Abstract
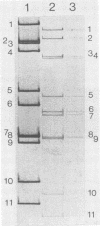
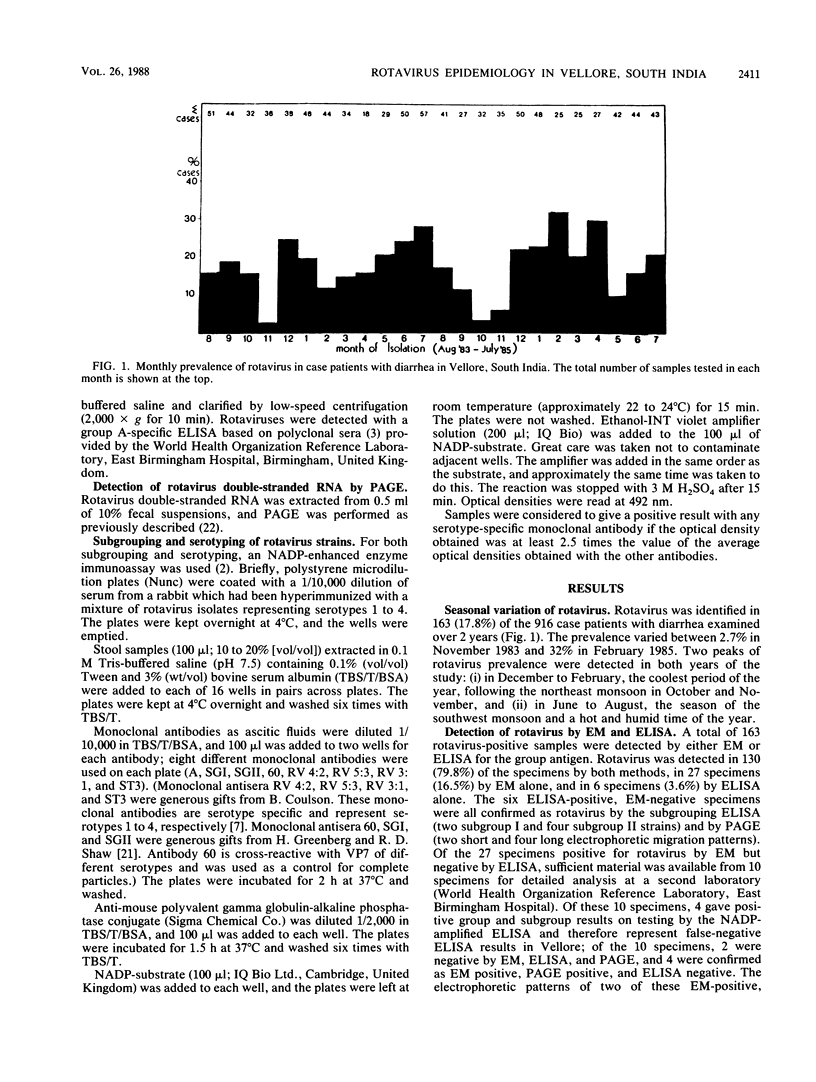
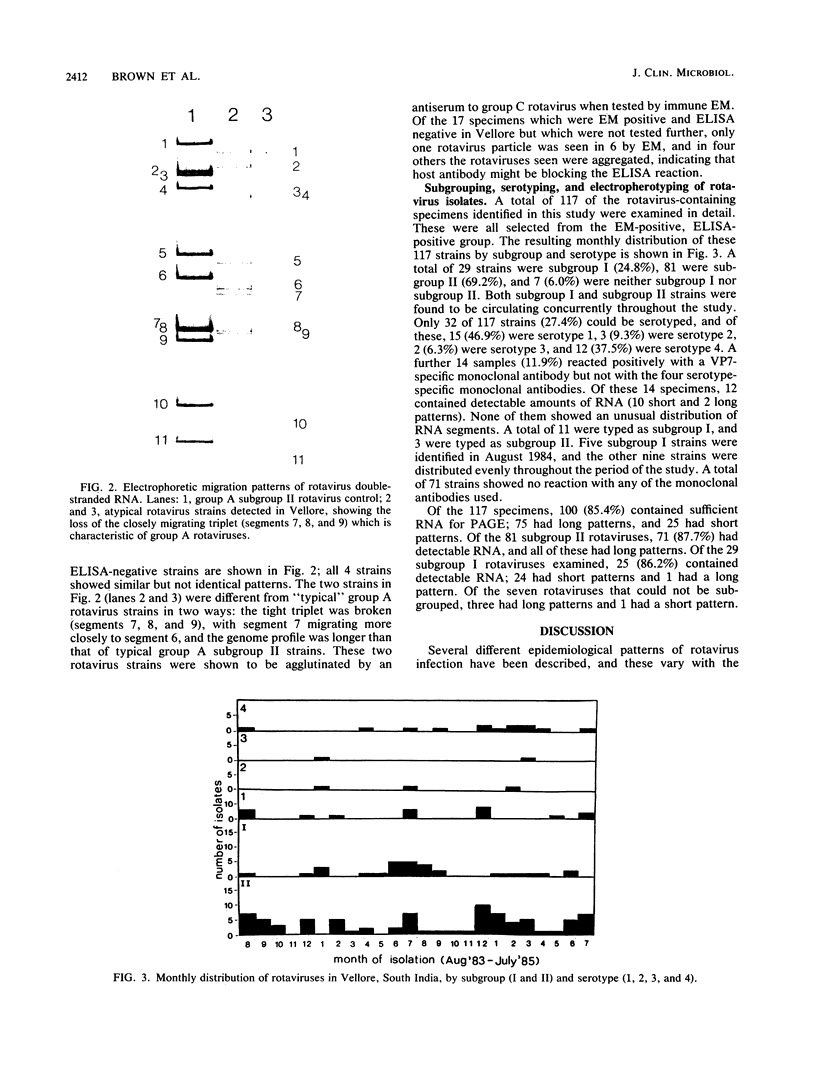
Rotaviruses were detected in 163 of 916 (17.8%) specimens collected from children under 3 years of age with gastroenteritis in Vellore, South India, between August 1983 and July 1985. Rotaviruses were detected throughout the study period, with a peak prevalence in December to February (winter) and June to August (southwest monsoon season). A total of 117 rotavirus strains were tested for subgroup, serotype, and rotavirus double-stranded RNA electrophoretic migration pattern; 24.8% of the strains were subgroup I, 69.2% were subgroup II, and 6.0% were neither subgroup I nor subgroup II. Subgroup I and II strains were circulating concurrently throughout the study. Of the 117 rotavirus strains, 32 (27.4%) were serotyped; 15 were serotype 1, 3 were serotype 2, 2 were serotype 3, and 12 were serotype 4. Three serotypes were circulating concurrently during the periods of peak rotavirus prevalence. In 100 of the 117 strains (85.4%) an RNA pattern was detected. One unusual subgroup I group A rotavirus with a long migration pattern and four atypical rotaviruses serologically related to group C were also detected.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Beards G. M., Campbell A. D., Cottrell N. R., Peiris J. S., Rees N., Sanders R. C., Shirley J. A., Wood H. C., Flewett T. H. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays based on polyclonal and monoclonal antibodies for rotavirus detection. J Clin Microbiol. 1984 Feb;19(2):248–254. doi: 10.1128/jcm.19.2.248-254.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beards G. M. Polymorphism of genomic RNAs within rotavirus serotypes and subgroups. Arch Virol. 1982;74(1):65–70. doi: 10.1007/BF01320783. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beards G. M. Serotyping of rotavirus by NADP-enhanced enzyme-immunoassay. J Virol Methods. 1987 Nov;18(2-3):77–85. doi: 10.1016/0166-0934(87)90113-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bridger J. C., Pedley S., McCrae M. A. Group C rotaviruses in humans. J Clin Microbiol. 1986 Apr;23(4):760–763. doi: 10.1128/jcm.23.4.760-763.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coulson B. S., Tursi J. M., McAdam W. J., Bishop R. F. Derivation of neutralizing monoclonal antibodies to human rotaviruses and evidence that an immunodominant neutralization site is shared between serotypes 1 and 3. Virology. 1986 Oct 30;154(2):302–312. