Abstract
Isoenzyme profiles were obtained following polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis of crude extracts of Candida albicans and C. tropicalis. The two species were separated by distinct isoenzyme patterns. Within each species, variations were found for several isoenzymes. This allowed the development of a method for biotyping these fungi. Isoenzyme patterns of the sucrose-negative variants "C. stellatoidea" and "C. paratropicalis Baker, Salkin, Pincus, and D'Amato" were obtained and subjected to cluster analysis. This procedure failed to place the variants into clusters that were clearly distinct from the conventional sucrose-positive strains. All sucrose-negative strains were found to have alpha-glucosidase activity. There was an almost complete lack of heterogeneity in the isoenzyme patterns of 11 C. stellatoidea type I strains.
Full text
PDF




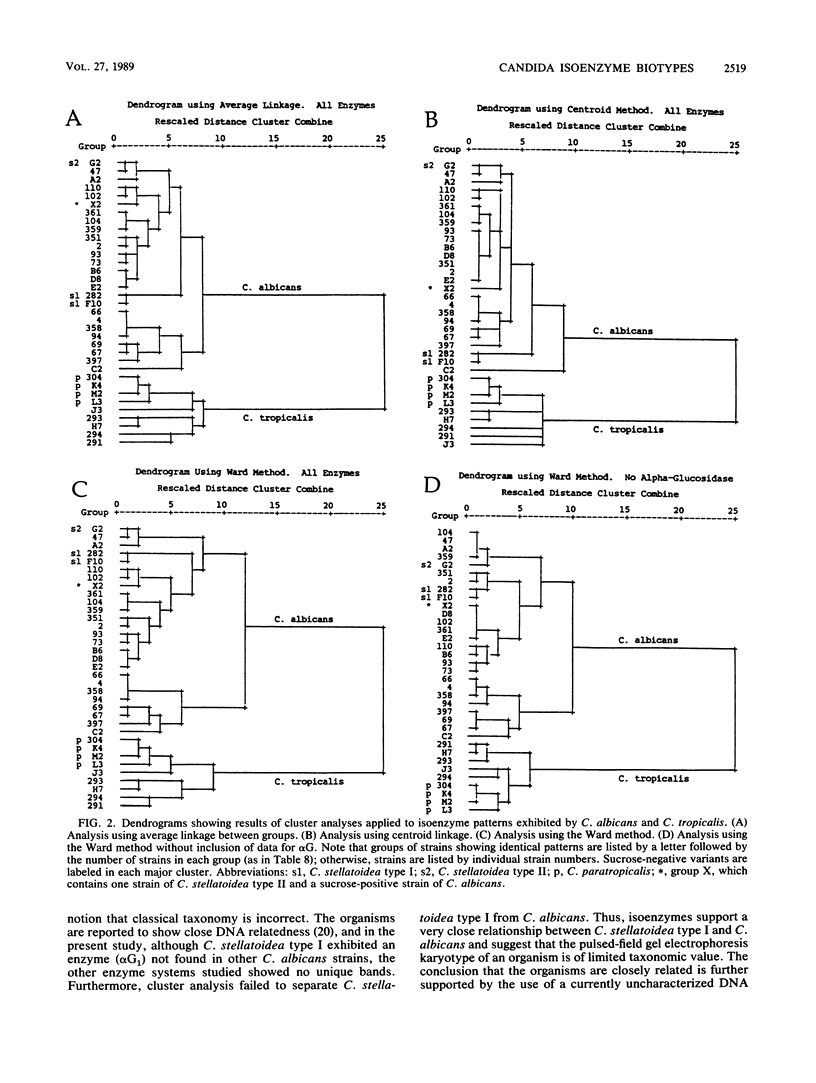


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Burnie J., Matthews R. C. Immunoblot analysis: a new method for fingerprinting hospital pathogens. J Immunol Methods. 1987 Jun 26;100(1-2):41–46. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(87)90171-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cutler J. E., Glee P. M., Horn H. L. Candida albicans- and Candida stellatoidea-specific DNA fragment. J Clin Microbiol. 1988 Sep;26(9):1720–1724. doi: 10.1128/jcm.26.9.1720-1724.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gabriel O., Wang S. F. Determination of enzymatic activity in polyacrylamide gels. I. Enzymes catalyzing the conversion of nonreducing substrates to reducing products. Anal Biochem. 1969 Mar;27(3):545–554. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(69)90068-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HASENCLEVER H. F., MITCHELL W. O. Antigenic studies of Candida. I. Observation of two antigenic groups in Candida albicans. J Bacteriol. 1961 Oct;82:570–573. doi: 10.1128/jb.82.4.570-573.1961. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hubbard M. J., Markie D., Poulter R. T. Isolation and morphological characterization of a mycelial mutant of Candida albicans. J Bacteriol. 1986 Jan;165(1):61–65. doi: 10.1128/jb.165.1.61-65.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones M. G., Noble W. C. An electrophoretic study of enzymes as a tool in the taxonomy of the dermatophytes. J Gen Microbiol. 1982 May;128(5):1101–1107. doi: 10.1099/00221287-128-5-1101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kwon-Chung K. J., Riggsby W. S., Uphoff R. A., Hicks J. B., Whelan W. L., Reiss E., Magee B. B., Wickes B. L. Genetic differences between type I and type II Candida stellatoidea. Infect Immun. 1989 Feb;57(2):527–532. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.2.527-532.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kwon-Chung K. J., Wickes B. L., Merz W. G. Association of electrophoretic karyotype of Candida stellatoidea with virulence for mice. Infect Immun. 1988 Jul;56(7):1814–1819. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.7.1814-1819.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehmann P. F., Hsiao C. B., Salkin I. F. Protein and enzyme electrophoresis profiles of selected Candida species. J Clin Microbiol. 1989 Mar;27(3):400–404. doi: 10.1128/jcm.27.3.400-404.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Magee B. B., D'Souza T. M., Magee P. T. Strain and species identification by restriction fragment length polymorphisms in the ribosomal DNA repeat of Candida species. J Bacteriol. 1987 Apr;169(4):1639–1643. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.4.1639-1643.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Magee B. B., Magee P. T. Electrophoretic karyotypes and chromosome numbers in Candida species. J Gen Microbiol. 1987 Feb;133(2):425–430. doi: 10.1099/00221287-133-2-425. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mason M. M., Lasker B. A., Riggsby W. S. Molecular probe for identification of medically important Candida species and Torulopsis glabrata. J Clin Microbiol. 1987 Mar;25(3):563–566. doi: 10.1128/jcm.25.3.563-566.