Abstract
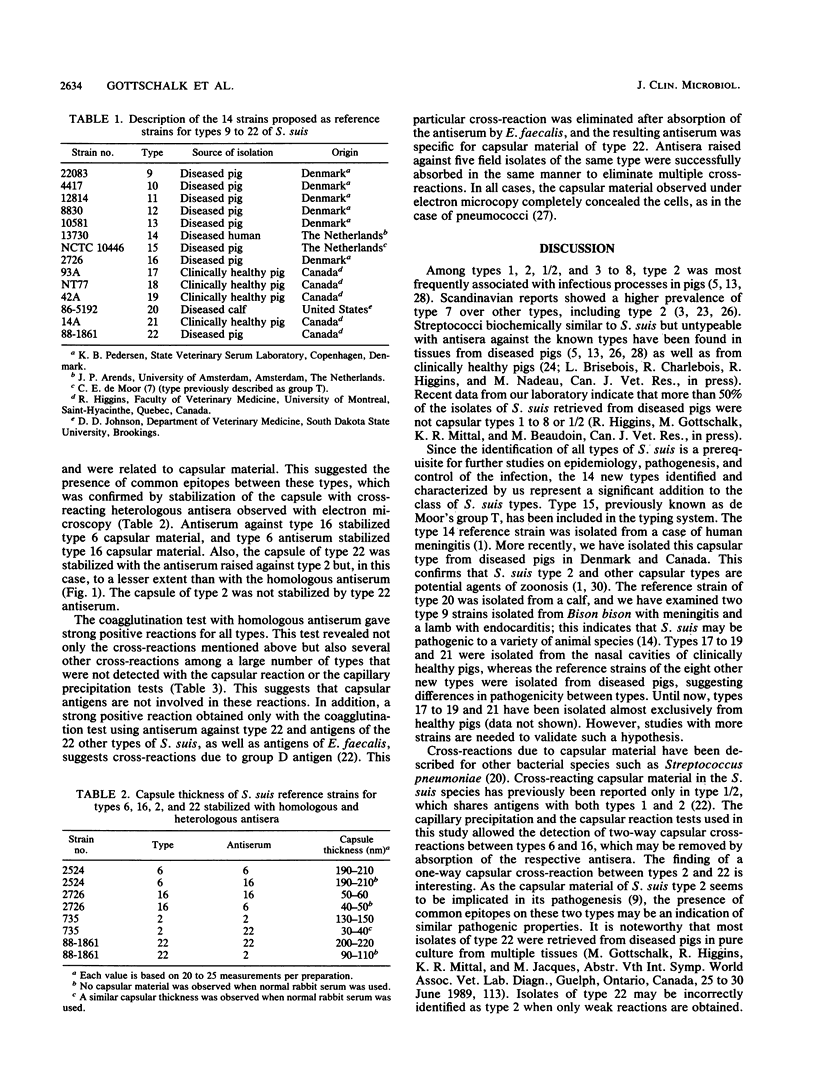
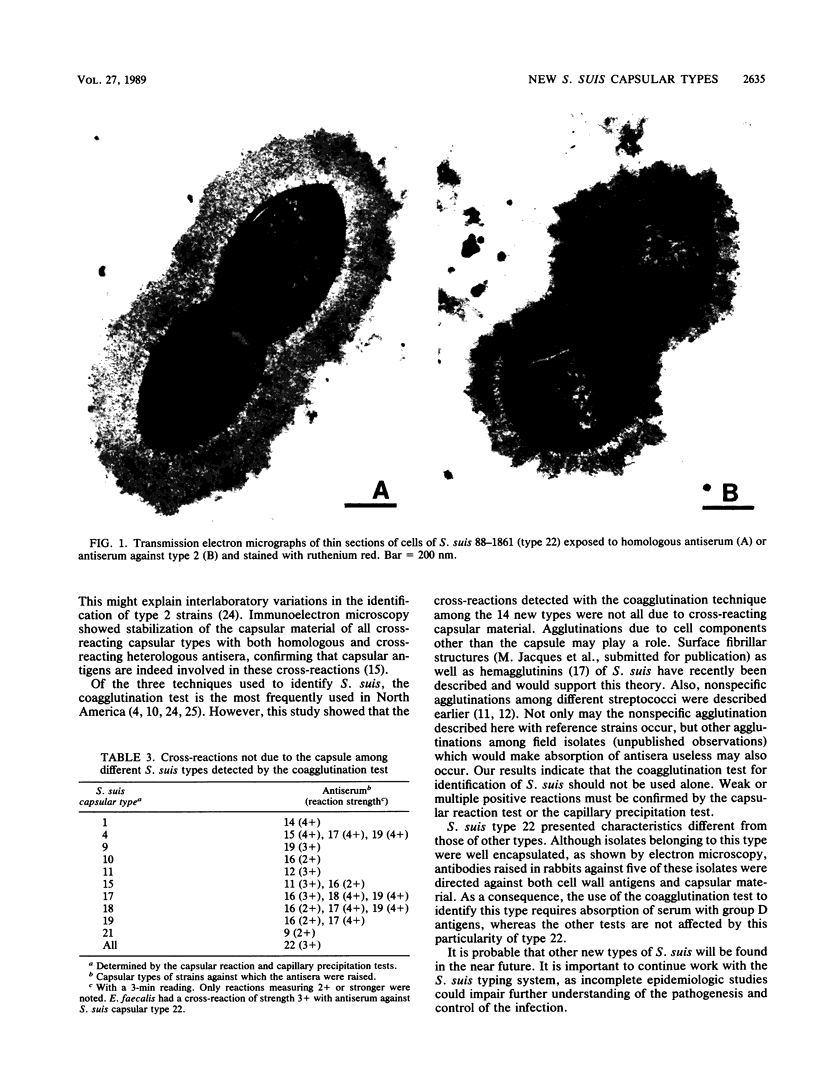
Fourteen new capsular types of Streptococcus suis (types 9 to 22) are described. All reference strains are morphologically and biochemically similar to types previously described. Reference strain types 9 to 13, 15, 16, and 22 were isolated from diseased pigs, whereas types 17 to 19 and 21 came from clinically healthy pigs; type 14 was isolated from a human case of meningitis, and type 20 was isolated from a diseased calf. The group T streptococcus of de Moor has been included in the typing system as type 15. Two-way cross-reactions between types 6 and 16 and a one-way cross-reaction between types 2 and 22 have been demonstrated. In addition, several cross-reactions probably not due to capsular material were detected among different types by using the coagglutination test. This test should not be used alone; weak or multiple positive reactions must be confirmed by the capsular reaction test or the capillary precipitation test.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arends J. P., Zanen H. C. Meningitis caused by Streptococcus suis in humans. Rev Infect Dis. 1988 Jan-Feb;10(1):131–137. doi: 10.1093/clinids/10.1.131. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Azuma R., Hara F., Oonuma Y., Sugimoto C. Streptococcus R (Streptococcus suis type II) infection in pigs in Japan. Natl Inst Anim Health Q (Tokyo) 1983 Winter;23(4):117–126. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boetner A. G., Binder M., Bille-Hansen V. Streptococcus suis infections in Danish pigs and experimental infection with Streptococcus suis serotype 7. Acta Pathol Microbiol Immunol Scand B. 1987 Aug;95(4):233–239. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1987.tb03118.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breton J., Mitchell W. R., Rosendal S. Streptococcus suis in slaughter pigs and abattoir workers. Can J Vet Res. 1986 Jul;50(3):338–341. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chau P. Y., Huang C. Y., Kay R. Streptococcus suis meningitis. An important underdiagnosed disease in Hong Kong. Med J Aust. 1983 Apr 30;1(9):414-6, 417. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DEMOOR C. E. SEPTICAEMIC INFECTIONS IN PIGS, CAUSED BY HAEMOLYTIC STREPTOCOCCI OF NEW LANCEFIELD GROUPS DESIGNATED R, S, AND T. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek. 1963;29:272–280. doi: 10.1007/BF02046069. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elliott S. D. Streptococcal infection in young pigs. I. An immunochemical study of the causative agent (PM streptococcus). J Hyg (Lond) 1966 Jun;64(2):205–212. doi: 10.1017/s0022172400040468. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elliott S. D., Tai J. Y. The type-specific polysaccharides of Streptococcus suis. J Exp Med. 1978 Dec 1;148(6):1699–1704. doi: 10.1084/jem.148.6.1699. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erickson E. D., Doster A. R., Pokorny T. S. Isolation of Streptococcus suis from swine in Nebraska. J Am Vet Med Assoc. 1984 Sep 15;185(6):666–668. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finch R. G., Phillips I. Serological grouping of streptococci by a slide coagglutination method. J Clin Pathol. 1977 Feb;30(2):168–170. doi: 10.1136/jcp.30.2.168. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giunta S., Sampaoli G., Galeazzi L., Bilei L., Rinaldi R., Groppa G. Inhibition of nonspecific streptococcal coagglutination reactions. J Clin Microbiol. 1983 Feb;17(2):192–194. doi: 10.1128/jcm.17.2.192-194.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hommez J., Devriese L. A., Henrichsen J., Castryck F. Identification and characterization of Streptococcus suis. Vet Microbiol. 1986 Apr;11(4):349–355. doi: 10.1016/0378-1135(86)90065-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hommez J., Wullepit J., Cassimon P., Castryck F., Ceyssens K., Devriese L. A. Streptococcus suis and other streptococcal species as a cause of extramammary infection in ruminants. Vet Rec. 1988 Dec 10;123(24):626–627. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacques M., Foiry B., Higgins R., Mittal K. R. Electron microscopic examination of capsular material from various serotypes of Actinobacillus pleuropneumoniae. J Bacteriol. 1988 Jul;170(7):3314–3318. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.7.3314-3318.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurl D. N., Haataja S., Finne J. Hemagglutination activities of group B, C, D, and G streptococci: demonstration of novel sugar-specific cell-binding activities in Streptococcus suis. Infect Immun. 1989 Feb;57(2):384–389. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.2.384-389.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lamont M. H., Edwards P. T., Windsor R. S. Streptococcal meningitis in pigs: results of a five-year survey. Vet Rec. 1980 Nov 15;107(20):467–469. doi: 10.1136/vr.107.20.467. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mittal K. R., Higgins R., Larivière S. Identification and serotyping of Haemophilus pleuropneumoniae by coagglutination test. J Clin Microbiol. 1983 Dec;18(6):1351–1354. doi: 10.1128/jcm.18.6.1351-1354.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perch B., Kjems E., Slot P., Pedersen K. B. Biochemical and serological properties of R, S, and RS streptococci. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand B. 1981 Jun;89(3):167–171. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1981.tb00171_89b.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perch B., Pedersen K. B., Henrichsen J. Serology of capsulated streptococci pathogenic for pigs: six new serotypes of Streptococcus suis. J Clin Microbiol. 1983 Jun;17(6):993–996. doi: 10.1128/jcm.17.6.993-996.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Porcine streptococci causing meningitis and septicaemia in man. Lancet. 1975 Jun 7;1(7919):1286–1288. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosendal S., Breton J., Henrichsen J., Hilt L., Mitchell W. R. Isolation of Streptococcus suis using a selective medium. Can J Vet Res. 1986 Oct;50(4):537–539. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanford S. E. Gross and histopathological findings in unusual lesions caused by Streptococcus suis in pigs. I. Cardiac lesions. Can J Vet Res. 1987 Oct;51(4):481–485. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sihvonen L., Kurl D. N., Henrichsen J. Streptococcus suis isolated from pigs in Finland. Acta Vet Scand. 1988;29(1):9–13. doi: 10.1186/BF03548386. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skov Sørensen U. B., Blom J., Birch-Andersen A., Henrichsen J. Ultrastructural localization of capsules, cell wall polysaccharide, cell wall proteins, and F antigen in pneumococci. Infect Immun. 1988 Aug;56(8):1890–1896. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.8.1890-1896.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Touil F., Higgins R., Nadeau M. Isolation of Streptococcus suis from diseased pigs in Canada. Vet Microbiol. 1988 Jun;17(2):171–177. doi: 10.1016/0378-1135(88)90008-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Windsor R. S., Elliott S. D. Streptococcal infection in young pigs. IV. An outbreak of streptococcal meningitis in weaned pigs. J Hyg (Lond) 1975 Aug;75(1):69–78. doi: 10.1017/s0022172400047070. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]