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(86)90456-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coulson B. S. Variation in neutralization epitopes of human rotaviruses in relation to genomic RNA polymorphism. Virology. 1987 Aug;159(2):209–216. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(87)90457-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cubitt W. D., McSwiggan D. A., Moore W. Winter vomiting disease caused by calicivirus. J Clin Pathol. 1979 Aug;32(8):786–793. doi: 10.1136/jcp.32.8.786. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Estes M. K., Graham D. Y., Dimitrov D. H. The molecular epidemiology of rotavirus gastroenteritis. Prog Med Virol. 1984;29:1–22. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flores J., Perez-Schael I., Gonzalez M., Garcia D., Perez M., Daoud N., Cunto W., Chanock R. M., Kapikian A. Z. Protection against severe rotavirus diarrhoea by rhesus rotavirus vaccine in Venezuelan infants. Lancet. 1987 Apr 18;1(8538):882–884. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(87)92858-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaul S. K., Simpson T. F., Woode G. N., Fulton R. W. Antigenic relationships among some animal rotaviruses: virus neutralization in vitro and cross-protection in piglets. J Clin Microbiol. 1982 Sep;16(3):495–503. doi: 10.1128/jcm.16.3.495-503.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green K. Y., Sears J. F., Taniguchi K., Midthun K., Hoshino Y., Gorziglia M., Nishikawa K., Urasawa S., Kapikian A. Z., Chanock R. M. Prediction of human rotavirus serotype by nucleotide sequence analysis of the VP7 protein gene. J Virol. 1988 May;62(5):1819–1823. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.5.1819-1823.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanlon P., Hanlon L., Marsh V., Byass P., Shenton F., Hassan-King M., Jobe O., Sillah H., Hayes R., M'Boge B. H. Trial of an attenuated bovine rotavirus vaccine (RIT 4237) in Gambian infants. Lancet. 1987 Jun 13;1(8546):1342–1345. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(87)90649-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maiya P. P., Pereira S. M., Mathan M., Bhat P., Albert M. J., Baker S. J. Aetiology of acute gastroenteritis in infancy and early childhood in southern India. Arch Dis Child. 1977 Jun;52(6):482–485. doi: 10.1136/adc.52.6.482. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakagomi O., Nakagomi T., Hoshino Y., Flores J., Kapikian A. Z. Genetic analysis of a human rotavirus that belongs to subgroup I but has an RNA pattern typical of subgroup II human rotaviruses. J Clin Microbiol. 1987 Jul;25(7):1159–1164. doi: 10.1128/jcm.25.7.1159-1164.