NEUROSCIENCE Correction for “Wnt/β-catenin signaling is required for CNS, but not non-CNS, angiogenesis,” by Richard Daneman, Dritan Agalliu, Lu Zhou, Frank Kuhnert, Calvin J. Kuo, and Ben A. Barres, which appeared in issue 2, January 13, 2009, of Proc Natl Acad Sci USA (106:641–646; first published January 7, 2009; 10.1073/pnas.0805165106).
The authors note that in Fig. 2Bi an image of Wnt1 in situ hybridization was mistakenly inserted instead of an image of Wnt3a in situ hybridization. This error did not affect the conclusions of this article. The corrected figure appears below.
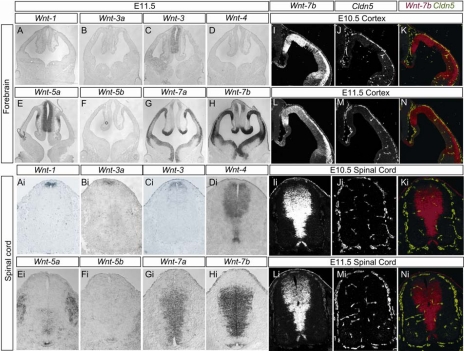
Fig. 2.
Expression of Wnts in the developing mouse CNS. In situ hybridizations demonstrating Wnt ligand expression in the developing forebrain (A–H) and spinal cord (Ai–Hi) of E11.5 mice. Canonical Wnt ligands Wnt7a and Wnt7b are expressed by neural progenitors in the ventricular zone in the ventral-lateral spinal cord and cortical forebrain, whereas canonical Wnt ligands Wnt1, Wnt3, and Wnt3a are expressed by neural progenitors in the ventricular zone of the dorsal spinal cord and the hindbrain. Non-canonical Wnt ligands Wnt4, Wnt5a, and Wnt5b are also expressed by neural progenitors located in spatially distinct regions of the spinal cord and cortex. Double fluorescent in situ hybridizations in the developing forebrain (E10.5 I–K, E11.5 L–N) and spinal cord (E10.5 Ii–Ki, E11.5 Li–Ni) with Wnt7b (I, L, Ii, Li) and Claudin 5 (J, M, Ji, Mi) and merged (K, N, Ki, Ni) demonstrate that claudin 5 positive vessels vascularize Wnt7b positive regions of the developing CNS.