Abstract
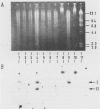
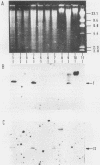
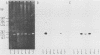
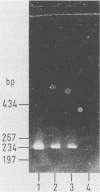
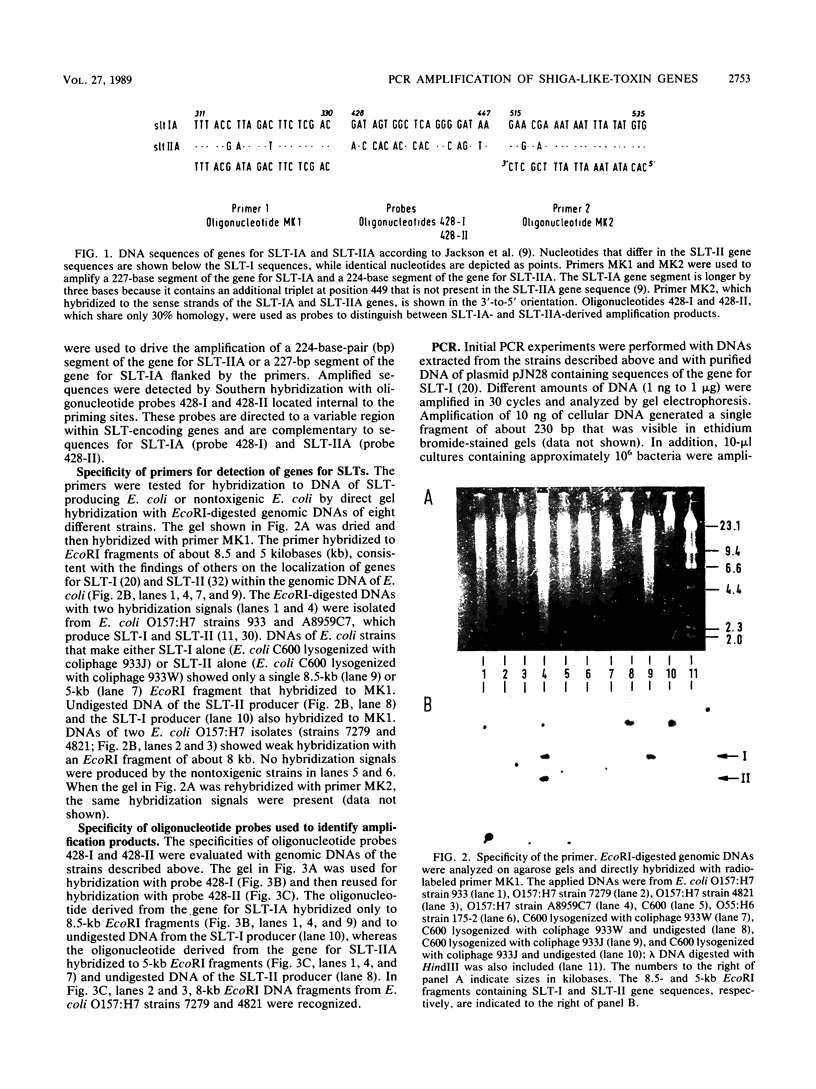
By using a single synthetic oligonucleotide primer pair in the polymerase chain reaction, we amplified specific Shiga-like-toxin (SLT) gene segments from DNAs of 20 clinical Escherichia coli isolates, irrespective of whether they produce SLT-I, SLT-II, or heretofore uncategorized SLTs. These segments were not detectable in any of 20 nontoxigenic E. coli strains. The primers deduced from a conserved region among SLT genes are so-called degenerate-sequence primers; i.e., they contain intentionally introduced sequence ambiguities to overcome minor sequence variations within different SLT genes. In direct gel hybridization with genomic DNA, both primers recognized SLT-I and SLT-II DNA sequences. Amplified sequences of target DNA obtained by polymerase chain reaction were visualized after gel electrophoresis by ethidium bromide staining, and definitive identification of the amplification product as an SLT gene segment was achieved by hybridization to SLT-I- and SLT-II-specific 20-base oligonucleotide probes complementary to a portion of the amplified sequences but not to the primers. The detecting oligonucleotide probes shared only 30% base homology and were shown to recognize specifically SLT-I or SLT-II sequences within genomic DNA. Moreover, they were used to distinguish whether the amplified sequence originated from SLT-I or SLT-II genes. The PCR system with the primers described here is a powerful technique to amplify SLT sequences in E. coli strains that produce serologically distinct SLTs and will facilitate identification of these pathogens, particularly among a multitude of nonpathogenic E. coli strains.