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakagomi O., Nakagomi T., Oyamada H., Suto T. Relative frequency of human rotavirus subgroups 1 and 2 in Japanese children with acute gastroenteritis. J Med Virol. 1985 Sep;17(1):29–34. doi: 10.1002/jmv.1890170105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paniker C. K., Mathew S., Mathan M. Rotavirus and acute diarrhoeal disease in children in a southern Indian coastal town. Bull World Health Organ. 1982;60(1):123–127. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pedley S., Bridger J. C., Brown J. F., McCrae M. A. Molecular characterization of rotaviruses with distinct group antigens. J Gen Virol. 1983 Oct;64(Pt 10):2093–2101. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-64-10-2093. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rowland M. G., Goh S. G., Williams K., Campbell A. D., Beards G. M., Sanders R. C., Flewett T. H. Epidemiological aspects of rotavirus infection in young Gambian children. Ann Trop Paediatr. 1985 Mar;5(1):23–28. doi: 10.1080/02724936.1985.11748354. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanders R. C., Campbell A. D., Jenkins M. F. Routine detection of human rotavirus by latex agglutination: comparison with enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay, electron microscopy and polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. J Virol Methods. 1986 Jul;13(4):285–290. doi: 10.1016/0166-0934(86)90053-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaw R. D., Stoner-Ma D. L., Estes M. K., Greenberg H. B. Specific enzyme-linked immunoassay for rotavirus serotypes 1 and 3. J Clin Microbiol. 1985 Aug;22(2):286–291. doi: 10.1128/jcm.22.2.286-291.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woode G. N., Kelso N. E., Simpson T. F., Gaul S. K., Evans L. E., Babiuk L. Antigenic relationships among some bovine rotaviruses: serum neutralization and cross-protection in gnotobiotic calves. J Clin Microbiol. 1983 Aug;18(2):358–364. doi: 10.1128/jcm.18.2.358-364.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woode G. N., Zheng S. L., Rosen B. I., Knight N., Gourley N. E., Ramig R. F. Protection between different serotypes of bovine rotavirus in gnotobiotic calves: specificity of serum antibody and coproantibody responses. J Clin Microbiol. 1987 Jun;25(6):1052–1058. doi: 10.1128/jcm.25.6.1052-1058.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Zoysa I., Feachem R. G. Interventions for the control of diarrhoeal diseases among young children: rotavirus and cholera immunization. Bull World Health Organ. 1985;63(3):569–583. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]