Abstract
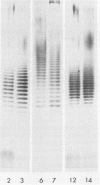
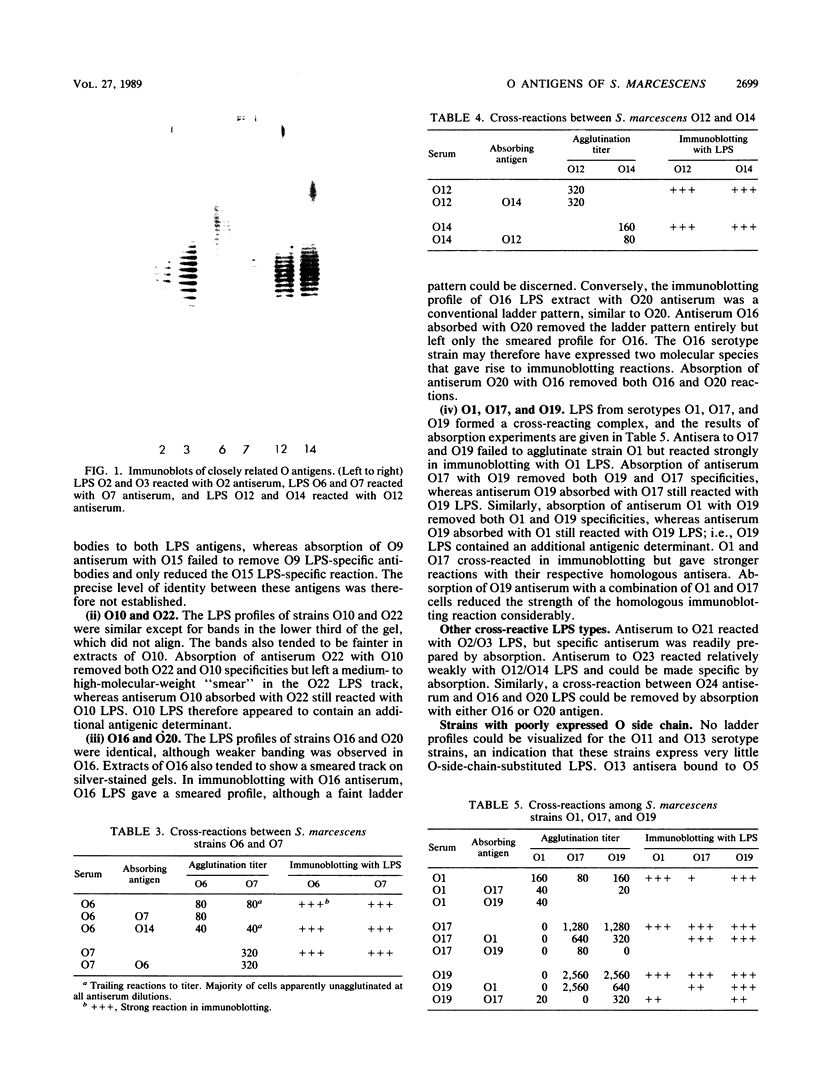
O antigens of the 24 O-serotype strains of Serratia marcescens were investigated in dot enzyme immunoassay with whole-cell antigens and by immunoblotting with lipopolysaccharide (LPS) antigens. Three pairs of strains, O2/O3, O6/O7, and O12/O14, had indistinguishable LPS antigens, despite having distinct specificities in agglutination tests with whole-cell antigens. Strong cross-reactions were also found in LPS antigens from strains O9/O15, O17/O19, O10/O22, and O16/O20. No high-molecular-weight LPS corresponding to O-side-chain material was detected in strain O11 or O13. A panel of absorbed antisera was prepared to facilitate the detection of a reduced set of LPS antigens in a dot enzyme immunoassay. We conclude that there are discrepancies between the existing serotypes as defined by agglutination tests and the antigenic composition of LPS antigens extracted from the serotype strains and that surface antigens other than LPS make a major contribution to the definition of serotype in the species.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brigden C. J., Furn S., Wilkinson S. G. Structural studies of neutral polymers isolated from the lipopolysaccharides of Serratia marcescens O6 (strain C.D.C. 862-57) and O12 (C.D.C. 6320-58). Carbohydr Res. 1985 Jun 15;139:298–301. doi: 10.1016/0008-6215(85)90029-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAVIS B. R., WOODWARD J. M. Some relationships of the somatic antigens of a group of Serratia marcescens cultures. Can J Microbiol. 1957 Jun;3(4):591–597. doi: 10.1139/m57-064. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guinée P. A., Jansen W. H., Maas H. M. Serotyping of Serratia marcescens using passive haemagglutination. Zentralbl Bakteriol Mikrobiol Hyg A. 1987 Apr;264(1-2):105–119. doi: 10.1016/s0176-6724(87)80130-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hitchcock P. J., Brown T. M. Morphological heterogeneity among Salmonella lipopolysaccharide chemotypes in silver-stained polyacrylamide gels. J Bacteriol. 1983 Apr;154(1):269–277. doi: 10.1128/jb.154.1.269-277.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Le Minor S., Benazet F., Martin L. Nouveaux facteurs antigéniques O (O23) et H (H26) de Serratia marcescens. Ann Microbiol (Paris) 1983 Nov-Dec;134B(3):447–449. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Le Minor S., Pigache F. Etude antigénique de souches de Serratia marcescens isolées en France. II.--Caractérisation des antigènes O et individualisation de 5 nouveaux facteurs, fréquence des sérotypes et désignation des nouveaux facteurs H. Ann Microbiol (Paris) 1978 Oct;129 B(3):407–423. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Le Minor S., Sauvageot-Pigache F. Nouveaux facteurs antigéniques H (H21-H25) et O (O21) de Serratia marcescens: subdivision des facteurs O5, O10, O16. Ann Microbiol (Paris) 1981 May-Jun;132(3):239–252. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oxley D., Wilkinson S. G. Structural studies of glucorhamnans isolated from the lipopolysaccharides of reference strains for Serratia marcescens serogroups O4 and O7, and of an O14 strain. Carbohydr Res. 1988 Apr 1;175(1):111–117. doi: 10.1016/0008-6215(88)80161-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oxley D., Wilkinson S. G. Studies of lipopolysaccharides from two strains (C.D.C. 3607-60 and IP 421) of Serratia marcescens O13: structure of the putative O13 antigen. Carbohydr Res. 1988 Feb 1;172(2):275–286. doi: 10.1016/s0008-6215(00)90861-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pitt T. L., Erdman Y. J., Bucher C. The epidemiological type identification of Serratia marcescens from outbreaks of infection in hospitals. J Hyg (Lond) 1980 Apr;84(2):269–283. doi: 10.1017/s0022172400026772. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Traub W. H., Kleber I. Serotyping of Serratia marcescens: evaluation of Le Minor's H-immobilization test and description of three new flagellar H antigens. J Clin Microbiol. 1977 Feb;5(2):115–121. doi: 10.1128/jcm.5.2.115-121.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Traub W. H. Serotyping of Serratia marcescens: confirmation of five recently described new O-antigens and characterization of an additional O-antigen. Zentralbl Bakteriol Mikrobiol Hyg A. 1981 Sep;250(3):307–311. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsai C. M., Frasch C. E. A sensitive silver stain for detecting lipopolysaccharides in polyacrylamide gels. Anal Biochem. 1982 Jan 1;119(1):115–119. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(82)90673-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]