Abstract
Dopaminergic (DAergic) neuronal activity in the ventral tegmental area (VTA) is thought to contribute generally to pleasure, reward, and drug reinforcement and has been implicated in nicotine dependence. nAChRs expressed in the VTA exhibit diverse subunit compositions, but the functional and pharmacological properties are largely unknown. Here, using patch-clamp recordings in single DAergic neurons freshly dissociated from rat VTA, we clarified three functional subtypes of nAChRs (termed ID, IID and IIID receptors) based on whole-cell current kinetics and pharmacology. Kinetic analysis demonstrated that comparing to ID, IID receptor-mediated current had faster activation and decay constant and IIID receptor-mediated current had larger current density. Pharmacologically, ID receptor-mediated current was sensitive to the α4β2-nAChR agonist RJR-2403 and antagonist dihydro-β-erythroidine (DHβE); IID receptor-mediated current was sensitive to the selective α7-nAChR agonist choline and antagonist methyllycaconitine (MLA); while IIID receptor-mediated current was sensitive to the β4-containing nAChR agonist cytisine and antagonist mecamylamine (MEC). The agonist concentration–response relationships demonstrated that IID receptor-mediated current exhibited the highest EC50 value compared to ID and IIID receptors, suggesting a relatively low agonist affinity of type IID receptors. These results suggest that the type ID, IID and IIID nAChR-mediated currents are predominately mediated by activation of α4β2-nAChR, α7-nAChR and a novel nAChR subtype(s), respectively. Collectively, these findings indicate that the VTA DAergic neurons express diversity and multiplicity of functional nAChR subtypes. Interestingly, each DAergic neuron predominantly expresses only one particularly functional nAChR subtype, which may have distinct but important roles in regulation of VTA DA neuronal function, DA transmission and nicotine dependence.
Brain reward systems are essential for adaptation and survival, but their activation by exogenous agents can produce drug dependence (White, 2002). Although mechanisms involved in drug dependence are not fully defined, the mesocorticolimbic dopaminergic (DAergic) system, and the ventral tegmental area (VTA) in particular, appear to play major roles (Nisell et al. 1994; Pontieri et al. 1996; Spanagel & Weiss, 1999; Dani & De Biasi, 2001; Dani et al. 2001). For example, increases in dopamine (DA) release from VTA DAergic neurons onto their targets have been implicated in drug reinforcement (Spanagel & Weiss, 1999).
Studies linking nicotine dependence to VTA DAergic neurons, DA and nicotinic acetylcholine receptors (nAChRs) include indications that nicotine self-administration is significantly reduced after lesioning of midbrain DAergic neurons or injection of a nAChR antagonist into the VTA (Corrigall et al. 1994; Sziraki et al. 2002). Electrophysiological studies using brain slices showed that modulation of pre- or postsynaptic nAChRs altered DAergic neuronal activity and/or DA release in the VTA or substantia nigra pars compacta (SNc) through apparently complex mechanisms (Pidoplichko et al. 1997; Wonnacott et al. 2000; Klink et al. 2001; Mansvelder et al. 2003; Wooltorton et al. 2003; Pidoplichko et al. 2004). nAChR subunits are diversely expressed in the VTA (Wada et al. 1989; Le Novere et al. 1996; Charpantier et al. 1998; Zoli et al. 1998; Klink et al. 2001; Azam et al. 2002; Le Novere et al. 2002), thus positioning nAChRs to contribute to biologically rewarding events, but also to nicotine dependence (Dani & Heinemann, 1996).
Studies using wild-type and specific nAChR subunit knockout mice have suggested that two possible heteromeric nAChR subunit combinations in midbrain DAergic neurons are α4α5α6(β2)2 and α4α5(β2)2, whereas homomeric α7-nAChRs are expressed on less than one-half of VTA DAergic neurons (Klink et al. 2001). Other studies suggest that functional α6β2 (or α4α6β2)-nAChRs are mainly located at DAergic neuronal terminals (Champtiaux et al. 2003) and that α4β2-nAChRs represent the majority of functional, heteromeric nAChRs on DAergic neuronal soma (Champtiaux et al. 2003). nAChRs that contain the β2 subunit appear to be essential for nicotine reinforcement and self-administration, which are prerequisites for nicotine dependence (Picciotto et al. 1998; Mameli-Engvall et al. 2006). In mice lacking the nAChR α4 subunit, there is no nicotine-induced increase of DA release in the striatum (Marubio et al. 2003), although functional nAChRs remain on DAergic neurons (Picciotto et al. 1998). Moreover, nicotine-induced reward, tolerance and sensitization are enhanced in mice engineered to express gain-of-function α4*-nAChR (Tapper et al. 2004). However, our understanding of functional nAChR subtype expression in the VTA and the pharmacological properties remains incomplete, in part due to limitations in brain slice preparations in analysis of the kinetics of nAChR-mediated whole-cell currents and pharmacology (Pidoplichko et al. 1997; Klink et al. 2001; Mansvelder et al. 2003; Wooltorton et al. 2003). On the other hand, the use of neurons in primary culture allows for faster drug application and washout and has provided fundamental information about functional nAChRs in hippocampal neurons (Alkondon & Albuquerque, 1993), but with limited ability to determine neuronal phenotype and degree of maturation. Another difficulty when studying nAChRs is that their expression, function and pharmacology are altered during the first postnatal month in rodents (Azam et al. 2007).
To complement previous approaches and to deal with some of these confounds, we chose to use freshly dissociated, single neurons from the VTA of rats of known age in preparations allowing for determination of neuronal phenotype using electrophysiological and cytochemical approaches. We also used patch-clamp whole-cell current recording techniques that allow for rapid drug application and washout (using a computer-controlled U-tube drug application system) and exploited the ability to minimize space-clamp problems during recording. Based on work focusing on characterization of functional nAChR subtypes, we have identified three functional subtypes of nAChRs naturally expressed on the VTA DAergic neurons, and we provide evidence that while there are multiple functional subtypes of nAChRs on VTA DAergic neurons, each DAergic neuron predominantly expresses only one, a ID, IID or IIID receptor.
Methods
Single DAergic neuron dissociation
The protocol for the preparation of single neurons from the rat VTA was approved by the Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee of the Barrow Neurological Institute.
Single neurons were acutely dissociated from the VTA of 2–3-week-old Wistar rats following procedures previously described (Wu et al. 2004). Briefly, rats were anaesthetized with isoflurane, and brain tissue was rapidly removed and immersed in cold (2–4°C) dissection solution that contained (in mm): 136.7 NaCl, 5 KCl, 0.1 Na2HPO4, 0.2 KH2PO4, 9.84 Hepes, 16.6 d-glucose and 21.9 sucrose; pH 7.3; 330 mosmol l−1; oxygenated with 100% O2 (Ishihara et al. 1995). From each rodent, two 400 μm coronal slices containing the VTA were cut using a vibratome (Vibratome 1000 Plus, St Louis, MO, USA). After cutting, the slices were continuously bubbled with 95% O2–5% CO2 at room temperature (22 ± 1°C) for at least 1 h in artificial cerebrospinal fluid (ACSF), which contained (in mm): 124 NaCl, 5 KCl, 24 NaHCO3, 1.3 MgSO4, 1.2 KH2PO4, 2.4 CaCl2 and 10 glucose; pH 7.4. Thereafter, the slices were treated with pronase (1 mg per 6 ml) at 31°C for 30 min in ACSF. After enzyme treatment, the slices were washed twice with well-oxygenated ACSF. The VTA was first identified using a stereomicroscope and then micropunched out from the slices using a well-polished needle (0.6 mm diameter). Each punched piece was then separately transferred to a 35 mm culture dish filled with well-oxygenated standard extracellular solution, which contained (in mm): 150 NaCl, 5 KCl, 1 MgCl2, 2 CaCl2, 10 glucose and 10 Hepes; pH 7.4 (with Tris-base). Each punched piece was then dissociated mechanically using a fire-polished micro-Pasteur pipette under an inverted microscope (Olympus IX-70, Lake Success, NY, USA). The separated cells adhered to the bottom of the culture dish within 30 min. We used only VTA neurons that maintained their original morphological features of polygonal, large- or medium-sized somata with two to four thick, primary dendritic processes.
