Abstract
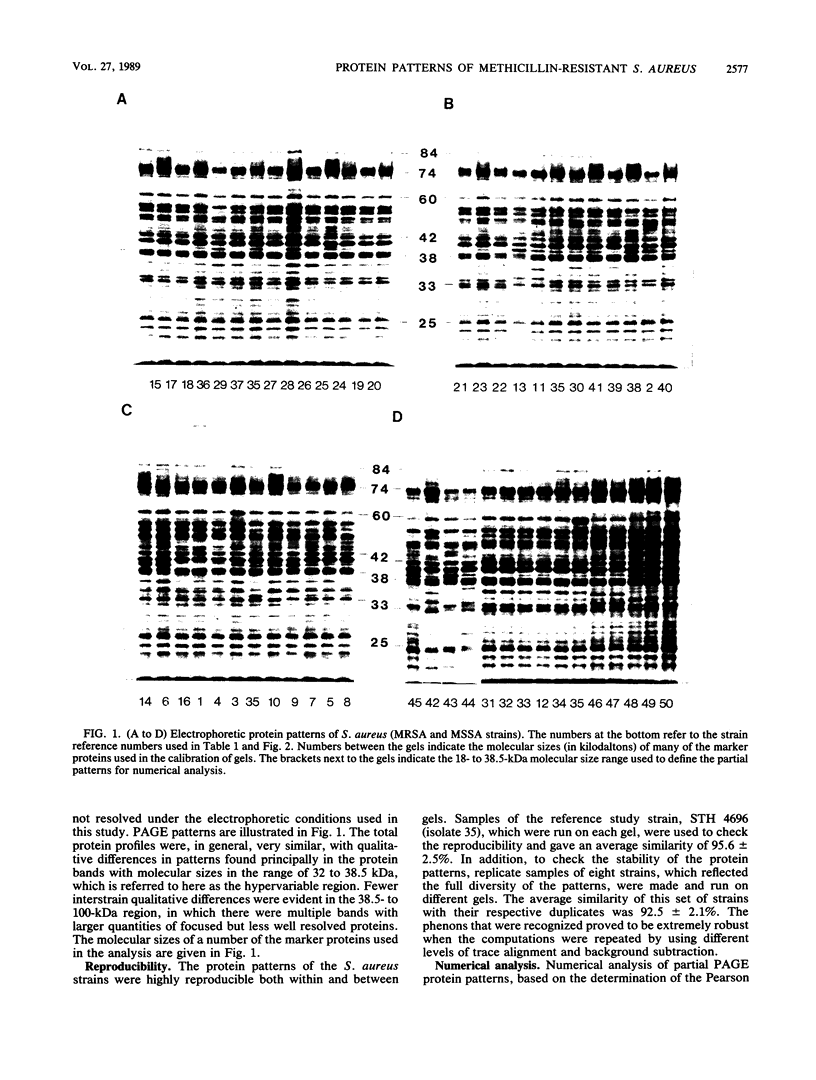
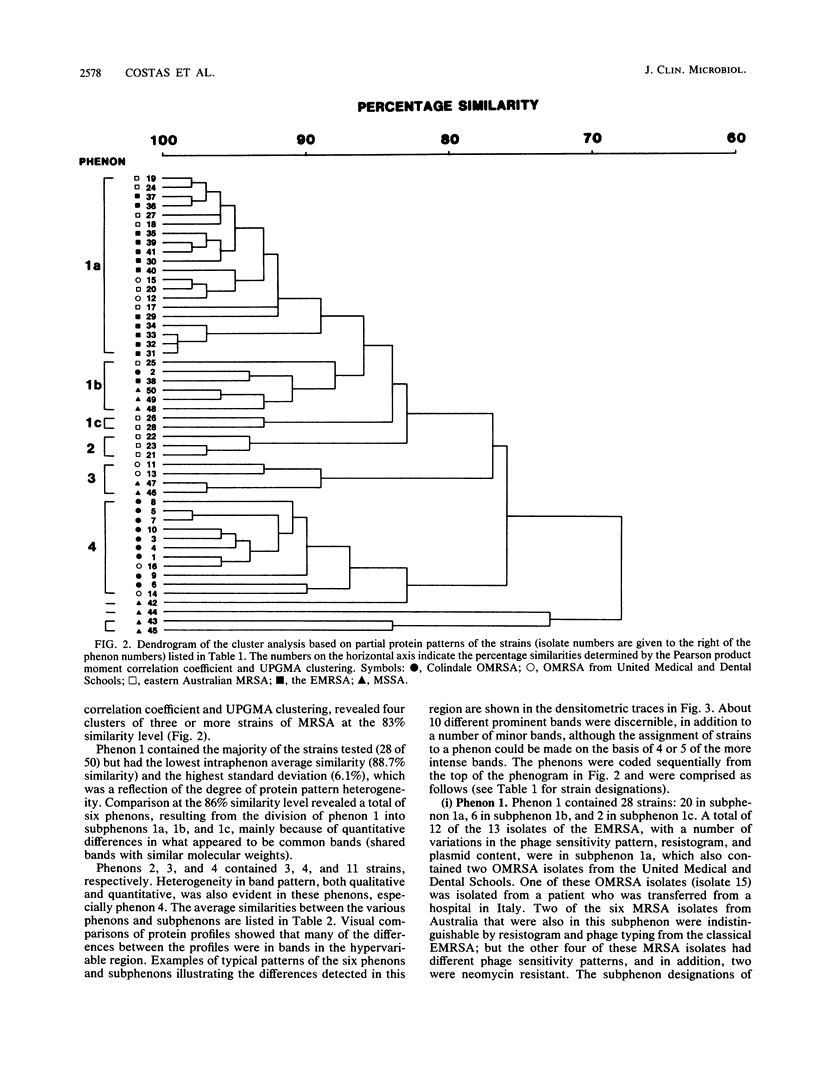
A total of 50 strains of Staphylococcus aureus, including 41 methicillin-resistant S. aureus (MRSA) strains, were characterized by one-dimensional sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis of whole-cell proteins. The protein patterns contained 40-50 discrete bands and were highly reproducible. Partial patterns were used as the basis of a computer-assisted numerical analysis. The MRSA strains clustered into four phenons at the 83% similarity level; and further division of phenon 1, at the 86% similarity level, resulted in a total of six clusters. All of the MRSA isolates from an MRSA epidemic in the United Kingdom were found to cluster in phenon 1 together with 9 of the 12 MRSA isolates from eastern Australia and 3 other MRSA isolates from the United Kingdom. The remaining three eastern Australian isolates clustered separately in phenon 2. Phenon 3 appeared to be exclusive to strains that were both susceptible and resistant to methicillin and that reacted with group V phages, and phenon 4 comprised 11 isolates, all of which were other MRSA isolates from the United Kingdom. We conclude that computer-assisted numerical analysis by high-resolution sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis of whole-cell proteins provides additional criteria for the study of the epidemiology and the evolution of MRSA.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ASHESHOV E. H., RIPPON J. E. Changes in typing pattern of phage-type 80 staphylococci. J Gen Microbiol. 1959 Jun;20(3):634–643. doi: 10.1099/00221287-20-3-634. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Asheshov E. H., Coe A. W., Porthouse A. Properties of strains of Staphylococcus aureus in the 94, 96 complex. J Med Microbiol. 1977 May;10(2):171–178. doi: 10.1099/00222615-10-2-171. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clink J., Pennington T. H. Staphylococcal whole-cell polypeptide analysis: evaluation as a taxonomic and typing tool. J Med Microbiol. 1987 Feb;23(1):41–44. doi: 10.1099/00222615-23-1-41. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cookson B. D., Phillips I. Epidemic methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1988 Apr;21 (Suppl 100):57–65. doi: 10.1093/jac/21.suppl_c.57. