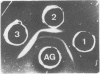
Abstract
Brucella melitensis native haptens (NH) are polysaccharides identical to the O-side chain of the smooth lipopolysaccharide (S-LPS) (E. Moreno, H. Mayer, and I. Moriyón, Infect. Immun. 55:2850-2853, 1987) which precipitate with sera from infected cattle but not from strain 19-vaccinated cattle. In the present work, NH was extracted by the hot-water method (R. Díaz, J. Toyos, M.D. Salvo, and M.L. Pardo, Ann. Rech. Vet. 12:35-39, 1981) and purified free of S-LPS and protein. Purified NH lacked the ability to coat polystyrene and sheep erythrocytes. In contrast, NH acylated with stearoyl chloride bound to both polystyrene and erythrocytes. By hemagglutination and enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA), S-LPS and acylated NH gave similar results with blood sera from brucellosis-free, strain 19-vaccinated, and infected cattle. Moreover, a significant correlation between the results of NH ELISA and S-LPS ELISA was demonstrated with milk sera. However, in a competitive ELISA with milk sera, S-LPS in the liquid phase abrogated the binding of antibodies to acylated NH adsorbed to polystyrene, while NH in the liquid phase did not influence the binding of antibodies to polystyrene-adsorbed S-LPS. It is hypothesized that the different precipitations of NH and S-LPS with sera from infected or strain 19-vaccinated cattle are due to differences in the affinity of the antibodies produced upon vaccination or infection and in the physical state of aggregation of NH and S-LPS in aqueous solutions.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ANACKER R. L., FINKELSTEIN R. A., HASKINS W. T., LANDY M., MILNER K. C., RIBI E., STASHAK P. W. ORIGIN AND PROPERTIES OF NATURALLY OCCURRING HAPTEN FROM ESCHERICHIA COLI. J Bacteriol. 1964 Dec;88:1705–1720. doi: 10.1128/jb.88.6.1705-1720.1964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berman D. T., Jones L. M. Radial immunodiffusion--a confirmatory test for bovine brucellosis. Proc Annu Meet U S Anim Health Assoc. 1980;84:118–127. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bundle D. R., Cherwonogrodzky J. W., Caroff M., Perry M. B. The lipopolysaccharides of Brucella abortus and B. melitensis. Ann Inst Pasteur Microbiol. 1987 Jan-Feb;138(1):92–98. doi: 10.1016/0769-2609(87)90083-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bundle D. R., Cherwonogrodzky J. W., Perry M. B. The structure of the lipopolysaccharide O-chain (M antigen) and polysaccharide B produced by Brucella melitensis 16M. FEBS Lett. 1987 Jun 1;216(2):261–264. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(87)80702-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diaz R., Garatea P., Jones L. M., Moriyon I. Radial immunodiffusion test with a Brucella polysaccharide antigen for differentiating infected from vaccinated cattle. J Clin Microbiol. 1979 Jul;10(1):37–41. doi: 10.1128/jcm.10.1.37-41.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diaz R., Jones L. M., Leong D., Wilson J. B. Surface antigens of smooth brucellae. J Bacteriol. 1968 Oct;96(4):893–901. doi: 10.1128/jb.96.4.893-901.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diaz R., Jones L. M., Wilson J. B. Antigenic relationship of Brucella ovis and Brucella melitensis. J Bacteriol. 1967 Apr;93(4):1262–1268. doi: 10.1128/jb.93.4.1262-1268.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diaz R., Levieux D. Rôle respiectif en sérologie de la brucellose bovine des antigènes et des immunoglobulines G 1 et G 2 dans les tests d'agglutination, de Coombs et au Rose Bengale ainsi que dans le phénomène de zone. C R Acad Sci Hebd Seances Acad Sci D. 1972 Mar 6;274(10):1593–1596. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diaz R., Toyos J., Salvo M. D., Fernandez-Lago L., Alonso B., Moriyon I., Dorronsoro I. Studies on the polysaccharide B and native haptene of Brucella and Yersinia enterocolitica serotype 9. Dev Biol Stand. 1984;56:213–220. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diaz R., Toyos J., Salvó M. D., Pardo M. L. A simple method for the extraction of polysaccharide B from Brucella cells for use in the radial immunodiffusion test diagnosis of bovine brucellosis. Ann Rech Vet. 1981;12(1):35–39. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dubray G. Progrès récents sur la biochimie et les propriétés biologiques des antigènes de Brucella. Dev Biol Stand. 1984;56:131–150. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fernandex-Lago L., Diaz R. Demonstration of antibodies against Brucella melitensis 16M lipopolysaccharide and native hapten in human sera by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. J Clin Microbiol. 1986 Jul;24(1):76–80. doi: 10.1128/jcm.24.1.76-80.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galanos C., Lüderitz O., Westphal O. A new method for the extraction of R lipopolysaccharides. Eur J Biochem. 1969 Jun;9(2):245–249. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1969.tb00601.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galanos C., Rietschel E. T., Lüderitz O., Westphal O., Kim Y. B., Watson D. W. Biological activities of lipid A complexed with bovine-serum albumin. Eur J Biochem. 1972 Dec 4;31(2):230–233. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1972.tb02524.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hämmerling U., Westphal O. Synthesis and use of O-stearoyl polysaccharides in passive hemagglutination and hemolysis. Eur J Biochem. 1967 Mar;1(1):46–50. doi: 10.1007/978-3-662-25813-2_9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones L. M., Berman D. T., Moreno E., Deyoe B. L., Gilsdorf M. J., Huber J. D., Nicoletti P. Evaluation of a radial immunodiffusion test with polysaccharide B antigen for diagnosis of bovine brucellosis. J Clin Microbiol. 1980 Dec;12(6):753–760. doi: 10.1128/jcm.12.6.753-760.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lamb V. L., Jones L. M., Schurig G. G., Berman D. T. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for bovine immunoglobulin subclass-specific response to Brucella abortus lipopolysaccharides. Infect Immun. 1979 Oct;26(1):240–247. doi: 10.1128/iai.26.1.240-247.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leong D., Diaz R., Milner K., Rudbach J., Wilson J. B. Some structural and biological properties of Brucella endotoxin. Infect Immun. 1970 Feb;1(2):174–182. doi: 10.1128/iai.1.2.174-182.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merril C. R., Switzer R. C., Van Keuren M. L. Trace polypeptides in cellular extracts and human body fluids detected by two-dimensional electrophoresis and a highly sensitive silver stain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4335–4339. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4335. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moreno E., Borowiak D., Mayer H. Brucella lipopolysaccharides and polysaccharides. Ann Inst Pasteur Microbiol. 1987 Jan-Feb;138(1):102–105. doi: 10.1016/0769-2609(87)90085-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moreno E., Mayer H., Moriyon I. Characterization of a native polysaccharide hapten from Brucella melitensis. Infect Immun. 1987 Nov;55(11):2850–2853. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.11.2850-2853.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moreno E., Speth S. L., Jones L. M., Berman D. T. Immunochemical characterization of Brucella lipopolysaccharides and polysaccharides. Infect Immun. 1981 Jan;31(1):214–222. doi: 10.1128/iai.31.1.214-222.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Péterfy F., Kuusela P., Mäkelä O. Affinity requirements for antibody assays mapped by monoclonal antibodies. J Immunol. 1983 Apr;130(4):1809–1813. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rudbach J. A., Anacker R. L., Haskins W. T., Milner K. C., Ribi E. Physical structure of a native protoplasmic polysaccharide from Escherichia coli. J Immunol. 1967 Jan;98(1):1–7. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stemshorn B. W. Recent progress in the diagnosis of brucellosis. Dev Biol Stand. 1984;56:325–340. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WARREN L. The thiobarbituric acid assay of sialic acids. J Biol Chem. 1959 Aug;234(8):1971–1975. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zygmunt M. S., Dubray G. Preparation by ultrafiltration and control by high-performance liquid chromatography of the native hapten of Brucella abortus for use in radial immunodiffusion diagnostic test. J Clin Microbiol. 1987 Oct;25(10):1860–1863. doi: 10.1128/jcm.25.10.1860-1863.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]