Perforated patch-clamp whole-cell recordings
Perforated-patch whole-cell recording techniques were employed (Wu et al. 2004). Compared to performing conventional whole-cell recordings, this approach was crucial for obtaining stable nicotinic responses from dissociated VTA neurons, presumably due to minimal perturbation of the intracellular environment. Pipettes (3–5 MΩ) used for perforated-patch recordings were filled with intracellular recording solution, which contained (in mm): 140 potassium gluconate, 10 KCl, 5 MgCl2 and 10 Hepes; pH 7.2 (with Tris-OH) freshly supplemented before use with amphotericin B to 200 μg ml−1 from a 40 mg ml−1 DMSO stock. The liquid-junction potential was −14 mV (calculated using Clampex 9.2, Axon Instruments, Union City, CA, USA), and corrections were made for junction potentials post hoc. After tight seal (> 2 GΩ) formation, about 5–20 min was required for conversion to the perforated-patch mode, and an access resistance of < 60 MΩ was accepted to start the experiments. Series resistance was not compensated in this study. Data were acquired at 10 kHz, filtered at 2 kHz, digitized on-line (Digidata 1322 series A/D board, Axon Instruments), and displayed and stored on a PC computer. Rapid application of drugs was performed using a computer-controlled ‘U-tube’ system (Wu et al. 2004) that allowed for complete exchange of solution surrounding the recorded cell within 30 ms. Periods of drug exposure are specified in the text and figures or legends. When ACh was used as a nicotinic agonist, 1 μm atropine was routinely added to exclude actions mediated via endogenous muscarinic receptors, and this manipulation is known to have no clear effect on ACh-induced currents (Wu et al. 2004). All experiments were performed at room temperature. To enable identification of single, dissociated VTA neurons, cells were labelled with a fluorescent dye (lucifer yellow; Sigma-Aldrich, St Louis, MO, USA; 1.0 mg ml−1 in the recording electrode) in some experiments. After conversion from perforated to conventional whole-cell recording mode, the dye was injected into the cytoplasm by a pulse (200 ms, 0.5 Hz) of hyperpolarizing current (1.0 nA) for 3 min. Labelled cells were visualized using epifluorescence microscopy.
Immunocytochemical staining
Dissociated VTA neurons were fixed with 4% paraformaldehyde for 15 min, rinsed three times with phosphate-buffered saline (PBS), and treated with saponin (1 mg ml−1, Sigma-Aldrich) for 5 min as a permeabilizing agent. After rinsing four times with PBS, the neurons were incubated at room temperature in anti-tyrosine hydroxylase (TH) primary antibody (AB152; Chemicon International, Temecula, CA, USA) diluted 1 : 1000 in Hanks’ balanced salt solution (supplemented with 5% bovine serum albumin as a blocking agent) for 30 min. Following another three rinses with PBS, a secondary antibody (cy3-conjugated, anti-mouse IgG; Sigma-Aldrich) was applied at room temperature for 30 min (diluted 1 : 100). After rinsing a final three times with PBS, the labelled cells were visualized using fluorescence microscopy.
nAChR subunit mRNA detection
RT-PCR assays followed by Southern hybridization with nested oligonucleotides were done as previously described to identify nAChR subunit transcripts and to quantify levels of expression normalized both to housekeeping gene expression and levels of expression in whole brain (Zhao et al. 2003; Wu et al. 2004), but using primers designed to detect rat nAChR subunits (see Table 1). The Southern hybridization technique coupled with quantification using electronic isotope counting (Instant Imager, Canaberra Instruments, Meridien, CT, USA) yielded results equivalent to those obtained using real-time PCR analysis.
Table 1.
Primers used for initial amplification and Southern hybridization analysis of VTA nAChR subunit expression
| Rat nAChR subunit | Sense primer (5′→3′) | Antisense primer (5′→3′) |
|---|---|---|
| α2 | CTTCTGAGATGATCTGGATCC | GAGGTGACAGCAGAATCTCGCTAG |
| α3 | CATGTCTCAGCTGGTGAAG | GCCGGCGGGATCCAAGTCACTTC |
| α4 | GAATGTCACCTCCATCCGCATC | CCGGCA(A/G)TTGTC(C/T)TTGACCAC |
| α5 | GGGTTCG(T/C)CCTGTGGAACACCTGA | GGTCCTCTAG(A/G)ATTATATCAACCTG |
| α6 | TGTTCCAGCAGATAACATCTG | CTACCTCCTT(G/T)GTTTCATTGTGGCT |
| α7 | GTTCTATGAGTGCTGCAAAGAGCC | CTCCACACTGGCCAGGCTGCAG |
| α9 | GCTCAGAAATTGTTCAGCGATC | CAGCAGGCATGCCATGGACC |
| β2 | CTCCAACTCAATGGCGCTGTTCAG | CCATGAGCGAAACTTCATGGTGCAA |
| β3 | GGTTCCATCAGAATCGCTC | CCGTGAGAAAAGACAACCCCAGG |
| β4 | CAAGAGTGCCTGCAAGATTGAGGTG | GGAGCTGACTGCAGACTTAGGAGC |
| GAPDH | CGGATTTGGCCGTATCGGACGCC | GCCTTGGCAGCACCAGTGGATGC |
Chemicals and statistics
The drugs used in the present study were (–)nicotine, ACh, choline, cytisine, methyllycaconitine (MLA), mecamylamine (MEC), dihydro-β-erythroidine (DHβE), DA (all purchased from Sigma-Aldrich), and RJR-2403 (purchased from Tocris Bioscience, Ellisville, MO, USA). The α-conotoxin MII was a gift obtained from Dr J. Michael McIntosh. Concentration–response relationships for nicotinic ligand action on nAChR-mediated whole cell currents were normalized, averaged, and fitted to the Hill equation to derive both EC50 and Hill coefficient values. All results are presented as mean ±s.e.m. Student's t test was used to compare two groups of data, and significance was set at P < 0.05.
Results
Naturally expressed nAChR subunits in the rat VTA
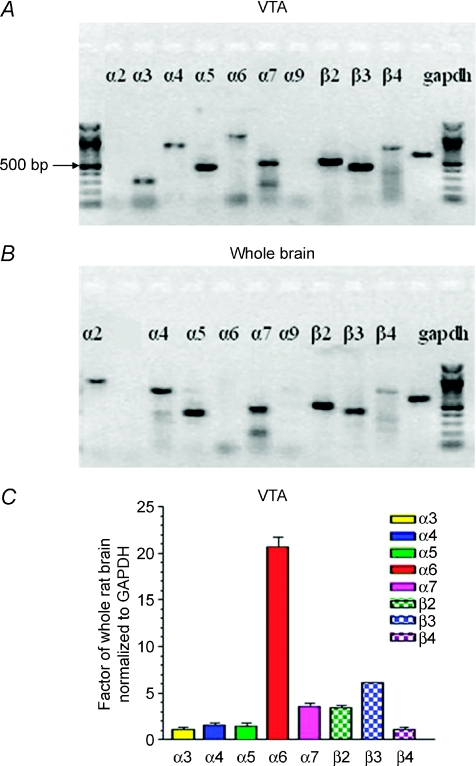
Diverse expression of nAChR subunits by VTA neurons might have important functional consequences related to nicotine dependence. RT-PCR analysis was done to identify expressed nAChR subunits in micropunched VTA samples from Wistar rats like those processed for electrophysiological studies as described below. Data were analysed to quantify nAChR subunit mRNA levels from the VTA compared to levels of expression across whole brain. Expression of nAChR α3–α7 and β2–β4 subunits, but not α2 or α9 subunits, was evident in the VTA (Fig. 1A), whereas whole-brain samples showed the richest expression of nAChR α2, α4, α5, α7 and β2–β3 subunits (Fig. 1B; note that the α3 subunit product was not applied to this representative, ethidium-stained gel). RT-PCR followed by Southern hybridization using 32P-labelled, nested oligonucleotide probes was used to give real-time PCR-quality quantification of nAChR subunit message levels in the VTA. When expressed as a factor of whole-brain expression for all data normalized to mRNA encoding glyceraldehyde phosphate dehydrogenase (GAPDH) as a control for the amount of input mRNA, the data indicated that VTA levels of expression of nAChR α3, α4, α5 and β4 subunits were comparable to those in whole brain, whereas levels of α7 and β2 subunits were enriched ∼3.5-fold in the VTA (Fig. 1C). There was a ∼6-fold enrichment of nAChR β3 subunit message in the VTA (Fig. 1C), and nAChR α6 subunit message levels were > 20-fold higher in the VTA (Fig. 1C). The VTA contains both DAergic and GABAergic neurons, which could contribute to the diversity in nAChR subunit expression. However, the complex pattern of nAChR subunit expression as mRNA (α3–α7, β2–β4) in the rat VTA is consistent with both previous observations (Wada et al. 1989; Azam et al. 2002) and findings from patch-clamp recordings combined with single-cell RT-PCR studies using mouse midbrain slices (Klink et al. 2001).
Figure 1. RT-PCR analysis of nAChR subunit mRNA levels expressed in the rat VTA.