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCreight M. C., Warnock D. W. Enhanced differentiation of isolates of Candida albicans using a modified resistogram method. Mykosen. 1982 Nov;25(11):589–598. doi: 10.1111/j.1439-0507.1982.tb01926.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meloni B. P., Lymbery A. J., Thompson R. C. Isoenzyme electrophoresis of 30 isolates of Giardia from humans and felines. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1988 Jan;38(1):65–73. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1988.38.65. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merz W. G., Connelly C., Hieter P. Variation of electrophoretic karyotypes among clinical isolates of Candida albicans. J Clin Microbiol. 1988 May;26(5):842–845. doi: 10.1128/jcm.26.5.842-845.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milkman R. Electrophoretic variation in Escherichia coli from natural sources. Science. 1973 Dec 7;182(4116):1024–1026. doi: 10.1126/science.182.4116.1024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Odds F. C., Abbott A. B. A simple system for the presumptive identification of Candida albicans and differentiation of strains within the species. Sabouraudia. 1980 Dec;18(4):301–317. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Odds F. C., Abbott A. B. Modification and extension of tests for differentiation of Candida species and strains. Sabouraudia. 1983 Mar;21(1):79–81. doi: 10.1080/00362178385380111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Odds F. C. Biotyping of medically important fungi. Curr Top Med Mycol. 1985;1:155–171. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4613-9547-8_6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Polonelli L., Archibusacci C., Sestito M., Morace G. Killer system: a simple method for differentiating Candida albicans strains. J Clin Microbiol. 1983 May;17(5):774–780. doi: 10.1128/jcm.17.5.774-780.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Román M. C., Linares Sicilia M. J. Preliminary investigation of Candida albicans biovars. J Clin Microbiol. 1983 Aug;18(2):430–431. doi: 10.1128/jcm.18.2.430-431.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scherer S., Stevens D. A. A Candida albicans dispersed, repeated gene family and its epidemiologic applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Mar;85(5):1452–1456. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.5.1452. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scherer S., Stevens D. A. Application of DNA typing methods to epidemiology and taxonomy of Candida species. J Clin Microbiol. 1987 Apr;25(4):675–679. doi: 10.1128/jcm.25.4.675-679.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slutsky B., Buffo J., Soll D. R. High-frequency switching of colony morphology in Candida albicans. Science. 1985 Nov 8;230(4726):666–669. doi: 10.1126/science.3901258. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soll D. R., Langtimm C. J., McDowell J., Hicks J., Galask R. High-frequency switching in Candida strains isolated from vaginitis patients. J Clin Microbiol. 1987 Sep;25(9):1611–1622. doi: 10.1128/jcm.25.9.1611-1622.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spieth P. T. Population genetics of allozyme variation in Neurospora intermedia. Genetics. 1975 Aug;80(4):785–805. doi: 10.1093/genetics/80.4.785. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warnock D. W., Speller D. C., Day J. K., Farrell A. J. Resistogram method for differentiation of strains of Candida albicans. J Appl Bacteriol. 1979 Jun;46(3):571–578. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2672.1979.tb00857.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williamson M. I., Samaranayake L. P., MacFarlane T. W. Biotypes of oral Candida albicans and Candida tropicalis isolates. J Med Vet Mycol. 1986 Feb;24(1):81–84. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wills J. W., Troutman W. B., Riggsby W. S. Circular mitochondrial genome of Candida albicans contains a large inverted duplication. J Bacteriol. 1985 Oct;164(1):7–13. doi: 10.1128/jb.164.1.7-13.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