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cookson B., Talsania H., Naidoo J., Phillips I. Strategies for typing and properties of epidemic methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Eur J Clin Microbiol. 1986 Dec;5(6):702–709. doi: 10.1007/BF02013309. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Costas M., Holmes B., Sloss L. L. Numerical analysis of electrophoretic protein patterns of Providencia rustigianii strains from human diarrhoea and other sources. J Appl Bacteriol. 1987 Oct;63(4):319–328. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2672.1987.tb02709.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Costas M., Leach R. H., Mitchelmore D. L. Numerical analysis of PAGE protein patterns and the taxonomic relationships within the 'Mycoplasma mycoides cluster'. J Gen Microbiol. 1987 Dec;133(12):3319–3329. doi: 10.1099/00221287-133-12-3319. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GORRILL R. H., GRAY R. A. The induction of bacteriophage in staphylococci. J Gen Microbiol. 1956 Feb;14(1):167–173. doi: 10.1099/00221287-14-1-167. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaston M. A., Duff P. S., Naidoo J., Ellis K., Roberts J. I., Richardson J. F., Marples R. R., Cooke E. M. Evaluation of electrophoretic methods for typing methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. J Med Microbiol. 1988 Jul;26(3):189–197. doi: 10.1099/00222615-26-3-189. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krikler S. J., Pennington T. H., Petrie D. Typing of strains of Staphylococcus aureus by Western Blot analysis of culture supernates. J Med Microbiol. 1986 Mar;21(2):169–171. doi: 10.1099/00222615-21-2-169. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lacey R. W., Grinsted J. Genetic analysis of methicillin-resistant strains of Staphylococcus aureus; evidence for their evolution from a single clone. J Med Microbiol. 1973 Nov;6(4):511–526. doi: 10.1099/00222615-6-4-511. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lyon B. R., Skurray R. Antimicrobial resistance of Staphylococcus aureus: genetic basis. Microbiol Rev. 1987 Mar;51(1):88–134. doi: 10.1128/mr.51.1.88-134.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marples R. R., Cooke E. M. Workshop on methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus held at the headquarters of the Public Health Laboratory Service on 8 January 1985. J Hosp Infect. 1985 Sep;6(3):342–348. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDougal L. K., Thornsberry C. The role of beta-lactamase in staphylococcal resistance to penicillinase-resistant penicillins and cephalosporins. J Clin Microbiol. 1986 May;23(5):832–839. doi: 10.1128/jcm.23.5.832-839.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Owen R. J., Costas M., Sloss L., Bolton F. J. Numerical analysis of electrophoretic protein patterns of Campylobacter laridis and allied thermophilic campylobacters from the natural environment. J Appl Bacteriol. 1988 Jul;65(1):69–78. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2672.1988.tb04319.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richardson J. F., Chittasobhon N., Marples R. R. Supplementary phages for the investigation of strains of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. J Med Microbiol. 1988 Jan;25(1):67–74. doi: 10.1099/00222615-25-1-67. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stephenson J. R., Crook S. J., Tabaqchali S. New method for typing Staphylococcus aureus resistant to methicillin based on sulphur-35 methionine labelled proteins: its application in an outbreak. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed) 1986 Sep 6;293(6547):581–583. doi: 10.1136/bmj.293.6547.581. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomson-Carter F. M., Pennington T. H. Characterisation of methicillin-resistant isolates of Staphylococcus aureus by analysis of whole-cell and exported proteins. J Med Microbiol. 1989 Jan;28(1):25–32. doi: 10.1099/00222615-28-1-25. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Townsend D. E., Ashdown N., Bolton S., Bradley J., Duckworth G., Moorhouse E. C., Grubb W. B. The international spread of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. J Hosp Infect. 1987 Jan;9(1):60–71. doi: 10.1016/0195-6701(87)90097-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Townsend D. E., Ashdown N., Bradley J. M., Pearman J. W., Grubb W. B. "Australian" methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus in a London hospital? Med J Aust. 1984 Sep 15;141(6):339–340. doi: 10.5694/j.1326-5377.1984.tb132800.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Saxe M. J., Notley C. M. Experiences with the typing of coagulase-negative staphylococci and micrococci. Zentralbl Bakteriol Orig A. 1978 Jul;241(1):46–59. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]