RT-PCR products in the VTA (A) or in the whole brain (B) from postnatal 14–21-day-old Wistar rats and corresponding to the indicated nAChR subunits or to the housekeeping gene GAPDH were resolved on an agarose gel calibrated by the flanking 100 bp ladders (heavy band is 500 bp) and visualized using ethidium staining. Note that the representative gel shown for whole brain did not contain a sample for the nAChR α3 subunit RT-PCR product, which typically is similar in intensity to the sample on the gel for the VTA. C, results of RT-PCR amplification followed by Southern hybridization with 32P-labelled, nested oligonucleotides were quantitatively compared after normalization to the GAPDH internal control and to levels of each specific mRNA in whole rat brain (ordinate: +s.e.m.) for the indicated. Note that it is not possible to compare the level of expression of one subunit as message to another's based on the approach used.
Identification of VTA DAergic neurons
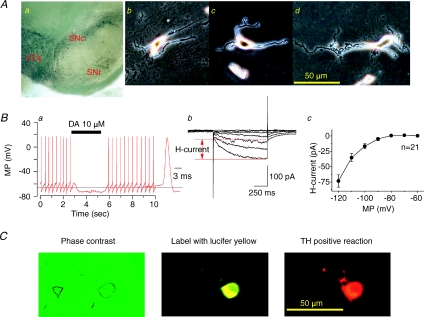
We desired to evaluate nAChR function on single DAergic neurons freshly dissociated from the rat VTA (Fig. 2Ab–d), which required that we first defined the region of interest and the cells contained within it. The VTA was identified in coronal slices made through the midbrain with reference to the SN, and TH immunostaining patterns of sister samples were used to verify selection of the micropunched VTA (Fig. 2Aa). Under perforated-patch recording conditions, the average resting potential for dissociated VTA neurons was −41.8 ± 1.4 mV (before a correction for junction potential, n= 52). Junction potentials for potassium gluconate electrodes used are about −14 mV as estimated using pCLAMP 9.2. Identification of DAergic neurons was confirmed early in the recording session based on: (1) 0.5–3.2 Hz (1.77 ± 0.14 Hz, n= 52) spontaneous action potential firing with each action potential having a long duration (3.84 ± 0.18 ms decay to 50% of peak amplitude, n= 52, Fig. 2Ba), (2) inhibition of spontaneous firing during exposure to 10 μm DA in all recorded neurons represented either as a complete block of action potentials (Fig. 2Ba) or as significantly reduced neuronal firing, and (3) expression of a hyperpolarization-induced current (H-current; voltage-clamp mode, Fig. 2Bb). The peak current at −120 mV was −73.4 ± 10.1 pA, n= 21; Fig. 2Bc). Retrospective confirmation of the DAergic phenotype was accomplished by labelling the recorded neuron (Fig. 2Ca) with a fluorescent dye (lucifer yellow, 1 mg ml−1; injected at the end of the recording session after conversion from perforated to conventional whole-cell recording configuration) followed by microscopic visualization of the stained neuron based on both lucifer yellow fluorescence (Fig. 2Cb) and a positive immunocytochemical reaction for TH (Fig. 2Cc). Whereas electrophysiological properties were used to identify all VTA DAergic neurons studied in this work, anti-TH immunostaining was only conducted on a subset of recorded neurons, but TH-positive staining always correlated with electrophysiological features in all 11 neurons tested. We realize that there are indications that H-current-positive neurons may not always be DAergic (Margolis et al. 2006), but we are confident that the collective properties of the cells identified in this study as DAergic reliably allowed us to make those identifications. We also identified VTA non-DAergic neurons in the course of these studies based on electrophysiological properties (supplementary Fig. 1). However, because we were not able to confirm a GABAergic phenotype of these non-DAergic neurons through systematic studies employing immunohistochemistry (i.e. GAD67 staining), we focused on DAergic but not GABAergic neurons in the present study.
Figure 2. Identification of VTA DAergic neurons.
A, TH immunostaining of a slice containing the VTA region revealing DAergic neurons (small black cells, a) clustered below the SN. Phase contrast images of acutely dissociated, single neurons from the rat VTA in reference to a 50 μm calibration bar (b–d). B, patch-clamp recording under current-clamp mode of an acutely dissociated, VTA DAergic neuron showing characteristic spontaneous action potential firing at ∼3 Hz with a long (> 2.5 ms) spike duration (see inset and 3 ms calibration bar) and sensitivity to 10 μm DA (horizontal bar denotes period of application; a) and hyperpolarization-induced current (H-current in voltage-clamp mode (b)), and a summary of current amplitude of H-current from 21 neurons tested (c). C, images (left to right) of an acutely dissociated single neuron from the VTA examined after recording under phase contrast microscopy (left), identified by injection with lucifer yellow (middle), and subjected to TH immunostaining (right; scale bar = 50 μm).
ACh-induced whole-cell currents in VTA DAergic neurons
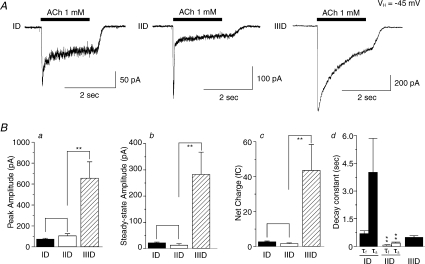
We characterized functional nAChR subtypes expressed on VTA DAergic neurons because of their potential relevance in mediating nicotine dependence. To accomplish this, we performed perforated patch-clamp recordings using single DAergic neurons freshly dissociated from the rat VTA (from 117 rats, a total of 188 neurons responded to ACh). Response kinetics allowed for classification, at least operationally, of three types of nAChR subtypes based on their functional nAChR phenotypes (Fig. 3). Type ID receptor-mediated currents showed rapid activation of a peak inward current and moderate and incomplete decay during agonist challenge from peak to steady-state current levels with steady-state currents being 28.7 ± 2.3% (n= 32) of peak values (Fig. 3A, left). Type IID receptor-mediated currents exhibited fast activation and rapid, more complete decay to steady-state levels that were 10.5 ± 3.4% (n= 11) of peak current values (Fig. 3A, middle). Whole-cell current profiles of type IIID receptors exhibited slow activation and inactivation and typically had larger peak and steady-state current amplitudes (the ratio of steady-state/peak was 41.3 ± 4.4%; n= 8) than responses mediated by type ID or IID receptors (Fig. 3A, right). The values for current rising time (10–90% of peak response) for type ID, IID or IIID receptors were 87.6 ± 7.3 (n= 20), 45.2 ± 3.3 (n= 20), or 144.8 ± 15.6 ms (n= 20), respectively. Analyses showed statistically significant differences in rising time for ID versus IID responses (P < 0.001), ID versus IIID responses (P < 0.01), and IID versus IIID responses (P < 0.001). To validate impressions formed based on whole-cell current traces (Fig. 3A), statistical analyses indicated larger peak amplitudes, steady-state amplitudes and total current net charge for responses mediated by type IIID receptors to 1 mm ACh (Fig. 3Ba–c). Steady-state/peak current ratios and net charge were higher for type ID than for type IID receptor-mediated currents (Fig. 3Bb–c). The whole-cell current decay constant showed two phases for ID and IID, and statistical analyses indicated that both tau-fast (τf) and tau-slow (τs) were larger for ID than that for IID receptor-mediated currents. There was only one phase of current decay for IIID responses (Fig. 3Bd). Table 2 summarizes kinetic analyses of these three different kinds of ACh-induced whole-cell currents from 51 recorded VTA DAergic neurons.
Figure 3. ACh-induced whole-cell currents in VTA DAergic neurons.
A, under voltage-clamp at a holding potential of −45 mV, 1 mm ACh applied for 2 s induced whole-cell currents in VTA DAergic neurons. Whole-cell currents were classified based on response amplitudes and kinetics as type ID responses displaying modest peak but more robust steady-state responses, type IID responses displaying large peak but low steady-state responses, or type IIID responses displaying large peak components that were only slowly inactivating (left to right: 50, 100 and 200 pA current amplitude calibration bars; 2 s time calibration bar; period of drug application denoted by horizontal bars). Traces shown were recorded from different VTA DAergic neurons and are representative of those obtained from neurons of the same class (see other representative traces in the following figures). B, features of ACh-induced whole-cell responses (ordinates: +s.e.m.; peak amplitude, pA, a; steady-state amplitude, pA, b; net charge, fC, c) for the identified type ID (filled bars, n= 32), IID (open bars, n= 11) or IIID receptor-mediated currents (cross-hatched bars, n= 8). The whole-cell current decay constant is shown in Bd, in which type ID (n= 9) and IID (n= 23) receptor-mediated whole-cell currents exhibited two phases (tau fast: τf and tau slow: τs), while type IIID (n= 8) responses exhibited only one decay phase. **P < 0.01.
Table 2.
