Abstract
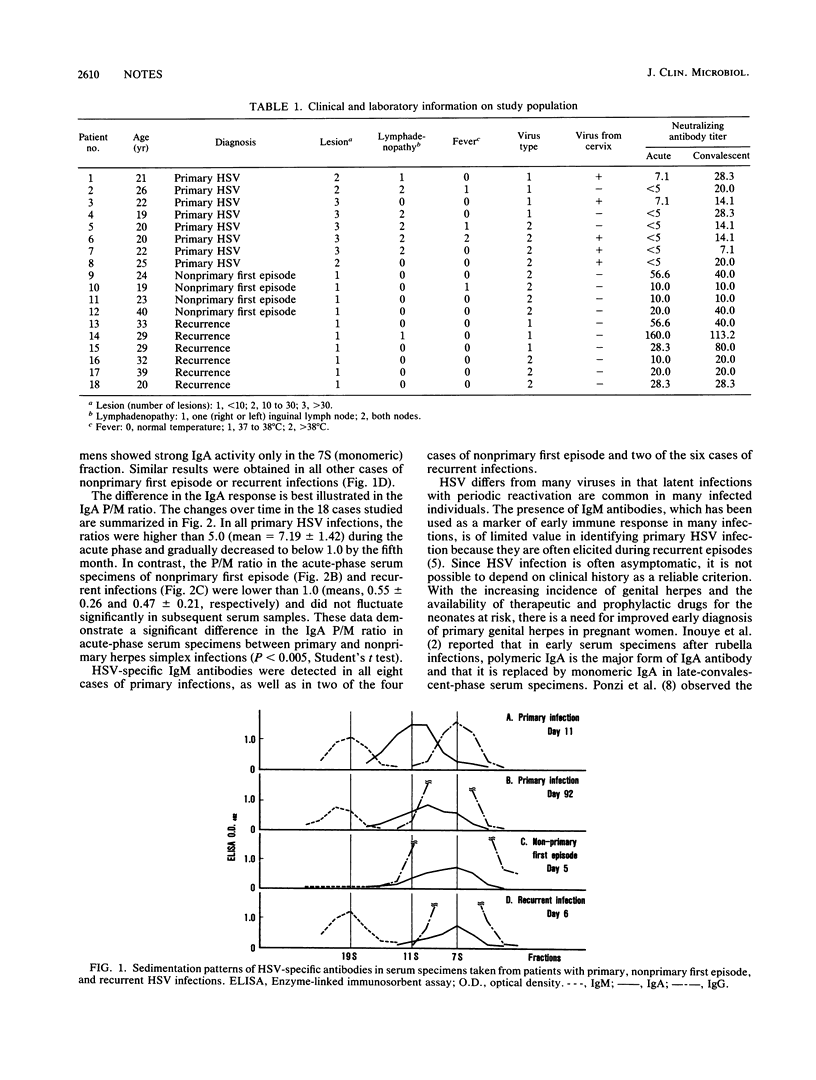
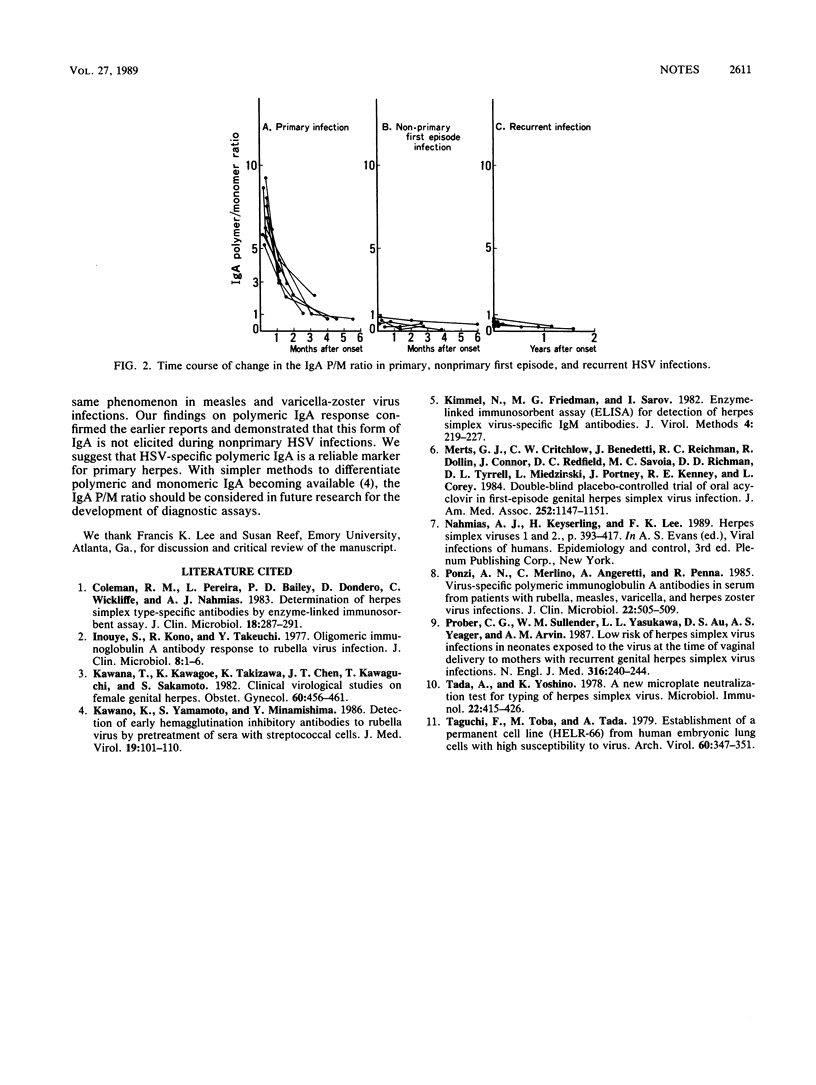
We analyzed antibody responses to herpes simplex virus (HSV) in 18 patients by using sucrose gradient centrifugation and an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for antibody determination. We found that the HSV-specific immunoglobulin A (IgA) antibody in early-convalescent-phase serum specimens from all of 8 primary cases consisted solely of polymeric forms, whereas in all 10 nonprimary cases, the major component was monomeric. These results indicate that the ratio of polymeric IgA to monomeric IgA antibody activity may be useful for differentiating primary from nonprimary HSV infections.
Full text
PDF
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Coleman R. M., Pereira L., Bailey P. D., Dondero D., Wickliffe C., Nahmias A. J. Determination of herpes simplex virus type-specific antibodies by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. J Clin Microbiol. 1983 Aug;18(2):287–291. doi: 10.1128/jcm.18.2.287-291.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inouye S., Kono R., Takeuchi Y. Oligomeric immunoglobulin A antibody response to rubella virus infection. J Clin Microbiol. 1978 Jul;8(1):1–6. doi: 10.1128/jcm.8.1.1-6.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawana T., Kawagoe K., Takizawa K., Chen J. T., Kawaguchi T., Sakamoto S. Clinical and virologic studies on female genital herpes. Obstet Gynecol. 1982 Oct;60(4):456–461. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawano K., Yamamoto S., Minamishima Y. Detection of early hemagglutination inhibitory antibodies to rubella virus by pretreatment of sera with streptococcal cells. J Med Virol. 1986 Jun;19(2):101–110. doi: 10.1002/jmv.1890190202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimmel N., Friedman M. G., Sarov I. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) for detection of herpes simplex virus-specific IgM antibodies. J Virol Methods. 1982 May;4(4-5):219–227. doi: 10.1016/0166-0934(82)90068-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mertz G. J., Critchlow C. W., Benedetti J., Reichman R. C., Dolin R., Connor J., Redfield D. C., Savoia M. C., Richman D. D., Tyrrell D. L. Double-blind placebo-controlled trial of oral acyclovir in first-episode genital herpes simplex virus infection. JAMA. 1984 Sep 7;252(9):1147–1151. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Negro Ponzi A., Merlino C., Angeretti A., Penna R. Virus-specific polymeric immunoglobulin A antibodies in serum from patients with rubella, measles, varicella, and herpes zoster virus infections. J Clin Microbiol. 1985 Oct;22(4):505–509. doi: 10.1128/jcm.22.4.505-509.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prober C. G., Sullender W. M., Yasukawa L. L., Au D. S., Yeager A. S., Arvin A. M. Low risk of herpes simplex virus infections in neonates exposed to the virus at the time of vaginal delivery to mothers with recurrent genital herpes simplex virus infections. N Engl J Med. 1987 Jan 29;316(5):240–244. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198701293160503. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tada A., Yoshino K. A new microplate neutralization test for typing of herpes simplex virus. Microbiol Immunol. 1978;22(7):415–426. doi: 10.1111/j.1348-0421.1978.tb00387.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taguchi F., Toba M., Tada A. Establishment of a permanent cell line (HEL-R66) from human embryonic lung cells with high susceptibility to viruses. Brief report. Arch Virol. 1979;60(3-4):347–351. doi: 10.1007/BF01317506. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


