Abstract
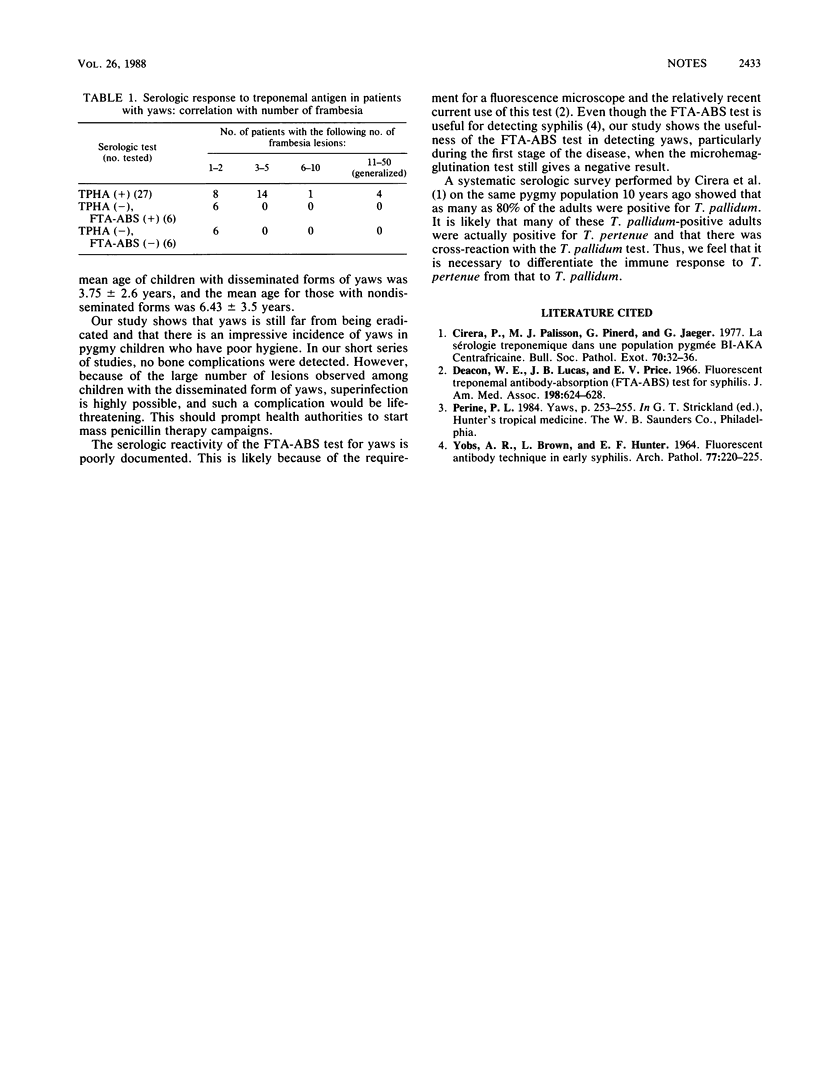
The incidence of yaws in 533 pygmies from the Central African Republic was surveyed. It appeared that there is still an impressive incidence of yaws in pygmy children who have poor hygiene. Laboratory investigations showed that the Treponema pallidum hemagglutination assay is often negative during the first stage of the disease, while the fluorescent treponemal antibody absorption test is positive and, thus, more sensitive.
Full text
PDF
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Cirera P., Palisson M. J., Pinerd G., Jaeger G. La sérologie tréponémique dans une population Pygmée Bi-Aka centrafricaine. Bull Soc Pathol Exot Filiales. 1977 Jan-Feb;70(1):32–36. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deacon W. E., Lucas J. B., Price E. V. Fluorescent treponemal antibody-absorption (FTA-ABS) test for syphilis. JAMA. 1966 Nov 7;198(6):624–628. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- YOBS A. R., BROWN L., HUNTER E. F. FLUORESCENT ANTIBODY TECHNIQUE IN EARLY SYPHILIS; AS APPLIED TO THE DEMONSTRATION OF T PALLIDUM IN LESIONS IN THE RABBIT AND IN THE HUMAN. Arch Pathol. 1964 Feb;77:220–225. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