Features of whole-cell current responses evoked by 1 mm ACh in VTA DAergic neuronal classes
| τ (ms) | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Type | n | Age (days) | Rt (ms) | Peak (pA) | Steady state (pA) | Fast | Slow |
| ID | 32 | 17 ± 1 | 64 ± 8 | 75 ± 8 | 22 ± 3 | 700 ± 162 (n= 9) | 4040 ± 1833 (n= 9) |
| IID | 11 | 16 ± 1 | 41 ± 7 | 107 ± 19 | 13 ± 5 | 56 ± 8 (n= 23)** | 200 ± 46 (n= 23)** |
| IIID | 8 | 16 ± 1 | 101 ± 22# | 658 ± 154**## | 283 ± 85**## | 505 ± 87 | |
Whole-cell current responses of acutely dissociated VTA DAergic neurons segregated into three classes, types ID, IID and IIID as described in the text, were analysed (numbers of neurons tested, n; age of animals used to isolate neurons, age) to yield mean ±s.e.m. for the parameters indicated (Rt, rising time: time to peak current, ms; peak: peak current amplitude, pA; steady-state: steady-state current amplitude, pA; τ: e-fold current decay time, ms).
P < 0.01 compared to ID.
P < 0.05 compared between IID and IIID;
P < 0.01 compared between IID and IIID.
Responses to nicotinic agonists
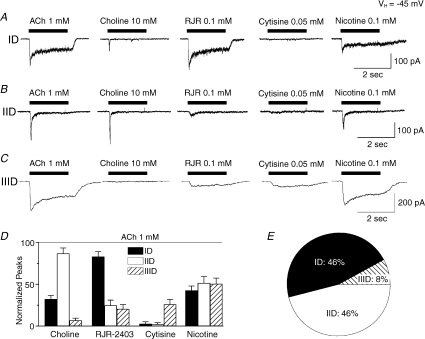
In order to further define functional nAChR profiles of VTA DAergic neurons, agonist sensitivity profiles were determined. Type ID receptors were strongly activated by the α4β2-nAChR-selective agonist RJR-2403 (0.1 mm; Papke et al. 2000), weakly by the α7-nAChR-selective agonist choline (10 mm; although sometimes there was elicitation of a quickly inactivating peak current), but not by cytisine (50 μm; cytisine is a weak, partial agonist at α4β2-nAChR but is much more efficacious at α3β4- or α4β4-nAChR) (Fig. 4A and D). These findings suggest that α4β2-nAChR is the dominant, functional nAChR subtype to mediate type ID responses. Type IID receptors were strongly activated by the α7-nAChR-selective agonist choline (which elicited virtually no steady-state current response), weakly by RJR-2403 (and then predominantly of a steady-state response), but not by cytisine, suggesting that α7-nAChR is the functionally predominant nAChR to mediate type IID responses (Figs 4B and D). Type IIID responses to ACh or nicotine were large and decayed slowly. These cells responded weakly to RJR-2403, were insensitive to choline, but exhibited greater responsiveness to cytisine compared to type ID or IID receptor-mediated currents (Fig. 4C and D). This profile suggests that the predominant, functional nAChR subtype(s) of type IIID responses is neither α4β2- nor α7-nAChR, but must be one or more nAChRs of different subunit composition. Classification of 188 ACh-responsive VTA DAergic neurons (from 117 rats) based on nAChR agonist sensitivity indicated that 46% were type ID, 46% were type IID, and 8% were type IIID nAChR-mediated responses (Fig. 4E).
Figure 4. Agonist sensitivity of VTA DAergic neuronal responses.
Whole-cell current responses to the indicated agonists (ACh, choline, RJR-2403, cytisine and nicotine at the indicated concentrations; left to right; period of drug application denoted by bar; 2 s time and 100 or 200 pA current amplitude calibration bars) for type ID (A), IID (B), or IIID receptor-mediated currents (C). Traces in each row (ID, IID or IIID) were recorded from the same neuron. D, efficacies of the indicated agonists at the concentrations shown in A–C in eliciting peak whole-cell currents (ordinate: normalized to the peak current response in the presence of 1 mm ACh; indicated as a horizontal dashed line) for type ID (filled bars), type IID (open bars) or type IIID (cross-hatched bars) responses averaged (+s.e.m.) from 6 to 8 neurons tested. E, percentages of VTA DAergic neuronal responses from 188 VTA dissociated neurons tested.
Agonist concentration dependence of VTA DAergic nAChRs
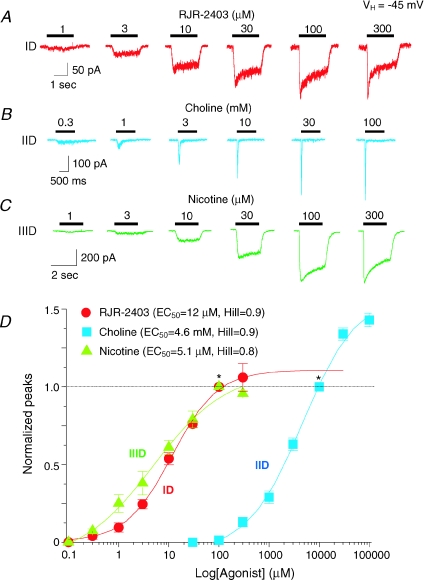
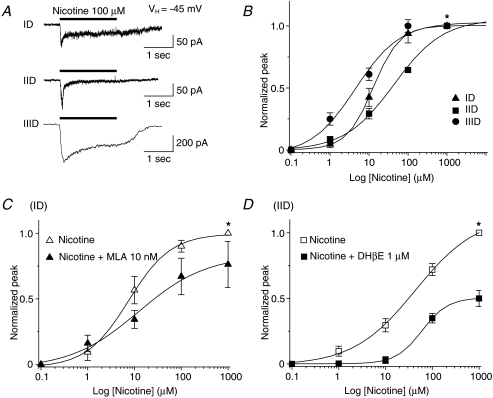
Concentration–response profiles (Fig. 5A–C) were obtained for agonists other than ACh showing highest efficacy in eliciting responses from different VTA DAergic neuronal types (Figs 4E and 5). EC50 values (and 95% confidence intervals) for peak currents and Hill coefficients (±s.e.m.), respectively, were 12 μm (8.5–16.0) and 0.9 ± 0.1 for RJR-2403 for type ID receptor-mediated currents (n= 6; Fig. 5A and D); 4.6 mm (3.5–5.9) and 0.9 ± 0.1 for type IID responses induced by choline (n= 5; Fig. 5B and D), and 5.1 μm (1.9–13.0) and 0.7 ± 0.2 for type IIID responses to nicotine (n= 4; Fig. 5C and D). These results indicate that pharmacological profiling of acutely dissociated DAergic neurons from the rat VTA underscores their classification, at least operationally, and provides further insight into the predominance of nAChR subtypes expressed on VTA DAergic neurons. To further characterize type ID, IID and IIID receptor subtypes, we also derived concentration–response relationships for type ID, IID and IIID responses to nicotine (Fig. 6). Nicotine at 100 μm induced three types of whole-cell current responses (Fig. 6A). Based on concentration–response curves, nicotine EC50 values (and 95% confidence intervals) for peak current responses and Hill coefficients were 12.6 μm (11.8–13.4) and 1.3 ± 0.04 for type ID responses (n= 9), 35.4 μm (17.5–71.6) and 0.8 ± 0.1 for type IID responses (n= 10), and 6.2 μm (2.5–15.5) and 0.7 ± 0.1 for type IIID responses (n= 5). Studies also were done using nAChR subtype-selective antagonists, which were applied for 2 min to cells prior to continued application during a 2 s challenge with nicotine. Nicotine concentration–response profiles were obtained for type ID receptor-mediated currents in the absence or presence of the α7-nAChR-selective antagonist, MLA (10 nm; Fig. 6C) or for type IID receptor-mediated currents in the absence or presence of the α4β2-nAChR-selective antagonist, DHβE (1 μm; Fig. 6D). EC50 values and Hill coefficients for peak current of type ID responses to nicotine were 7.5 μm and 1.0 in the absence of MLA compared to 12.1 μm and 0.6 in the presence of MLA (n= 3). EC50 values and Hill coefficients for type IID responses to nicotine were 43.2 μm and 0.7 in the absence of DHβE and 60.2 μm and 1.6 in the presence of DHβE (n= 5). The shift to lower apparent potency and a larger Hill slope for type IID responses in the presence of DHβE is consistent with sharpening of the nicotine response more toward one dominated by a lower-affinity, α7-nAChR. It is less clear why the type ID response changes as it does in the absence or presence of MLA. However, most important are the observations that MLA predominantly reduces peak and not steady-state components in type ID responses and has modest effects, and that DHβE has modest effects on type IID receptor-mediated currents that include reductions in peak and steady-state components. Thus, these data are consistent with dominance of α4β2-nAChR-mediated currents for type ID responses and of α7-nAChR-mediated currents for type IID responses.
Figure 5. Concentration–response relationships for VTA DAergic neuronal responses to nicotinic agonists.
