Abstract
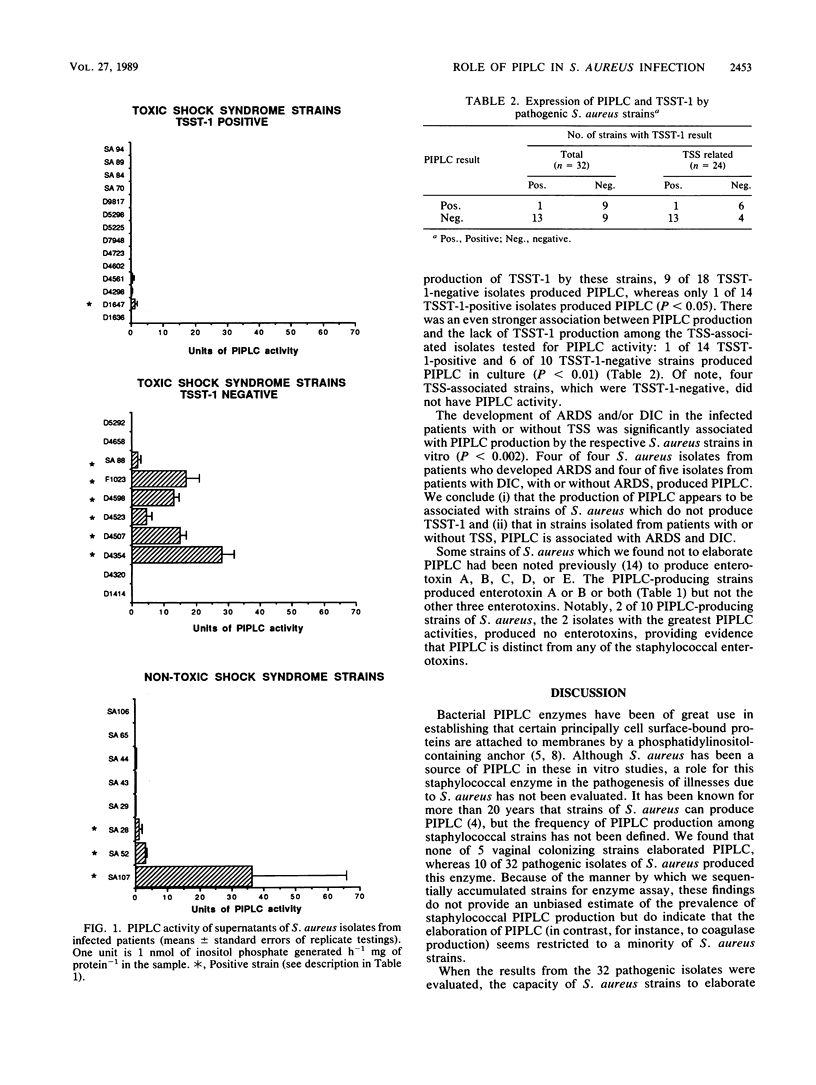
Phosphatidylinositol-specific phospholipase C (PIPLC), an enzyme that can specifically release phosphatidylinositol-linked proteins from host cells, is one of the extracellular enzymes produced by Staphylococcus aureus. To investigate whether PIPLC might be a virulence factor, we assessed PIPLC production by S. aureus strains that had been isolated from healthy carriers and from infected patients with or without toxic shock syndrome. Although none of five vaginal isolates from healthy women was a PIPLC producer, only 10 of 32 selected pathogenic strains that caused significant infections or toxic shock syndrome elaborated PIPLC enzyme activity. Seven of 24 toxic-shock-associated strains, compared with 3 of 8 non-toxic-shock-associated strains, were positive for PIPLC. The majority of strains that produced PIPLC were negative for toxic shock syndrome toxin 1 (P less than 0.05); this association between PIPLC production and strains negative for toxic shock syndrome toxin 1 was even stronger among strains isolated only from patients with toxic shock syndrome (P less than 0.01). Among all 32 pathogenic isolates, PIPLC-producing S. aureus strains were isolated from four of four patients developing adult respiratory distress syndrome and four of five patients with disseminated intravascular coagulation, suggesting a significant association between PIPLC production and adult respiratory distress syndrome and/or disseminated intravascular coagulation (P less than 0.002). On the basis of these results, we propose that PIPLC is a virulence factor of S. aureus and is implicated in the development of adult respiratory distress syndrome and disseminated intravascular coagulation.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Crass B. A., Bergdoll M. S. Involvement of staphylococcal enterotoxins in nonmenstrual toxic shock syndrome. J Clin Microbiol. 1986 Jun;23(6):1138–1139. doi: 10.1128/jcm.23.6.1138-1139.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crass B. A., Bergdoll M. S. Toxin involvement in toxic shock syndrome. J Infect Dis. 1986 May;153(5):918–926. doi: 10.1093/infdis/153.5.918. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davitz M. A., Gurnett A. M., Low M. G., Turner M. J., Nussenzweig V. Decay-accelerating factor (DAF) shares a common carbohydrate determinant with the variant surface glycoprotein (VSG) of the African Trypanosoma brucei. J Immunol. 1987 Jan 15;138(2):520–523. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doery H. M., Magnusson B. J., Gulasekharam J., Pearson J. E. The properties of phospholipase enzymes in staphylococcal toxins. J Gen Microbiol. 1965 Aug;40(2):283–296. doi: 10.1099/00221287-40-2-283. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferguson M. A., Williams A. F. Cell-surface anchoring of proteins via glycosyl-phosphatidylinositol structures. Annu Rev Biochem. 1988;57:285–320. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.57.070188.001441. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hänsch G. M., Weller P. F., Nicholson-Weller A. Release of C8 binding protein (C8bp) from the cell membrane by phosphatidylinositol-specific phospholipase C. Blood. 1988 Sep;72(3):1089–1092. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Langlois P. F., Gawryl M. S. Complement activation occurs through both classical and alternative pathways prior to onset and resolution of adult respiratory distress syndrome. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1988 May;47(2):152–163. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(88)90068-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Low M. G., Finean J. B. The action of phosphatidylinositol-specific phospholipases C on membranes. Biochem J. 1976 Jan 15;154(1):203–208. doi: 10.1042/bj1540203. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Medof M. E., Walter E. I., Roberts W. L., Haas R., Rosenberry T. L. Decay accelerating factor of complement is anchored to cells by a C-terminal glycolipid. Biochemistry. 1986 Nov 4;25(22):6740–6747. doi: 10.1021/bi00370a003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Musch M. W., Siegel M. I. Antigen-stimulated metabolism of inositol phospholipids in the cloned murine mast-cell line MC9. Biochem J. 1986 Feb 15;234(1):205–212. doi: 10.1042/bj2340205. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicholson-Weller A., Burge J., Fearon D. T., Weller P. F., Austen K. F. Isolation of a human erythrocyte membrane glycoprotein with decay-accelerating activity for C3 convertases of the complement system. J Immunol. 1982 Jul;129(1):184–189. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Onderdonk A. B., Zamarchi G. R., Walsh J. A., Mellor R. D., Muñoz A., Kass E. H. Methods for quantitative and qualitative evaluation of vaginal microflora during menstruation. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1986 Feb;51(2):333–339. doi: 10.1128/aem.51.2.333-339.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parsonnet J., Gillis Z. A., Pier G. B. Induction of interleukin-1 by strains of Staphylococcus aureus from patients with nonmenstrual toxic shock syndrome. J Infect Dis. 1986 Jul;154(1):55–63. doi: 10.1093/infdis/154.1.55. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schönermark S., Rauterberg E. W., Shin M. L., Löke S., Roelcke D., Hänsch G. M. Homologous species restriction in lysis of human erythrocytes: a membrane-derived protein with C8-binding capacity functions as an inhibitor. J Immunol. 1986 Mar 1;136(5):1772–1776. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seidenfeld J. J., Pohl D. F., Bell R. C., Harris G. D., Johanson W. G., Jr Incidence, site, and outcome of infections in patients with the adult respiratory distress syndrome. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1986 Jul;134(1):12–16. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1986.134.1.12. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watkins J. Complement and clinical intervention. Ann Fr Anesth Reanim. 1985;4(2):129–132. doi: 10.1016/S0750-7658(85)80186-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zalman L. S., Wood L. M., Müller-Eberhard H. J. Isolation of a human erythrocyte membrane protein capable of inhibiting expression of homologous complement transmembrane channels. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Sep;83(18):6975–6979. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.18.6975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


