fermented sorbose, whereas the nonenterotoxigenic strain did not. All of the O8:K "2829" strains hybridized with the STb probe only. For each O8:K "2829" strain, the STb genes were located on a single plasmid of 61 or 22 megadaltons. None of the strains demonstrated homology with the genes encoding the F4 (K88), F5 (K99), F6 (987P), and F41 fimbrial antigens and STaP and STaH.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brauner A., Boeufgras J. M., Jacobson S. H., Kaijser B., Källenius G., Svenson S. B., Wretlind B. The use of biochemical markers, serotype and fimbriation in the detection of Escherichia coli clones. J Gen Microbiol. 1987 Oct;133(10):2825–2834. doi: 10.1099/00221287-133-10-2825. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Broes A., Fairbrother J. M., Larivière S., Jacques M., Johnson W. M. Virulence properties of enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli O8: KX105 strains isolated from diarrheic piglets. Infect Immun. 1988 Jan;56(1):241–246. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.1.241-246.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burke V., Robinson J., Gracey M. Biotyping as a method of screening for enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli. Pathology. 1987 Jan;19(1):80–83. doi: 10.3109/00313028709065143. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Echeverria P., Seriwatana J., Taylor D. N., Tirapat C., Rowe B. Escherichia coli contains plasmids coding for heat-stable b, other enterotoxins, and antibiotic resistance. Infect Immun. 1985 Jun;48(3):843–846. doi: 10.1128/iai.48.3.843-846.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FREDERICQ P. Colicins. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1957;11:7–22. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.11.100157.000255. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harnett N. M., Gyles C. L. Resistance to drugs and heavy metals, colicin production, and biochemical characteristics of selected bovine and porcine Escherichia coli strains. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1984 Nov;48(5):930–935. doi: 10.1128/aem.48.5.930-935.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hultgren S. J., Schwan W. R., Schaeffer A. J., Duncan J. L. Regulation of production of type 1 pili among urinary tract isolates of Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1986 Dec;54(3):613–620. doi: 10.1128/iai.54.3.613-620.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kado C. I., Liu S. T. Rapid procedure for detection and isolation of large and small plasmids. J Bacteriol. 1981 Mar;145(3):1365–1373. doi: 10.1128/jb.145.3.1365-1373.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee C. H., Moseley S. L., Moon H. W., Whipp S. C., Gyles C. L., So M. Characterization of the gene encoding heat-stable toxin II and preliminary molecular epidemiological studies of enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli heat-stable toxin II producers. Infect Immun. 1983 Oct;42(1):264–268. doi: 10.1128/iai.42.1.264-268.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lugtenberg B., Meijers J., Peters R., van der Hoek P., van Alphen L. Electrophoretic resolution of the "major outer membrane protein" of Escherichia coli K12 into four bands. FEBS Lett. 1975 Oct 15;58(1):254–258. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(75)80272-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maas R., Silva R. M., Gomes T. A., Trabulsi L. R., Maas W. K. Detection of genes for heat-stable enterotoxin I in Escherichia coli strains isolated in Brazil. Infect Immun. 1985 Jul;49(1):46–51. doi: 10.1128/iai.49.1.46-51.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mainil J. G., Moseley S. L., Schneider R. A., Sutch K., Casey T. A., Moon H. W. Hybridization of bovine Escherichia coli isolates with gene probes for four enterotoxins (STaP, STaH, STb, LT) and one adhesion factor (K99). Am J Vet Res. 1986 May;47(5):1145–1148. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mainil J., Bex F., Couturier M., Kaeckenbeeck A. Hybridization on bovine enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli with two heat-stable enterotoxin gene probes. Am J Vet Res. 1985 Dec;46(12):2582–2584. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McMichael J. C., Ou J. T. Structure of common pili from Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1979 Jun;138(3):969–975. doi: 10.1128/jb.138.3.969-975.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mooi F. R., de Graaf F. K., van Embden J. D. Cloning, mapping and expression of the genetic determinant that encodes for the K88ab antigen. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Mar;6(3):849–865. doi: 10.1093/nar/6.3.849. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moon H. W., Schneider R. A., Moseley S. L. Comparative prevalence of four enterotoxin genes among Escherichia coli isolated from swine. Am J Vet Res. 1986 Feb;47(2):210–212. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrissey P. M., Dougan G. Expression of a cloned 987P adhesion-antigen fimbrial determinant in Escherichia coli K-12 strain HB101. Gene. 1986;43(1-2):79–84. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(86)90010-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moseley S. L., Dougan G., Schneider R. A., Moon H. W. Cloning of chromosomal DNA encoding the F41 adhesin of enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli and genetic homology between adhesins F41 and K88. J Bacteriol. 1986 Sep;167(3):799–804. doi: 10.1128/jb.167.3.799-804.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orskov F., Orskov I. From the national institutes of health. Summary of a workshop on the clone concept in the epidemiology, taxonomy, and evolution of the enterobacteriaceae and other bacteria. J Infect Dis. 1983 Aug;148(2):346–357. doi: 10.1093/infdis/148.2.346. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orskov I., Orskov F. Serology of Escherichia coli fimbriae. Prog Allergy. 1983;33:80–105. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pohl P., Lintermans P., Vandergheynst M. C., Van Muylem K., Schlicker C., Van Robaeys G. Milieu sélectif citrate-adonitol pour l'isolement de certaines souches de Escherichia coli K99. Ann Microbiol (Paris) 1984 Jul-Aug;135B(1):29–33. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sherman P. M., Houston W. L., Boedeker E. C. Functional heterogeneity of intestinal Escherichia coli strains expressing type 1 somatic pili (fimbriae): assessment of bacterial adherence to intestinal membranes and surface hydrophobicity. Infect Immun. 1985 Sep;49(3):797–804. doi: 10.1128/iai.49.3.797-804.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith H. W., Huggins M. B. The influence of plasmid-determined and other characteristics of enteropathogenic Escherichia coli on their ability to proliferate in the alimentary tracts of piglets, calves and lambs. J Med Microbiol. 1978 Nov;11(4):471–492. doi: 10.1099/00222615-11-4-471. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- So M., Dallas W. S., Falkow S. Characterization of an Escherichia coli plasmid encoding for synthesis of heat-labile toxin: molecular cloning of the toxin determinant. Infect Immun. 1978 Aug;21(2):405–411. doi: 10.1128/iai.21.2.405-411.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- So M., McCarthy B. J. Nucleotide sequence of the bacterial transposon Tn1681 encoding a heat-stable (ST) toxin and its identification in enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli strains. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jul;77(7):4011–4015. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.7.4011. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Graaf F. K., Klaasen P. Organization and expression of genes involved in the biosynthesis of 987P fimbriae. Mol Gen Genet. 1986 Jul;204(1):75–81. doi: 10.1007/BF00330190. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Embden J. D., de Graaf F. K., Schouls L. M., Teppema J. S. Cloning and expression of a deoxyribonucleic acid fragment that encodes for the adhesive antigen K99. Infect Immun. 1980 Sep;29(3):1125–1133. doi: 10.1128/iai.29.3.1125-1133.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]