Typical whole-cell current response traces (see time and current amplitude calibrations bars) were recorded in the presence of the indicated concentration (presented above the horizontal bar denoting the duration of agonist exposure) of RJR-2403 acting at type ID receptors (A), choline acting at type IID receptors (B), or nicotine acting at type IIID receptors (C). D, concentration–response curves for the three classes of nAChR (ID, IID, IIID)-mediated currents responding (ordinate: peak current amplitude normalized to that in the presence of 100 μm nicotine or RJR-2403 or 10 mm choline indicated by *; vertical bars: ±s.e.m.) to the indicated concentration (abscissa: μm, log scale) of RJR-2403 (type ID responses; •), choline (type IID responses; ▴) or nicotine (type IIID responses; ▪) yielded the indicated EC50 values and Hill coefficients (see inset and text). These values were determined based on fits of the data to the logistic equation where EC50 values are the concentrations of agonists needed to achieve 50% of the calculated maximum response to agonist. Hill coefficients indicated are for fits from zero basal levels to maximum peak current values that are 113%, 153% and 102%, respectively, for ID, IID and IIID responses at the agonist concentration used to normalize the data as described above. Data are from 4 to 6 cells for each class of neuron.
Figure 6. Concentration–response relationships for actions of nicotine on ID, IID and IIID receptors.
A, typical traces of nicotine-induced currents via ID, IID and IIID receptors. B, responses of type ID (▴), IID (▪) or IIID (•) receptors (ordinate: peak current amplitude normalized to that in the presence of 1000 μm nicotine indicated by *; mean values ±s.e.m.) to the indicated concentration (abscissa: μm, log scale) of nicotine. See text for EC50 values and Hill coefficients. C–D, comparison of nicotine-induced currents mediated by type ID receptors with or without MLA (C) or by type IID receptors with or without DHβE (D). For these experiments, whole-cell current responses were determined at different concentrations of nicotine and then again in the presence of nicotine and the indicated antagonists after a 2 min pretreatment with the antagonist, all using the same cell.
Antagonist inhibition of VTA DAergic neuronal responses to ACh
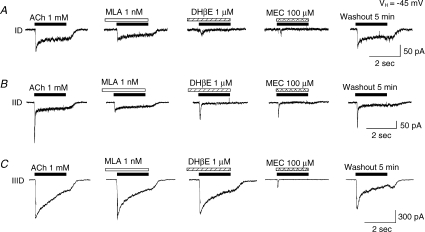
Sensitivity to functional blockade of VTA DAergic neuronal responses to 1 mm ACh was assessed using antagonists thought to be relatively selective for specific nAChR subtypes. MLA at 1 nm (2 min pretreatment followed by application of antagonist during agonist exposure) selectively blocked the rapidly activated, initial component of ACh-induced current but not the steady-state component of type ID (Fig. 7A) and IID (Fig. 7B) responses, and it did not block any element of type IIID responses (Fig. 7C). DHβE at 1 μm (2 min pretreatment followed by application of antagonist during agonist exposure) inhibited the steady-state component of ACh-induced type ID (Fig. 7A) and IID responses (Fig. 7B), but it less robustly inhibited type IIID neuronal responses (Fig. 7C). Effects of DHβE on peak currents were less robust although evident for type IID more than for type IIID and least for type ID responses (Fig. 7B and C). Sensitivity to 100 μm MEC (coapplied with agonist) was evident for responses from each nAChR subtype-mediated currents (Fig. 7A–C), and the steady-state components of type ID (Fig. 7A) and IIID responses (Fig. 7C) were most sensitive. Across nAChR subtypes, and at the concentrations used, the steady-state components of type ID responses were sensitive to both DHβE and MEC. Type IID receptor-mediated fast responses showed the highest sensitivity to MLA (accounting for the different concentrations used). Type IIID receptor-mediated responses were most sensitive to MEC. Interestingly, none of the nicotinic responses of acutely dissociated VTA DAergic neurons were blocked by 100 nmα-conotoxin MII, an α6/α3-nAChR subtype-selective antagonist (supplementary Fig. 2A) as has been demonstrated in other studies that used different preparations (Klink et al. 2001). However, using the same concentration of α-conotoxin MII, we found that this compound inhibited GABAergic, spontaneous inhibitory postsynaptic currents in DAergic neurons mechanically dissociated from rat VTA and apparently appose to GABAergic boutons (supplementary Fig. 2B). Sensitivity to nAChR antagonists also supports whole-cell current kinetic analyses and nAChR agonist sensitivity studies (Table 3) in discriminating three subtypes of functional nAChRs on VTA DAergic neurons. The collective results from antagonist profiling suggest that type ID and type IID responses are predominantly mediated by activities of α4β2- and α7-nAChRs, respectively, whereas type IIID receptor subtype seems to express a different, dominant nAChR subtype(s) insensitive to MLA and only weakly sensitive to DHβE.
Figure 7. Antagonist sensitivity of VTA DAergic neuronal responses.
A, representative whole-cell current traces are shown for responses to (left to right; agonist exposure periods are shown by the horizontal bars, and antagonist pre/coexposure duration is shown by the open/back slash bars) 1 mm ACh alone, ACh during and after 2 min of pre-exposure to 1 nm MLA or to 1 μm DHβE, ACh during exposure to 100 μm MEC, or ACh exposure after antagonist washout for type ID or IID responses (50 pA current amplitude calibration bar) or type IIID responses (300 pA current amplitude calibration bar); 2 s time calibration bar. VH=–45 mV.
Table 3.
Pharmacological features of nicotinic responses in VTA DAergic neurons – agonists
| Type | n | IAch (pA) | Icholine/IACh | IRJR/IACh | Icytisine(pA) | EC50 | Hill | Major subunits |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ID | 13 | 100 ± 14 | 32 ± 4%* | 78 ± 17% | 0 | RJR-2403: 12 μm | 0.9 | α4β2 |
| IID | 7 | 140 ± 14 | 87 ± 7% | 25 ± 7%** | 0 | Choline: 4.6 mm | 0.9 | α7 |
| IIID | 5 | 592 ± 139 | 7 ± 3%** | 20 ± 6%** | 148 ± 41* | Nicotine: 5.1 μm | 0.7 | β4-containing |
P < 0.05 compared to IACh,
P < 0.01 compared to IACh.
Antagonist concentration dependence for inhibition of functional nAChRs
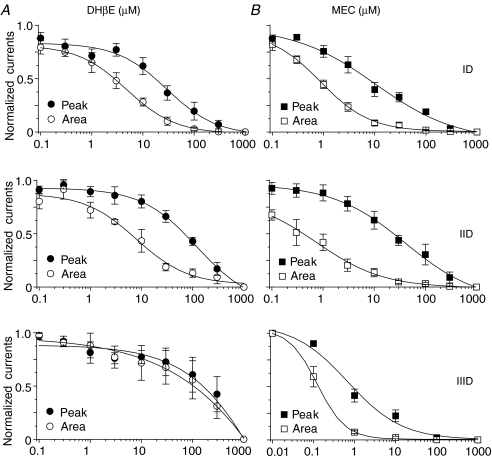
To lend further insight into the nAChR subtypes that are expressed on VTA DAergic neurons, perforated whole-cell current responses were obtained in the presence of 1 mm ACh coapplied with different concentrations of antagonists (no pretreatment). Since naturally expressed nAChR subtypes are expressed in the same VTA DAergic neuron, 1 mm ACh activated all possible nAChR subtypes. As shown in Fig. 7, the steady-state component of responses mediated by type ID and IID receptors likely reflected α4β2-nAChR-mediated currents while the sharp component of peak current mostly reflected α7-nAChR-mediated current. Thus, we analysed antagonist concentration-dependent inhibition by measuring current area for type ID responses but peak current for type IID responses. When evaluating current response area, IC50 values (and 95% confidence intervals) and Hill coefficients (±s.e.m.), respectively, for type ID responses were 5.3 μm (4.6–6.1) and 0.9 ± 0.1 (n= 6) for DHβE and 908.6 nm (647.7–1275.0) and 0.9 ± 0.1 (n= 6) for MEC. IC50 values (and 95% confidence intervals) and Hill coefficients (±s.e.m.), respectively, for peak current of type IID responses were 61.7 μm (39.4–93.4) and 0.7 ± 0.1 for DHβE (n= 6) and 21 μm (15.6–28.1) and 0.9 ± 0.1 for MEC (n= 6). IC50 values (and 95% confidence intervals) and Hill coefficients (±s.e.m.), respectively, for peak current of type IIID responses were > 100 μm for DHβE (n= 3) and 0.9 μm (0.2–4.8) and 0.7 ± 0.2 for MEC (n= 5, Fig. 8). Interestingly, IC50 values were ∼10-fold lower for DHβE and MEC when the effects were assessed on integrated whole-cell current (area) instead of peak current amplitude of type ID and type IID responses or for MEC actions at type IIID receptors (where the effects of DHβE were always weak), reflecting higher sensitivity to block of steady-state current components. For type ID and type IID receptor-mediated currents, this also could reflect lower sensitivity of quickly activating and inactivating responses mediated by α7-nAChR to either antagonist relative to more sustained responses characteristic of α4β2-nAChR. Overall, DHβE had weak effects and MEC had the strongest effects on type IIID nAChR-mediated responses.
