Abstract
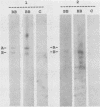
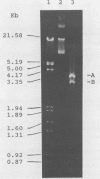
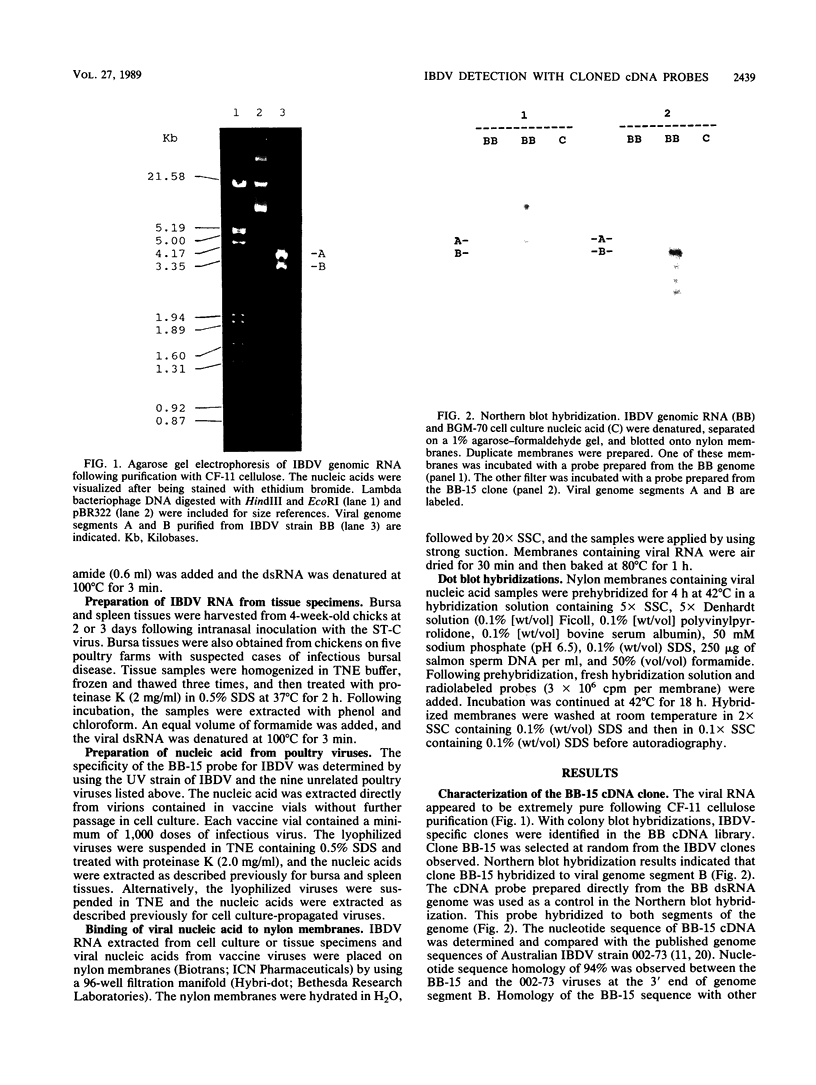
A molecular clone representing 445 base pairs at the 3' end of infectious bursal disease virus (IBDV) genome segment B was used in a dot blot hybridization assay to detect viral RNA from cell culture and from chicken bursa and spleen tissue specimens. The cloned nucleotide sequence represents approximately 14% of the virus-encoded polymerase (VP-1) gene. The lower detection limit of radiolabeled probes prepared from this clone was 0.1 ng of IBDV double-stranded RNA. The probe had broad specificity and was used to detect four serotype 1 IBDV strains and one serotype 2 IBDV strain. This probe, however, did not cross-react with nucleic acid extracted from nine unrelated poultry viruses. A rapid procedure for isolation of IBDV genomic RNA from bursa and spleen tissue specimens was developed and used with the dot blot hybridization assay to detect IBDV strains in tissue samples from experimentally infected and commercially reared chickens.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Azad A. A., Barrett S. A., Fahey K. J. The characterization and molecular cloning of the double-stranded RNA genome of an Australian strain of infectious bursal disease virus. Virology. 1985 May;143(1):35–44. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(85)90094-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Becht H., Müller H., Müller H. K. Comparative studies on structural and antigenic properties of two serotypes of infectious bursal disease virus. J Gen Virol. 1988 Mar;69(Pt 3):631–640. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-69-3-631. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birnboim H. C., Doly J. A rapid alkaline extraction procedure for screening recombinant plasmid DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Nov 24;7(6):1513–1523. doi: 10.1093/nar/7.6.1513. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diaz-Ruiz J. R., Kaper J. M. Isolation of viral double-stranded RNAs using a LiCl fractionation procedure. Prep Biochem. 1978;8(1):1–17. doi: 10.1080/00327487808068215. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fahey K. J., O'Donnell I. J., Bagust T. J. Antibody to the 32K structural protein of infectious bursal disease virus neutralizes viral infectivity in vitro and confers protection on young chickens. J Gen Virol. 1985 Dec;66(Pt 12):2693–2702. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-66-12-2693. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grunstein M., Wallis J. Colony hybridization. Methods Enzymol. 1979;68:379–389. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(79)68027-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gubler U., Hoffman B. J. A simple and very efficient method for generating cDNA libraries. Gene. 1983 Nov;25(2-3):263–269. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(83)90230-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang M. T., Manning D. S., Warner M., Stephens E. B., Leong J. C. A physical map of the viral genome for infectious pancreatic necrosis virus Sp: analysis of cell-free translation products derived from viral cDNA clones. J Virol. 1986 Dec;60(3):1002–1011. doi: 10.1128/jvi.60.3.1002-1011.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hudson P. J., McKern N. M., Power B. E., Azad A. A. Genomic structure of the large RNA segment of infectious bursal disease virus. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Jun 25;14(12):5001–5012. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.12.5001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackwood D. H., Saif Y. M. Antigenic diversity of infectious bursal disease viruses. Avian Dis. 1987 Oct-Dec;31(4):766–770. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackwood D. H., Saif Y. M., Hughes J. H. Replication of infectious bursal disease virus in continuous cell lines. Avian Dis. 1987 Apr-Jun;31(2):370–375. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackwood D. J., Saif Y. M., Hughes J. H. Characteristics and serologic studies of two serotypes of infectious bursal disease virus in turkeys. Avian Dis. 1982 Oct-Dec;26(4):871–882. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackwood D. J., Saif Y. M., Hughes J. H. Nucleic acid and structural proteins of infectious bursal disease virus isolates belonging to serotypes I and II. Avian Dis. 1984 Oct-Dec;28(4):990–1006. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mellor E. J., Brown F., Harris T. J. Analysis of the secondary structure of the poly(C) tract in foot-and-mouth disease virus RNAs. J Gen Virol. 1985 Sep;66(Pt 9):1919–1929. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-66-9-1919. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morgan M. M., Macreadie I. G., Harley V. R., Hudson P. J., Azad A. A. Sequence of the small double-stranded RNA genomic segment of infectious bursal disease virus and its deduced 90-kDa product. Virology. 1988 Mar;163(1):240–242. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(88)90258-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rigby P. W., Dieckmann M., Rhodes C., Berg P. Labeling deoxyribonucleic acid to high specific activity in vitro by nick translation with DNA polymerase I. J Mol Biol. 1977 Jun 15;113(1):237–251. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90052-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shockley L. J., Kapke P. A., Lapps W., Brian D. A., Potgieter L. N., Woods R. Diagnosis of porcine and bovine enteric coronavirus infections using cloned cDNA probes. J Clin Microbiol. 1987 Sep;25(9):1591–1596. doi: 10.1128/jcm.25.9.1591-1596.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tabor S., Richardson C. C. DNA sequence analysis with a modified bacteriophage T7 DNA polymerase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jul;84(14):4767–4771. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.14.4767. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tenover F. C. Diagnostic deoxyribonucleic acid probes for infectious diseases. Clin Microbiol Rev. 1988 Jan;1(1):82–101. doi: 10.1128/cmr.1.1.82. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas P. S. Hybridization of denatured RNA and small DNA fragments transferred to nitrocellulose. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Sep;77(9):5201–5205. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.9.5201. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yanisch-Perron C., Vieira J., Messing J. Improved M13 phage cloning vectors and host strains: nucleotide sequences of the M13mp18 and pUC19 vectors. Gene. 1985;33(1):103–119. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(85)90120-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]