Abstract
Coagulase-negative staphylococci are important nosocomial pathogens. At present, no wholly satisfactory typing scheme exists for these organisms. Therefore, sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (SDS-PAGE) and immunoblotting were assessed as characterization methods. A total of 100 type strains and nontyped isolates representing nine species of coagulase-negative staphylococci were analyzed. Each species had a reproducible, characteristic whole-cell banding pattern when analyzed by either method. These species-specific profiles were obtained for all isolates despite disparate geographical origins and clinical isolation sites. Intraspecies similarities, calculated by using the Dice coefficient, were significantly higher than interspecies similarities. Although some species were more heterogeneous than others, the allocation of isolates to any particular species was reinforced by the high degree of interspecies dissimilarity. Application of SDS-PAGE also distinguished discrete subspecies groups. These groups possessed the characteristic profile of their species but were distinguished by a group of variable polypeptides. Species-specific banding patterns were also obtained by immunoblotting of whole-cell polypeptides. Differences between immunoblot and SDS-PAGE profiles could be attributed to variations of antigenicity of particular polypeptides. However, both SDS-PAGE and immunoblotting provided reproducible and sensitive methods for characterization of coagulase-negative staphylococci. Standardization of these techniques could provide the basis for a primary typing scheme.
Full text
PDF
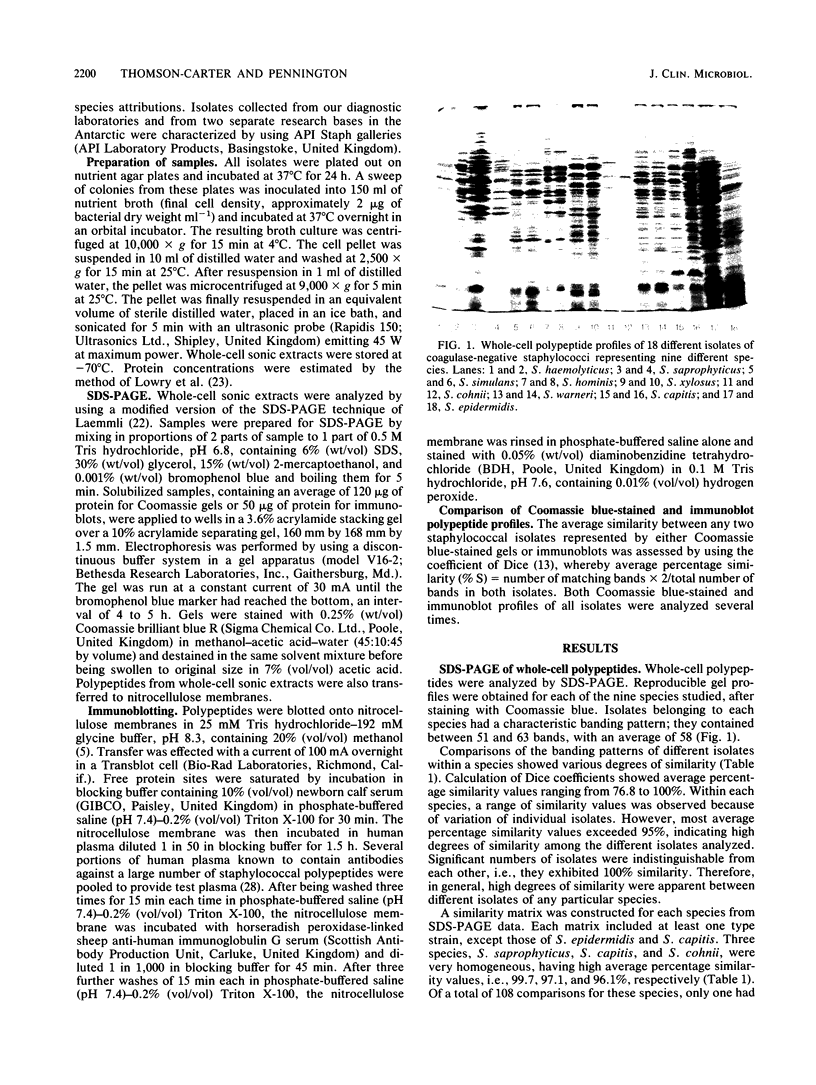
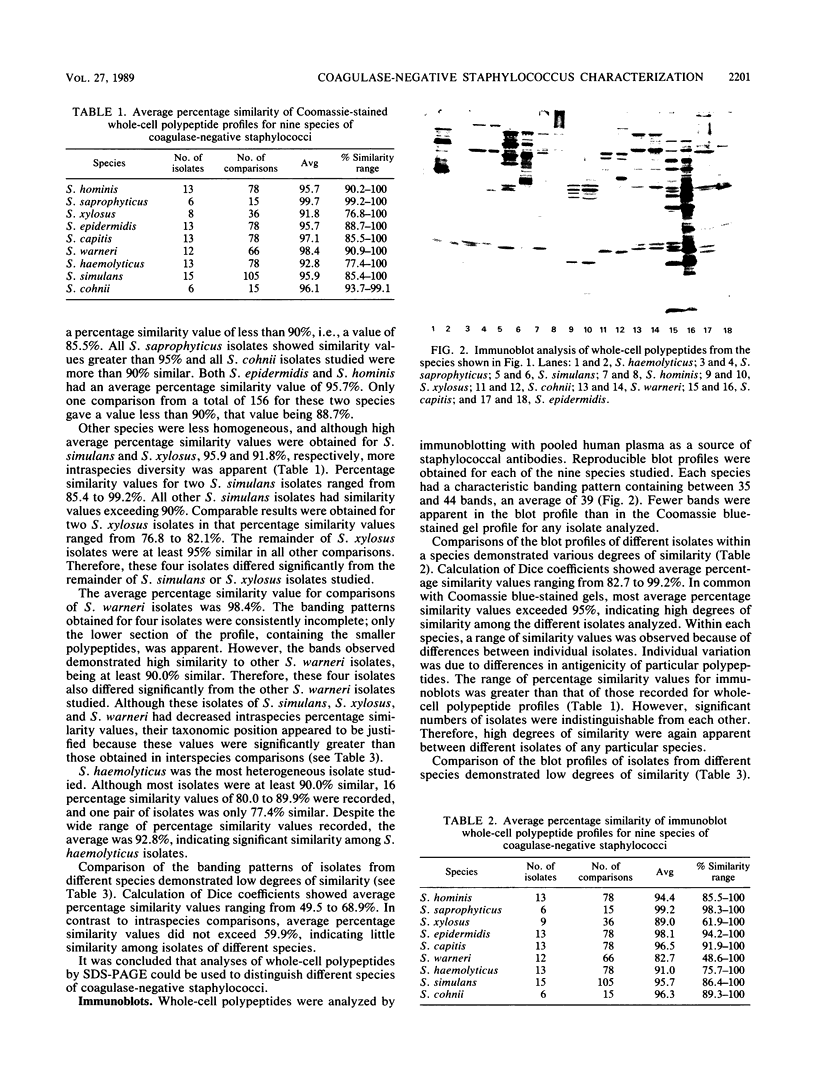
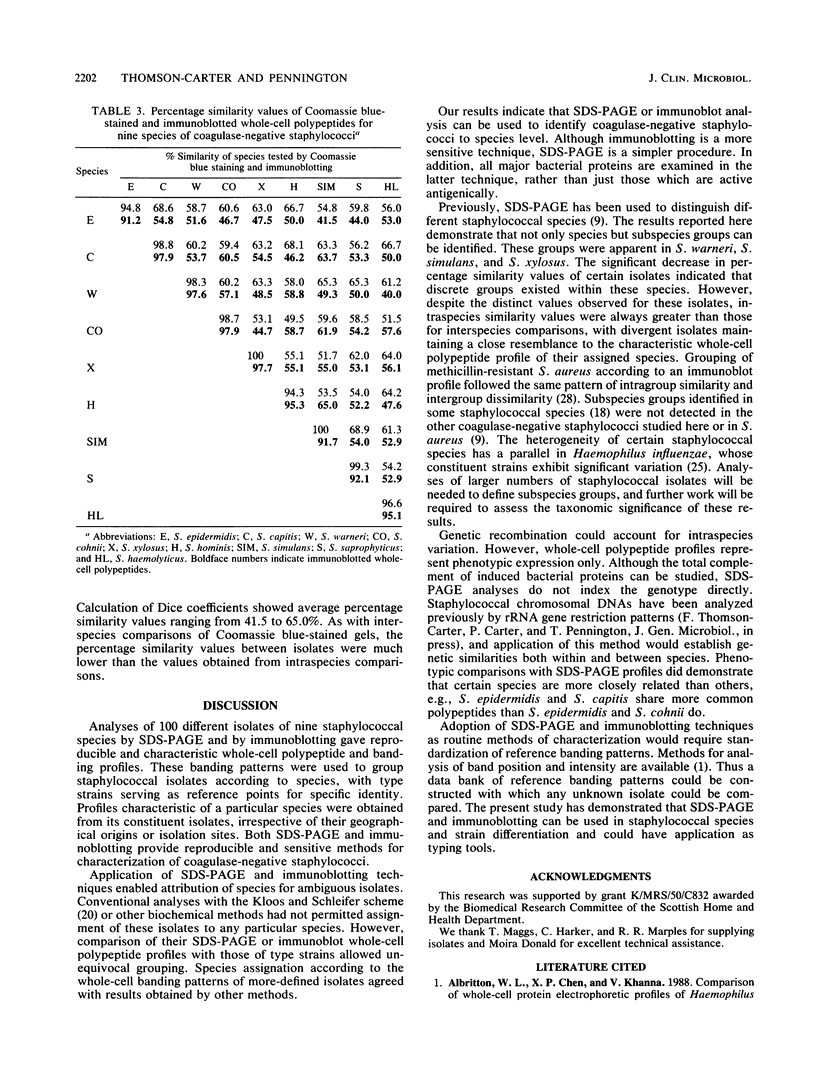

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Albritton W. L., Chen X. P., Khanna V. Comparison of whole-cell protein electrophoretic profiles of Haemophilus influenzae: implementation of a microcomputer mainframe linked system and description of a new similarity coefficient. Can J Microbiol. 1988 Oct;34(10):1129–1134. doi: 10.1139/m88-199. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Archer G. L., Karchmer A. W., Vishniavsky N., Johnston J. L. Plasmid-pattern analysis for the differentiation of infecting from noninfecting Staphylococcus epidermidis. J Infect Dis. 1984 Jun;149(6):913–920. doi: 10.1093/infdis/149.6.913. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Archer G. L. Molecular epidemiology of multiresistant Staphylococcus epidermidis. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1988 Apr;21 (Suppl 100):133–138. doi: 10.1093/jac/21.suppl_c.133. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BAIRD-PARKER A. C. A classification of micrococci and staphylococci based on physiological and biochemical tests. J Gen Microbiol. 1963 Mar;30:409–427. doi: 10.1099/00221287-30-3-409. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burnette W. N. "Western blotting": electrophoretic transfer of proteins from sodium dodecyl sulfate--polyacrylamide gels to unmodified nitrocellulose and radiographic detection with antibody and radioiodinated protein A. Anal Biochem. 1981 Apr;112(2):195–203. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90281-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burnie J. P., Lee W. A comparison of DNA and immunoblot fingerprinting of the SII biotype of coagulase negative staphylococci. Epidemiol Infect. 1988 Oct;101(2):203–212. doi: 10.1017/s095026880005411x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burnie J. P., Lee W., Matthews R. C., Bayston R. Immunoblot fingerprinting of coagulase negative staphylococci. J Clin Pathol. 1988 Jan;41(1):103–107. doi: 10.1136/jcp.41.1.103. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christensen G. D. The confusing and tenacious coagulase-negative staphylococci. Adv Intern Med. 1987;32:177–192. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deighton M. A., Franklin J. C., Spicer W. J., Balkau B. Species identification, antibiotic sensitivity and slime production of coagulase-negative staphylococci isolated from clinical specimens. Epidemiol Infect. 1988 Aug;101(1):99–113. doi: 10.1017/s0950268800029265. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kloos W. E., Schleifer K. H. Simplified scheme for routine identification of human Staphylococcus species. J Clin Microbiol. 1975 Jan;1(1):82–88. doi: 10.1128/jcm.1.1.82-88.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kocur M., Bergan T., Mortensen N. DNA base composition of Gram-positive cocci. J Gen Microbiol. 1971 Dec;69(2):167–183. doi: 10.1099/00221287-69-2-167. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pennington T. H., Freebairn E. M. Subtyping of Haemophilus influenzae type b strains from Europe and North America by SDS-PAGE of whole-cell polypeptides: the geographical distribution of subtypes. Epidemiol Infect. 1989 Feb;102(1):11–19. doi: 10.1017/s0950268800029630. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ponce de Leon S., Guenthner S. H., Wenzel R. P. Microbiologic studies of coagulase-negative staphylococci isolated from patients with nosocomial bacteraemias. J Hosp Infect. 1986 Mar;7(2):121–129. doi: 10.1016/0195-6701(86)90054-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schito G. C., Varaldo P. E. Trends in the epidemiology and antibiotic resistance of clinical Staphylococcus strains in Italy--a review. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1988 Apr;21 (Suppl 100):67–81. doi: 10.1093/jac/21.suppl_c.67. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stephenson J. R., Tabaqchali S. New method for typing coagulase negative staphylococci. J Clin Pathol. 1986 Nov;39(11):1271–1275. doi: 10.1136/jcp.39.11.1271. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomson-Carter F. M., Pennington T. H. Characterisation of methicillin-resistant isolates of Staphylococcus aureus by analysis of whole-cell and exported proteins. J Med Microbiol. 1989 Jan;28(1):25–32. doi: 10.1099/00222615-28-1-25. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winston D. J., Dudnick D. V., Chapin M., Ho W. G., Gale R. P., Martin W. J. Coagulase-negative staphylococcal bacteremia in patients receiving immunosuppressive therapy. Arch Intern Med. 1983 Jan;143(1):32–36. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]