Figure 8. Concentration–effect relationships for inhibition by DHβE or MEC of ACh-induced currents in VTA DAergic neurons.
The effects of nicotinic antagonists at the indicated concentrations (abscissa: log μm; DHβE effects are shown on the left, panel A, and MEC effects are shown on right, panel B) on peak current amplitude (peak) or net current during ligand application (integrated charge; area) upon exposure to 1 mm ACh were defined for each class of nAChR subtypes (ID, IID and IIID). DHβE (A) or MEC (B) were coapplied with ACh. Single neurons were used to obtain data at the entire set of antagonist concentrations. Each symbol was normalized to 1 mm ACh-induced response and represents the average response from 4 to 6 neurons (vertical bars represent s.e.m.).
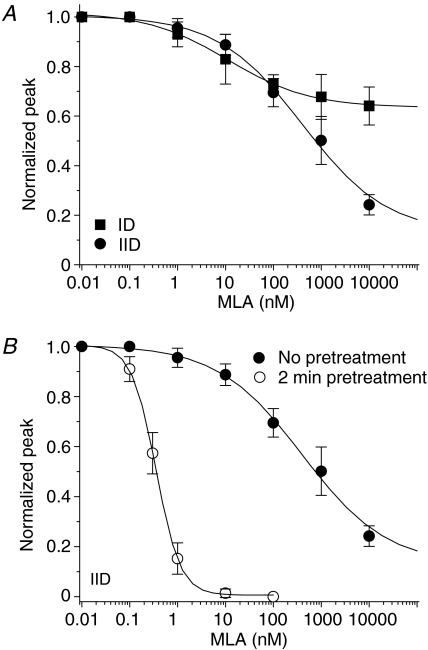
Relatively selective α7-nAChR antagonists such as α-bungarotoxin (α-BGT) and MLA are popular tools used in the nAChR field. The slow onset of functional block mediated by α-BGT and the slow recovery from those effects (Wu et al. 2004) confounds the obtaining of concentration–inhibition curves using toxin in dissociated neuron with patch-clamp recordings. Thus, and because type IIID responses were insensitive to MLA, we focused on studies using MLA and evaluated its effects on type ID and type IID responses to 1 mm ACh. Co-exposure to MLA during 2 s application of 1 mm ACh inhibited a small fraction of the peak current of type ID and IID responses (IC50= 17 nm, Hill = 0.6, n= 6 for ID responses; IC50= 130 nm, Hill = 0.7, n= 6 for IID responses; Fig. 9A), suggesting that without pretreatment, MLA exhibits relatively low-potency block of naturally expressed α7-nAChR. To confirm this notion, studies of type IID receptor-mediated currents subjected to no (IC50= 400 nm, Hill = 0.5) or 2 min pretreatment (IC50= 0.35 nm, Hill = 1.7) with MLA indicated that pretreatment markedly (∼1000 fold) increased the ability of MLA to block choline-induced peak (α7 type) current responses (Fig. 9B, Table 4), which was consistent with previous observations (Wu et al. 2004).
Figure 9. Pharmacological profiles for MLA inhibition of functional nAChR responses in VTA DAergic neurons.
Type ID or IID responses were induced by 1 mm ACh and type IID responses were induced by 10 mm choline in the presence of the indicated concentration (abscissa: log nm) of MLA coapplied with agonist (no pretreatment) or applied for 2 min prior to and then continuing during agonist exposure (pretreatment). Peak or integrated charge (area) of resultant whole-cell current responses were then determined (ordinates). A, comparison of effects of coincubation with MLA on peak current components to 1 mm ACh of type ID and IID responses. B, effects of MLA coapplication or pretreatment on 10 mm choline-induced peak current of type IID responses. All symbols represent average responses from 6 to 8 neurons (vertical bars represent ±s.e.m.).
Table 4.
Pharmacological features of nicotinic responses in VTA DAergic neurons – antagonists
| Peak | Area | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DHβE (μm) | MEC (μm) | MLA (nm) | DHβE (μm) | MEC (μm) | MLA (nm) | ||||||||
| Type | n | IC50 | Hill | IC50 | Hill | IC50 | Hill | IC50 | Hill | IC50 | Hill | IC50 | Hill |
| ID | 6 | 28 | 1.0 | 1.2 | 1.1 | 17 | 0.6 | 5.3 | 0.9 | 0.9 | 0.9 | 8.2 | 0.4 |
| IID | 6 | 62 | 0.7 | 21 | 0.9 | 130 | 0.7 | 1.2 | 0.6 | 0.4 | 0.6 | 156 | 0.5 |
| IIID | 4 | > 100 | 0.3 | 0.9 | 0.7 | NE | NE | > 100 | 0.4 | 0.1 | 1.2 | NE | NE |
Agonist used for these experiments was 1 mm ACh. All antagonists were coapplied with ACh. NE: no effect.
Discussion
In the present study, we have identified and characterized three functional subtypes of nAChRs in single DAergic neurons freshly dissociated from rat VTA using patch-clamp recordings combined with nicotinic pharmacological tools. Based on whole-cell current kinetics and pharmacological profiles, ACh induces three types of whole-cell currents, termed ID, IID and IIID type receptor-mediated currents, which are predominantly mediated by α4β2-nAChR, α7-nAChR and a receptor of more complex subuni composition (β4 containing), respectively. Interestingly, although most DAergic neurons express multiple functional nAChR subtypes, each DAergic neuron predominantly expresses only one particularly functional nAChR subtype, which may have distinct but important roles in regulation of VTA DA neuronal function, DA transmission, and nicotine dependence.
Diversity in nAChR subunit and subtype expression in VTA DAergic neurons
A large number of nAChR subunits have been found to be expressed in the current and in previous studies in the VTA or more broadly across midbrain DAergic or other brain regions (Wada et al. 1989; Le Novere et al. 1996; Charpantier et al. 1998; Zoli et al. 1998; Klink et al. 2001; Azam et al. 2002; Le Novere et al. 2002). This could reflect expression of a large number of nAChR subunits within a single type of cell in a brain region. The present study is consistent with and has extended these previous observations. We have shown that somatodendritic nAChRs are expressed on acutely dissociated DAergic neurons in a diverse manner. Type ID receptor reflects a predominance of α4β2-nAChR expression, type IID receptor is predominantly α7-nAChR, while type IIID receptor is assembled by nAChR subunits other than α4β2- or α7-nAChR.
Instead or in addition, this diversity of functional nAChR subtypes could also reflect an admixture of simpler patterns of subunit expression per specific cell type across several cell types. Indeed, projection or local neurons or different glial cell types, or even subsets of these cell types, could have different, and perhaps simpler, patterns of nAChR subunit expression. This possibility is supported by the current studies, which demonstrate that VTA DAergic neurons can be classified, at least operationally, based on their somatodendritic, functional nAChR phenotypes.
Pharmacological characterization of VTA DAergic neuronal nAChRs
Classification of functional nAChR subtypes was based mainly on pharmacological profiles in the present study.
In type ID receptor-mediated currents, the EC50 value for the relatively selective α4β2-nAChR full agonist RJR-2403 was 12 μm, which is comparable to that for the agonist acting at human α4β2-nAChRs heterologously expressed in SH-EP1 cells (Eaton et al. 2003). IC50 values (peak current, no pretreatment with antagonist) for the antagonists DHβE and MEC were 29 and 10 μm, respectively (Fig. 8A and B). However, these IC50 values are higher than those obtained in studies of their effects on α4β2-nAChRs heterologously expressed in Xenopus oocytes (Chavez-Noriega et al. 1997) or HEK 293 cells (Buisson et al. 1996). This could reflect real differences in native versus heterologously expressed receptors or in technique. For example, Buisson et al. (1996) measured the effects of DHβE on the steady-state component of nicotinic responses instead of on peak currents, and we found a ∼10-fold difference in IC50 values when making those comparisons internally (Fig. 8A). Rank order antagonist potency of DHβE and MEC is identical and their absolute IC50 values are comparable whether acting on steady-state components of type ID responses or on human α4β2-nAChRs heterologously expressed in SH-EP1 cells (Eaton et al. 2003). These findings indicate that type ID receptors have a predominant, functional α4β2-nAChR phenotype with regard to somatodendritic expression.
