Abstract
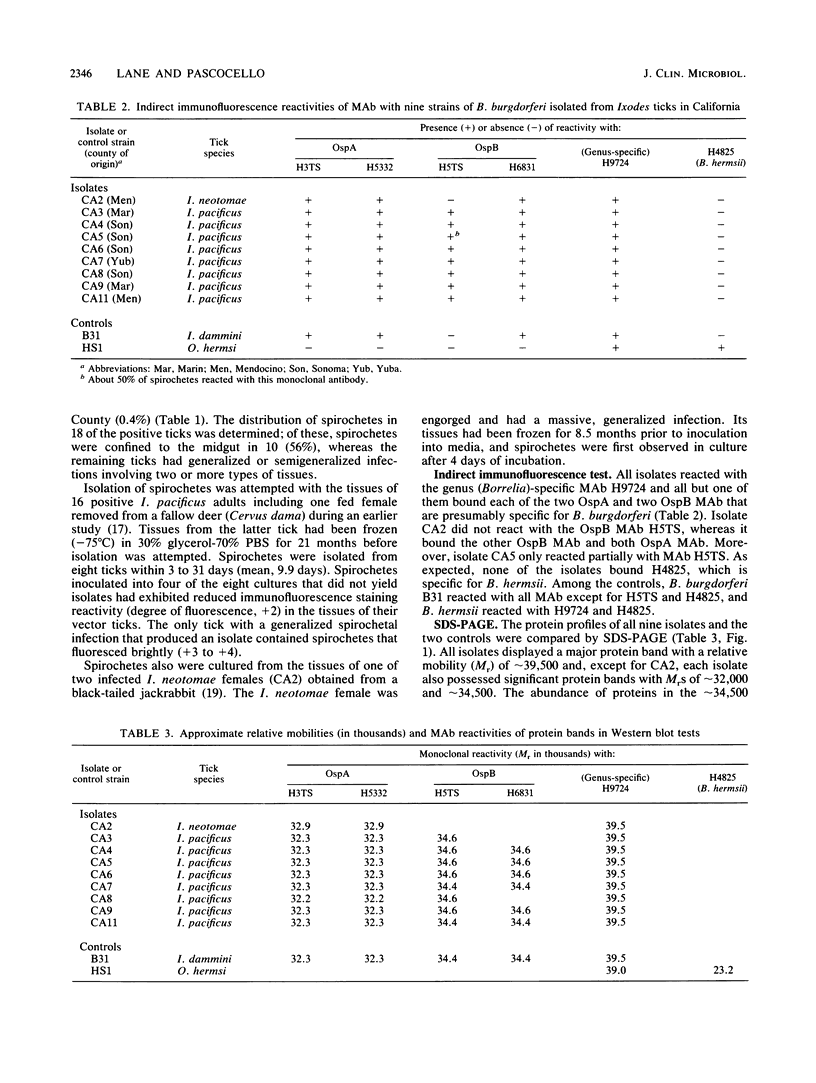
Twenty (1.4%) of 1,421 adult Ixodes pacificus ticks and 2 (20%) of 10 adult Ixodes neotomae ticks collected in five counties of northern California were found to contain spirochetes by direct immunofluorescence examination of their tissues with a polyvalent conjugate. Borreliae isolated from the tissues of nine of these ticks (I. pacificus, 8; I. neotomae, 1) were identified as Borrelia burgdorferi with specific monoclonal antibodies and characterized further by polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis and Western blot (immunoblot) analyses. The isolate from I. neotomae was the first to be characterized from a tick other than I. pacificus in western North America. All strains were relatively homogeneous with respect to the kind of OspA proteins they produced, whereas they were heterogeneous with regard to their OspB proteins and to several low-molecular-weight proteins in the 21,500-to-24,000 region. Significant phenotypic variation was observed among isolates obtained within and between populations of I. pacificus. This investigation nearly doubles the number of isolates of B. burgdorferi that have been characterized from ixodid ticks in the far western United States.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson J. F., Johnson R. C., Magnarelli L. A., Hyde F. W. Involvement of birds in the epidemiology of the Lyme disease agent Borrelia burgdorferi. Infect Immun. 1986 Feb;51(2):394–396. doi: 10.1128/iai.51.2.394-396.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson J. F., Magnarelli L. A., LeFebvre R. B., Andreadis T. G., McAninch J. B., Perng G. C., Johnson R. C. Antigenically variable Borrelia burgdorferi isolated from cottontail rabbits and Ixodes dentatus in rural and urban areas. J Clin Microbiol. 1989 Jan;27(1):13–20. doi: 10.1128/jcm.27.1.13-20.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson J. F., Magnarelli L. A., McAninch J. B. New Borrelia burgdorferi antigenic variant isolated from Ixodes dammini from upstate New York. J Clin Microbiol. 1988 Oct;26(10):2209–2212. doi: 10.1128/jcm.26.10.2209-2212.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Asbrink E., Olsson I. Clinical manifestations of erythema chronicum migrans Afzelius in 161 patients. A comparison with Lyme disease. Acta Derm Venereol. 1985;65(1):43–52. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barbour A. G., Hayes S. F., Heiland R. A., Schrumpf M. E., Tessier S. L. A Borrelia-specific monoclonal antibody binds to a flagellar epitope. Infect Immun. 1986 May;52(2):549–554. doi: 10.1128/iai.52.2.549-554.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barbour A. G., Heiland R. A., Howe T. R. Heterogeneity of major proteins in Lyme disease borreliae: a molecular analysis of North American and European isolates. J Infect Dis. 1985 Sep;152(3):478–484. doi: 10.1093/infdis/152.3.478. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barbour A. G. Isolation and cultivation of Lyme disease spirochetes. Yale J Biol Med. 1984 Jul-Aug;57(4):521–525. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barbour A. G., Schrumpf M. E. Polymorphisms of major surface proteins of Borrelia burgdorferi. Zentralbl Bakteriol Mikrobiol Hyg A. 1986 Dec;263(1-2):83–91. doi: 10.1016/s0176-6724(86)80107-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barbour A. G., Tessier S. L., Hayes S. F. Variation in a major surface protein of Lyme disease spirochetes. Infect Immun. 1984 Jul;45(1):94–100. doi: 10.1128/iai.45.1.94-100.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barbour A. G., Tessier S. L., Stoenner H. G. Variable major proteins of Borrellia hermsii. J Exp Med. 1982 Nov 1;156(5):1312–1324. doi: 10.1084/jem.156.5.1312. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barbour A. G., Tessier S. L., Todd W. J. Lyme disease spirochetes and ixodid tick spirochetes share a common surface antigenic determinant defined by a monoclonal antibody. Infect Immun. 1983 Aug;41(2):795–804. doi: 10.1128/iai.41.2.795-804.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bissett M. L., Hill W. Characterization of Borrelia burgdorferi strains isolated from Ixodes pacificus ticks in California. J Clin Microbiol. 1987 Dec;25(12):2296–2301. doi: 10.1128/jcm.25.12.2296-2301.