Abstract
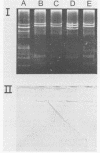
Five strains of hemolytic Escherichia coli isolated from dogs suffering from diarrhea were shown by radioactive and enzyme-labeled oligonucleotide probes to possess genes coding for heat-stable enterotoxin (STIa). Four of the strains were shown by immunoassay (enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay) and bioassay (infant mouse test) to produce STI in vitro. All five strains, however, were able to induce fluid accumulation in ligated dog intestinal loops. The four STI-producing strains all possessed the K99 fimbrial antigen (F5) and belonged to serotype O42:H37. In these strains, genes encoding STI were located on a 98-megadalton plasmid. In the fifth strain, which produced STI in vitro only after several subcultivations, the STI gene was located on an 80-megadalton plasmid. This strain was nontypable.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Dean A. G., Ching Y. C., Williams R. G., Harden L. B. Test for Escherichia coli enterotoxin using infant mice: application in a study of diarrhea in children in Honolulu. J Infect Dis. 1972 Apr;125(4):407–411. doi: 10.1093/infdis/125.4.407. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Echeverria P., Taylor D. N., Seriwatana J., Chatkaeomorakot A., Khungvalert V., Sakuldaipeara T., Smith R. D. A comparative study of enterotoxin gene probes and tests for toxin production to detect enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli. J Infect Dis. 1986 Feb;153(2):255–260. doi: 10.1093/infdis/153.2.255. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harnett N. M., Gyles C. L. Enterotoxin plasmids in bovine and porcine enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli of O groups 9, 20, 64 and 101. Can J Comp Med. 1985 Jan;49(1):79–87. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill W. E., Payne W. L., Zon G., Moseley S. L. Synthetic oligodeoxyribonucleotide probes for detecting heat-stable enterotoxin-producing Escherichia coli by DNA colony hybridization. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1985 Nov;50(5):1187–1191. doi: 10.1128/aem.50.5.1187-1191.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jablonski E., Moomaw E. W., Tullis R. H., Ruth J. L. Preparation of oligodeoxynucleotide-alkaline phosphatase conjugates and their use as hybridization probes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Aug 11;14(15):6115–6128. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.15.6115. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kado C. I., Liu S. T. Rapid procedure for detection and isolation of large and small plasmids. J Bacteriol. 1981 Mar;145(3):1365–1373. doi: 10.1128/jb.145.3.1365-1373.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lockwood D. E., Robertson D. C. Development of a competitive enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) for Escherichia coli heat-stable enterotoxin (STa). J Immunol Methods. 1984 Dec 31;75(2):295–307. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(84)90113-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nalin D. R., Levine M. M., Young C. R., Bergquist E. J., McLaughlin J. C. Increased Escherichia coli enterotoxin detection after concentrating culture supernatants: possible new enterotoxin detectable in dogs but not in infant mice. J Clin Microbiol. 1978 Dec;8(6):700–703. doi: 10.1128/jcm.8.6.700-703.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishibuchi M., Arita M., Honda T., Miwatani T. Evaluation of a nonisotopically labeled oligonucleotide probe to detect the heat-stable enterotoxin gene of Escherichia coli by the DNA colony hybridization test. J Clin Microbiol. 1988 Apr;26(4):784–786. doi: 10.1128/jcm.26.4.784-786.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olson P., Hedhammar A., Faris A., Krovacek K., Wadström T. Enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli (ETEC) and Klebsiella pneumoniae isolated from dogs with diarrhoea. Vet Microbiol. 1985 Dec;10(6):577–589. doi: 10.1016/0378-1135(85)90066-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olson P., Hedhammar A., Wadström T. Enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli infection in two dogs with acute diarrhea. J Am Vet Med Assoc. 1984 Apr 15;184(8):982–983. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olsvik O., Hushovd O. T., Berdal B. P., Bergan T., Mathiesen M. Production of enterotoxin by Escherichia coli at four, twenty-two and thirty-seven degrees centigrade. Eur J Clin Microbiol. 1982 Feb;1(1):12–16. doi: 10.1007/BF02014134. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olsvik O., Solberg R., Bergan T. Characterization of enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli. Serotypes, enterotoxins, adhesion fimbriae, and the presence of plasmids. Acta Pathol Microbiol Immunol Scand B. 1985 Aug;93(4):255–262. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oprandy J. J., Thornton S. A., Gardiner C. H., Burr D., Batchelor R., Bourgeois A. L. Alkaline phosphatase-conjugated oligonucleotide probes for enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli in travelers to South America and West Africa. J Clin Microbiol. 1988 Jan;26(1):92–95. doi: 10.1128/jcm.26.1.92-95.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sack R. B., Johnson J., Pierce N. F., Keren D. F., Yardley J. H. Challenge of dogs with live enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli and effects of repeated challenges on fluid secretion in jejunal Thiry-Vella loops. J Infect Dis. 1976 Jul;134(1):15–24. doi: 10.1093/infdis/134.1.15. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sommerfelt H., Svennerholm A. M., Kalland K. H., Haukanes B. I., Bjorvatn B. Comparative study of colony hybridization with synthetic oligonucleotide probes and enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for identification of enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli. J Clin Microbiol. 1988 Mar;26(3):530–534. doi: 10.1128/jcm.26.3.530-534.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilk S., Amtsberg G., Meier C. Serotypisierung und Resistenzprüfung von Escherichia-coli-Stämmen aus gesunden und enteritiskranken Hunden. Berl Munch Tierarztl Wochenschr. 1982 Jul 15;95(14):271–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]