In type IID receptor-mediated currents, the EC50 value for nicotine was 35.4 μm and for the selective α7-nAChR agonist choline was 4.6 mm, which nevertheless is consistent with the reported low agonist affinity of a variety of heterologously or naturally expressed α7-nAChRs (Alkondon & Albuquerque, 1993; Zhao et al. 2003; Wu et al. 2004). In the current and previous (Zhao et al. 2003; Wu et al. 2004) studies, type IID receptor-mediated current responses were sensitive to low concentrations of either α-BGT or MLA when the appropriate pretreatment was applied. Thus, somatodendritic expression of α7-nAChRs predominated on type IID receptors.
With regard to type IIID receptors, which seem to be expressed in the VTA but not in the SN (Matsubayashi et al. 2004), the sensitivity of their functional nAChRs to cytisine and insensitivity to DHβE is consistent with their expression of functional nAChRs containing the β4 subunit. Their insensitivity to MLA or choline suggests a lack of α7-nAChR, and their level of expression of α4β2-nAChRs must be low due to low sensitivity to RJR-2403. α6*-nAChRs are among the functional subtypes identified in midbrain neurons (Klink et al. 2001), but 100 nmα-conotoxin MII failed to inhibit functional responses mediated by all three types (ID, IID, IIID) of receptor-mediated currents (supplementary Fig. 2). These results suggest that under the natural conditions, the functional α6*-nAChRs are expressed on somatodendrite of VTA DAergic neurons at a level that seems to be too low to be detected. However, after genetic enhancement of α6*-nAChR expression, the function of α6*-nAChRs can be clearly tested using the whole-cell recording technique (Drenan et al. 2008). Although the subunit makeup of type IIID nAChRs is unknown, the number of possible assembly partners has been narrowed (e.g. at least β4-containing nAChRs).
Interestingly, our findings echo the theme developed by Albuquerque and colleagues in their classification of ACh-induced whole-cell currents in rat hippocampal cultures (Alkondon & Albuquerque, 1993) or slices (Albuquerque et al. 1997) in that rat VTA type ID and IID responses have features like rat hippocampal type II and type IA responses, respectively. Moreover, functional and pharmacological properties of naturally expressed, type 1, type 2 and type 3 nAChRs categorized based on studies using wild-type or β2 subunit knockout mice (Zoli et al. 1998) have pharmacological features like the nAChR subtypes that dominate responses of the currently described type IID, type ID or type IIID receptors, respectively. We show a detectable α7-nAChR-like component in type ID receptor-mediated current and a small, α4β2-nAChR-like component in type IID receptor-mediated current, suggesting that there may be a continuum in proportions of expression of these nAChR subtypes across operationally defined type ID and IID receptor classes in the rat VTA.
Our findings about type ID and IID receptors on VTA DAergic neurons are partially consistent with the observations that VTA/SNc DAergic neurons express α4α6α5β2-, α4α5β2 (not α6)-, and α7-nAChRs using midbrain slice preparations from nAChR subunit knockout mice (Klink et al. 2001). However, it is more difficult to reconcile previous findings by Klink et al. (2001) or by Matsubayashi et al. (2004), who studied slices or acutely dissociated neurons from rat SNc, with our findings regarding type IIID receptors in the rat VTA. Perhaps these differences are due to the different species and/or brain regions studied. The nAChRs studied by others might be expressed on more distal dendrites perhaps preserved in slices but not in acutely dissociated neurons. Also, it is possible that some nAChR subtypes might not survive the acute dissociation process. Functional nAChRs containing α6 subunits on DAergic neuronal terminals rather than on soma (Champtiaux et al. 2003) would have escaped detection in our studies. Moreover, only a few type IIID receptor-mediated currents were identified by us, and a very small component of type IIID responses could be due to α7- and/or α4β2-nAChRs. However, the large amplitude, slowly decaying constant responses showing sensitivity to cytisine but insensitivity to RJR-2403, choline, or DHβE suggest that type IIID receptors assemble with very little if any α4β2- or α7-nAChR. We doubt that inclusion of α5 or β3 ‘wild-card’ subunits would account for the observed functional profile of type IIID nAChRs composed of α4 and β2 or α7 subunits, and any contribution by α6 subunits is difficult to reconcile with α-conotoxin MII-insensitivity of responses. Responses to cytisine and low sensitivity to DHβE suggest the inclusion in functional nAChRs of β4 rather than (or in addition to) β2 and α7 or α4 subunits. α3 and α6 subunits are candidate subunits along with β2, β3 and/or β4 subunits in type IIID nAChRs although insensitivity of functional responses to α-conotoxin MII was observed. There also could be roles for α5 or β3 subunits in nAChRs expressed in type IIID (or type ID or IID) receptors.
Significance of the existence of multiple functional nAChR subtypes on VTA DAergic neurons
The current finding that there is diversity of functional nAChR expression just on the soma and minimal dendrites of acutely dissociated rat VTA DAergic neurons has many implications and possible interpretations. The VTA is the origin of several DAergic projections including those to the nucleus accumbens and prefrontal cortex. Perhaps the functional nAChR profile for these cells segregates with projection phenotype. A similar argument could be made about DAergic neuronal phenotype as influenced by neuronal inputs. Yet to be defined are how DAergic neuronal functional nAChR phenotypes change with development and ageing and whether or not they are plastic and responsive to environmental inputs and changes in behaviour as occur during initiation and development of drug dependence, especially if type ID and IID receptors actually lie on a continuum of nAChR phenotypes.
The current study demonstrates that the acutely dissociated neuronal preparation is a valuable complement to tissue slice, primary culture, and in vivo studies of nicotinic responses potentially relevant to nicotine dependence. We have been able to use this preparation to obtain heretofore unrealized detail in pharmacological characterization of freshly prepared neurons and their somatodendritic nAChRs. Not only do VTA DAergic neurons express multiple nAChR subtypes, but they also can be distinguished based on their functional nAChR phenotypes. Continuing studies of how properties of types ID, IID and IIID receptors respond to acute or chronic exposure to nicotine promises to improve our understanding of the roles of VTA nAChRs in nicotine reinforcement and dependence (Di Matteo et al. 2007), in VTA function, and in the control of DAergic signalling.
Acknowledgments
Work toward this project was supported by grants from the Arizona Biomedical Research Commission (0028 and 0057), the Institute for Mental Health Research, and Philip Morris International through their External Research Program, the Barrow Neurological Foundation (Robert and Gloria Wallace Foundation and Marjorie Newsome and Sandra Solheim Aiken funds), and National Institutes of Health grants NS40417 and DA15389. The authors thank Kevin Ellsworth for his assistance in preparing the manuscript.