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burgdorfer W., Lane R. S., Barbour A. G., Gresbrink R. A., Anderson J. R. The western black-legged tick, Ixodes pacificus: a vector of Borrelia burgdorferi. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1985 Sep;34(5):925–930. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1985.34.925. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson R. C., Marek N., Kodner C. Infection of Syrian hamsters with Lyme disease spirochetes. J Clin Microbiol. 1984 Dec;20(6):1099–1101. doi: 10.1128/jcm.20.6.1099-1101.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lane R. S., Burgdorfer W. Potential role of native and exotic deer and their associated ticks (Acari: Ixodidae) in the ecology of Lyme disease in California, USA. Zentralbl Bakteriol Mikrobiol Hyg A. 1986 Dec;263(1-2):55–64. doi: 10.1016/s0176-6724(86)80103-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lane R. S., Burgdorfer W. Spirochetes in mammals and ticks (Acari: Ixodidae) from a focus of Lyme borreliosis in California. J Wildl Dis. 1988 Jan;24(1):1–9. doi: 10.7589/0090-3558-24.1.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lane R. S., Burgdorfer W. Transovarial and transstadial passage of Borrelia burgdorferi in the western black-legged tick, Ixodes pacificus (Acari: Ixodidae). Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1987 Jul;37(1):188–192. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1987.37.188. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lane R. S., Lavoie P. E. Lyme borreliosis in California. Acarological, clinical, and epidemiological studies. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1988;539:192–203. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1988.tb31853.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lane R. S., Manweiler S. A. Borrelia coriaceae in its tick vector, Ornithodoros coriaceus (Acari: Argasidae), with emphasis on transstadial and transovarial infection. J Med Entomol. 1988 May;25(3):172–177. doi: 10.1093/jmedent/25.3.172. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Naversen D. N., Gardner L. W. Erythema chronicum migrans in America. Arch Dermatol. 1978 Feb;114(2):253–254. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rawlings J. A. Lyme disease in Texas. Zentralbl Bakteriol Mikrobiol Hyg A. 1987 Feb;263(3):483–487. doi: 10.1016/s0176-6724(87)80115-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwan T. G., Burgdorfer W. Antigenic changes of Borrelia burgdorferi as a result of in vitro cultivation. J Infect Dis. 1987 Nov;156(5):852–853. doi: 10.1093/infdis/156.5.852-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanek G., Wewalka G., Groh V., Neumann R., Kristoferitsch W. Differences between Lyme disease and European arthropod-borne Borrelia infections. Lancet. 1985 Feb 16;1(8425):401–401. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(85)91424-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steere A. C., Malawista S. E., Bartenhagen N. H., Spieler P. N., Newman J. H., Rahn D. W., Hutchinson G. J., Green J., Snydman D. R., Taylor E. The clinical spectrum and treatment of Lyme disease. Yale J Biol Med. 1984 Jul-Aug;57(4):453–461. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilske B., Preac-Mursic V., Schierz G. Antigenic heterogeneity of European Borrelia burgdorferi strains isolated from patients and ticks. Lancet. 1985 May 11;1(8437):1099–1099. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(85)92396-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilske B., Preac-Mursic V., Schierz G., Busch K. V. Immunochemical and immunological analysis of European Borrelia burgdorferi strains. Zentralbl Bakteriol Mikrobiol Hyg A. 1986 Dec;263(1-2):92–102. doi: 10.1016/s0176-6724(86)80108-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilske B., Preac-Mursic V., Schierz G., Gueye W., Herzer P., Weber K. Immunochemische Analyse der Immunantwort bei Spätmanifestationen der Lyme Borreliose. Zentralbl Bakteriol Mikrobiol Hyg A. 1988 Mar;267(4):549–558. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilske B., Preac-Mursic V., Schierz G., Kühbeck R., Barbour A. G., Kramer M. Antigenic variability of Borrelia burgdorferi. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1988;539:126–143. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1988.tb31846.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