Supplemental material
Online supplemental material for this paper can be accessed at:
http://jp.physoc.org/cgi/content/full/jphysiol.2008.162743/DC1
References
- Albuquerque EX, Alkondon M, Pereira EF, Castro NG, Schrattenholz A, Barbosa CT, Bonfante-Cabarcas R, Aracava Y, Eisenberg HM, Maelicke A. Properties of neuronal nicotinic acetylcholine receptors: pharmacological characterization and modulation of synaptic function. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1997;280:1117–1136. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alkondon M, Albuquerque EX. Diversity of nicotinic acetylcholine receptors in rat hippocampal neurons. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1993;265:1455–1473. I. Pharmacological and functional evidence for distinct structural subtypes. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Azam L, Chen Y, Leslie FM. Developmental regulation of nicotinic acetylcholine receptors within midbrain dopamine neurons. Neuroscience. 2007;144:1347–1360. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2006.11.011. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Azam L, Winzer-Serhan UH, Chen Y, Leslie FM. Expression of neuronal nicotinic acetylcholine receptor subunit mRNAs within midbrain dopamine neurons. J Comp Neurol. 2002;444:260–274. doi: 10.1002/cne.10138. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buisson B, Gopalakrishnan M, Arneric SP, Sullivan JP, Bertrand D. Human α4β2 neuronal nicotinic acetylcholine receptor in HEK 293 cells: a patch-clamp study. J Neurosci. 1996;16:7880–7891. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.16-24-07880.1996. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Champtiaux N, Gotti C, Cordero-Erausquin M, David DJ, Przybylski C, Lena C, Clementi F, Moretti M, Rossi FM, Le Novere N, McIntosh JM, Gardier AM, Changeux JP. Subunit composition of functional nicotinic receptors in dopaminergic neurons investigated with knock-out mice. J Neurosci. 2003;23:7820–7829. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.23-21-07820.2003. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Charpantier E, Barneoud P, Moser P, Besnard F, Sgard F. Nicotinic acetylcholine subunit mRNA expression in dopaminergic neurons of the rat substantia nigra and ventral tegmental area. Neuroreport. 1998;9:3097–3101. doi: 10.1097/00001756-199809140-00033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chavez-Noriega LE, Crona JH, Washburn MS, Urrutia A, Elliott KJ, Johnson EC. Pharmacological characterization of recombinant human neuronal nicotinic acetylcholine receptors hα2β2, hα2β4, hα3β2, hα3β4, hα4β2, hα4β4 and hα7 expressed in Xenopus oocytes. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1997;280:346–356. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corrigall WA, Coen KM, Adamson KL. Self-administered nicotine activates the mesolimbic dopamine system through the ventral tegmental area. Brain Res. 1994;653:278–284. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(94)90401-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dani JA, De Biasi M. Cellular mechanisms of nicotine addiction. Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 2001;70:439–446. doi: 10.1016/s0091-3057(01)00652-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dani JA, Heinemann S. Molecular and cellular aspects of nicotine abuse. Neuron. 1996;16:905–908. doi: 10.1016/s0896-6273(00)80112-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dani JA, Ji D, Zhou FM. Synaptic plasticity and nicotine addiction. Neuron. 2001;31:349–352. doi: 10.1016/s0896-6273(01)00379-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Di Matteo V, Pierucci M, Di Giovanni G, Benigno A, Esposito E. The neurobiological bases for the pharmacotherapy of nicotine addiction. Curr Pharmacol Des. 2007;13:1269–1284. doi: 10.2174/138161207780618920. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drenan RM, Grady SR, Whiteaker P, McClure-Begley T, McKinney S, Miwa JM, Bupp S, Heintz N, McIntosh JM, Bencherif M, Marks MJ, Lester HA. In vivo activation of midbrain dopamine neurons via sensitized, high-affinity α6 nicotinic acetylcholine receptors. Neuron. 2008;60:123–136. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2008.09.009. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eaton JB, Peng JH, Schroeder KM, George AA, Fryer JD, Krishnan C, Buhlman L, Kuo YP, Steinlein O, Lukas RJ. Characterization of human α4β2-nicotinic acetylcholine receptors stably and heterologously expressed in native nicotinic receptor-null SH-EP1 human epithelial cells. Mol Pharmacol. 2003;64:1283–1294. doi: 10.1124/mol.64.6.1283. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishihara K, Alkondon M, Montes JG, Albuquerque EX. Nicotinic responses in acutely dissociated rat hippocampal neurons and the selective blockade of fast-desensitizing nicotinic currents by lead. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1995;273:1471–1482. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klink R, de Kerchove d'Exaerde A, Zoli M, Changeux JP. Molecular and physiological diversity of nicotinic acetylcholine receptors in the midbrain dopaminergic nuclei. J Neurosci. 2001;21:1452–1463. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.21-05-01452.2001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Le Novere N, Corringer PJ, Changeux JP. The diversity of subunit composition in nAChRs: evolutionary origins, physiologic and pharmacologic consequences. J Neurobiol. 2002;53:447–456. doi: 10.1002/neu.10153. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Le Novere N, Zoli M, Changeux JP. Neuronal nicotinic receptor α 6 subunit mRNA is selectively concentrated in catecholaminergic nuclei of the rat brain. Eur J Neurosci. 1996;8:2428–2439. doi: 10.1111/j.1460-9568.1996.tb01206.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mameli-Engvall M, Evrard A, Pons S, Maskos U, Svensson TH, Changeux JP, Faure P. Hierarchical control of dopamine neuron-firing patterns by nicotinic receptors. Neuron. 2006;50:911–921. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2006.05.007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mansvelder HD, De Rover M, McGehee DS, Brussaard AB. Cholinergic modulation of dopaminergic reward areas: upstream and downstream targets of nicotine addiction. Eur J Pharmacol. 2003;480:117–123. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2003.08.099. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Margolis EB, Lock H, Hjelmstad GO, Fields HL. The ventral tegmental area revisited: is there an electrophysiological marker for dopaminergic neurons? J Physiol. 2006;577:907–924. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2006.117069. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marubio LM, Gardier AM, Durier S, David D, Klink R, Arroyo-Jimenez MM, McIntosh JM, Rossi F, Champtiaux N, Zoli M, Changeux JP. Effects of nicotine in the dopaminergic system of mice lacking the α4 subunit of neuronal nicotinic acetylcholine receptors. Eur J Neurosci. 2003;17:1329–1337. doi: 10.1046/j.1460-9568.2003.02564.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsubayashi H, Inoue A, Amano T, Seki T, Nakata Y, Sasa M, Sakai N. Involvement of α7- and α4β2-type postsynaptic nicotinic acetylcholine receptors in nicotine-induced excitation of dopaminergic neurons in the substantia nigra: a patch clamp and single-cell PCR study using acutely dissociated nigral neurons. Brain Res Mol Brain Res. 2004;129:1–7. doi: 10.1016/j.molbrainres.2004.06.040. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nisell M, Nomikos GG, Svensson TH. Systemic nicotine-induced dopamine release in the rat nucleus accumbens is regulated by nicotinic receptors in the ventral tegmental area. Synapse. 1994;16:36–44. doi: 10.1002/syn.890160105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Papke RL, Webster JC, Lippiello PM, Bencherif M, Francis MM. The activation and inhibition of human nicotinic acetylcholine receptor by RJR-2403 indicate a selectivity for the α4β2 receptor subtype. J Neurochem. 2000;75:204–216. doi: 10.1046/j.1471-4159.2000.0750204.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Picciotto MR, Zoli M, Rimondini R, Lena C, Marubio LM, Pich EM, Fuxe K, Changeux JP. Acetylcholine receptors containing the β2 subunit are involved in the reinforcing properties of nicotine. Nature. 1998;391:173–177. doi: 10.1038/34413. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pidoplichko VI, DeBiasi M, Williams JT, Dani JA. Nicotine activates and desensitizes midbrain dopamine neurons. Nature. 1997;390:401–404. doi: 10.1038/37120. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pidoplichko VI, Noguchi J, Areola OO, Liang Y, Peterson J, Zhang T, Dani JA. Nicotinic cholinergic synaptic mechanisms in the ventral tegmental area contribute to nicotine addiction. Learning Memory. 2004;11:60–69. doi: 10.1101/lm.70004. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pontieri FE, Tanda G, Orzi F, Di Chiara G. Effects of nicotine on the nucleus accumbens and similarity to those of addictive drugs. Nature. 1996;382:255–257. doi: 10.1038/382255a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spanagel R, Weiss F. The dopamine hypothesis of reward: past and current status. Trends Neurosci. 1999;22:521–527. doi: 10.1016/s0166-2236(99)01447-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sziraki I, Sershen H, Hashim A, Lajtha A. Receptors in the ventral tegmental area mediating nicotine-induced dopamine release in the nucleus accumbens. Neurochem Res. 2002;27:253–261. doi: 10.1023/a:1014844823534. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tapper AR, McKinney SL, Nashmi R, Schwarz J, Deshpande P, Labarca C, Whiteaker P, Marks MJ, Collins AC, Lester HA. Nicotine activation of α4* receptors: sufficient for reward, tolerance, and sensitization. Science. 2004;306:1029–1032. doi: 10.1126/science.1099420. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wada E, Wada K, Boulter J, Deneris E, Heinemann S, Patrick J, Swanson LW. Distribution of α 2, α 3, α 4, and β 2 neuronal nicotinic receptor subunit mRNAs in the central nervous system: a hybridization histochemical study in the rat. J Comp Neurol. 1989;284:314–335. doi: 10.1002/cne.902840212. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White FJ. A behavioral/systems approach to the neuroscience of drug addiction. J Neurosci. 2002;22:3303–3305. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.22-09-03303.2002. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wonnacott S, Kaiser S, Mogg A, Soliakov L, Jones IW. Presynaptic nicotinic receptors modulating dopamine release in the rat striatum. Eur J Pharmacol. 2000;393:51–58. doi: 10.1016/s0014-2999(00)00005-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wooltorton JR, Pidoplichko VI, Broide RS, Dani JA. Differential desensitization and distribution of nicotinic acetylcholine receptor subtypes in midbrain dopamine areas. J Neurosci. 2003;23:3176–3185. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.23-08-03176.2003. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu J, George AA, Schroeder KM, Xu L, Marxer-Miller S, Lucero L, Lukas RJ. Electrophysiological, pharmacological, and molecular evidence for α7-nicotinic acetylcholine receptors in rat midbrain dopamine neurons. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2004;311:80–91. doi: 10.1124/jpet.104.070417. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhao L, Kuo YP, George AA, Peng JH, Purandare MS, Schroeder KM, Lukas RJ, Wu J. Functional properties of homomeric, human α7-nicotinic acetylcholine receptors heterologously expressed in the SH-EP1 human epithelial cell line. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2003;305:1132–1141. doi: 10.1124/jpet.103.048777. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zoli M, Lena C, Picciotto MR, Changeux JP. Identification of four classes of brain nicotinic receptors using β2 mutant mice. J Neurosci. 1998;18:4461–4472. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.18-12-04461.1998. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.