Full text
PDF

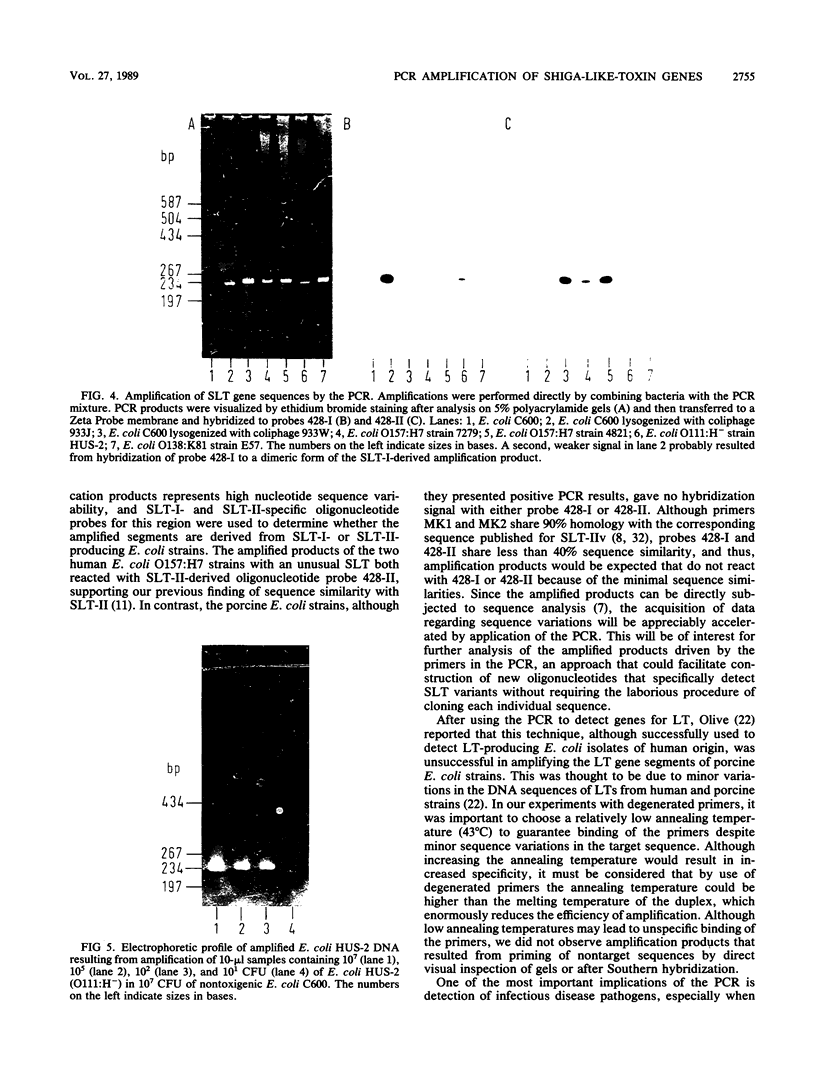


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bopp C. A., Greene K. D., Downes F. P., Sowers E. G., Wells J. G., Wachsmuth I. K. Unusual verotoxin-producing Escherichia coli associated with hemorrhagic colitis. J Clin Microbiol. 1987 Aug;25(8):1486–1489. doi: 10.1128/jcm.25.8.1486-1489.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown J. E., Echeverria P., Taylor D. N., Seriwatana J., Vanapruks V., Lexomboon U., Neill R. N., Newland J. W. Determination by DNA hybridization of Shiga-like-toxin-producing Escherichia coli in children with diarrhea in Thailand. J Clin Microbiol. 1989 Feb;27(2):291–294. doi: 10.1128/jcm.27.2.291-294.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calderwood S. B., Auclair F., Donohue-Rolfe A., Keusch G. T., Mekalanos J. J. Nucleotide sequence of the Shiga-like toxin genes of Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jul;84(13):4364–4368. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.13.4364. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crescenzi M., Seto M., Herzig G. P., Weiss P. D., Griffith R. C., Korsmeyer S. J. Thermostable DNA polymerase chain amplification of t(14;18) chromosome breakpoints and detection of minimal residual disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jul;85(13):4869–4873. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.13.4869. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Downes F. P., Barrett T. J., Green J. H., Aloisio C. H., Spika J. S., Strockbine N. A., Wachsmuth I. K. Affinity purification and characterization of Shiga-like toxin II and production of toxin-specific monoclonal antibodies. Infect Immun. 1988 Aug;56(8):1926–1933. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.8.1926-1933.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edelman R., Karmali M. A., Fleming P. A. From the National Institutes of Health. Summary of the International Symposium and Workshop on Infections due to Verocytotoxin (Shiga-like toxin)-producing Escherichia coli. J Infect Dis. 1988 May;157(5):1102–1104. doi: 10.1093/infdis/157.5.1102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guatelli J. C., Gingeras T. R., Richman D. D. Nucleic acid amplification in vitro: detection of sequences with low copy numbers and application to diagnosis of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 infection. Clin Microbiol Rev. 1989 Apr;2(2):217–226. doi: 10.1128/cmr.2.2.217. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gyles C. L., De Grandis S. A., MacKenzie C., Brunton J. L. Cloning and nucleotide sequence analysis of the genes determining verocytotoxin production in a porcine edema disease isolate of Escherichia coli. Microb Pathog. 1988 Dec;5(6):419–426. doi: 10.1016/0882-4010(88)90003-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karch H., Bitzan M., Pietsch R., Stenger K. O., von Wulffen H., Heesemann J., Düsing R. Purified verotoxins of Escherichia coli O157:H7 decrease prostacyclin synthesis by endothelial cells. Microb Pathog. 1988 Sep;5(3):215–221. doi: 10.1016/0882-4010(88)90024-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karch H., Bitzan M. Purification and characterization of a phage-encoded cytotoxin from an Escherichia coli O111 strain associated with hemolytic-uremic syndrome. Zentralbl Bakteriol Mikrobiol Hyg A. 1988 Nov;270(1-2):41–51. doi: 10.1016/s0176-6724(88)80140-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karch H., Meyer T. Evaluation of oligonucleotide probes for identification of shiga-like-toxin-producing Escherichia coli. J Clin Microbiol. 1989 Jun;27(6):1180–1186. doi: 10.1128/jcm.27.6.1180-1186.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karmali M. A. Infection by verocytotoxin-producing Escherichia coli. Clin Microbiol Rev. 1989 Jan;2(1):15–38. doi: 10.1128/cmr.2.1.15. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karmali M. A., Petric M., Lim C., Fleming P. C., Arbus G. S., Lior H. The association between idiopathic hemolytic uremic syndrome and infection by verotoxin-producing Escherichia coli. J Infect Dis. 1985 May;151(5):775–782. doi: 10.1093/infdis/151.5.775. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Konowalchuk J., Speirs J. I., Stavric S. Vero response to a cytotoxin of Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1977 Dec;18(3):775–779. doi: 10.1128/iai.18.3.775-779.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marques L. R., Moore M. A., Wells J. G., Wachsmuth I. K., O'Brien A. D. Production of Shiga-like toxin by Escherichia coli. J Infect Dis. 1986 Aug;154(2):338–341. doi: 10.1093/infdis/154.2.338. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyer T., Bitzan M., Sandkamp O., Karch H. Synthetic oligodeoxyribonucleotide probes to detect verocytotoxin-producing Escherichia coli in diseased pigs. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 1989 Jan 15;48(2):247–252. doi: 10.1111/j.1574-6968.1989.tb03308.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyer T., Karch H. Genes coding for Shiga-like toxin and heat-stabile enterotoxin in porcine strains of Escherichia coli. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 1989 Mar;49(1):115–119. doi: 10.1016/0378-1097(89)90353-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newland J. W., Neill R. J. DNA probes for Shiga-like toxins I and II and for toxin-converting bacteriophages. J Clin Microbiol. 1988 Jul;26(7):1292–1297. doi: 10.1128/jcm.26.7.1292-1297.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Brien A. D., Holmes R. K. Shiga and Shiga-like toxins. Microbiol Rev. 1987 Jun;51(2):206–220. doi: 10.1128/mr.51.2.206-220.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olive D. M. Detection of enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli after polymerase chain reaction amplification with a thermostable DNA polymerase. J Clin Microbiol. 1989 Feb;27(2):261–265. doi: 10.1128/jcm.27.2.261-265.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perera L. P., Marques L. R., O'Brien A. D. Isolation and characterization of monoclonal antibodies to Shiga-like toxin II of enterohemorrhagic Escherichia coli and use of the monoclonal antibodies in a colony enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. J Clin Microbiol. 1988 Oct;26(10):2127–2131. doi: 10.1128/jcm.26.10.2127-2131.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riley L. W., Remis R. S., Helgerson S. D., McGee H. B., Wells J. G., Davis B. R., Hebert R. J., Olcott E. S., Johnson L. M., Hargrett N. T. Hemorrhagic colitis associated with a rare Escherichia coli serotype. N Engl J Med. 1983 Mar 24;308(12):681–685. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198303243081203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saiki R. K., Gelfand D. H., Stoffel S., Scharf S. J., Higuchi R., Horn G. T., Mullis K. B., Erlich H. A. Primer-directed enzymatic amplification of DNA with a thermostable DNA polymerase. Science. 1988 Jan 29;239(4839):487–491. doi: 10.1126/science.2448875. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saiki R. K., Scharf S., Faloona F., Mullis K. B., Horn G. T., Erlich H. A., Arnheim N. Enzymatic amplification of beta-globin genomic sequences and restriction site analysis for diagnosis of sickle cell anemia. Science. 1985 Dec 20;230(4732):1350–1354. doi: 10.1126/science.2999980. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith H. R., Rowe B., Gross R. J., Fry N. K., Scotland S. M. Haemorrhagic colitis and Vero-cytotoxin-producing Escherichia coli in England and Wales. Lancet. 1987 May 9;1(8541):1062–1065. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(87)90485-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strockbine N. A., Marques L. R., Holmes R. K., O'Brien A. D. Characterization of monoclonal antibodies against Shiga-like toxin from Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1985 Dec;50(3):695–700. doi: 10.1128/iai.50.3.695-700.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strockbine N. A., Marques L. R., Newland J. W., Smith H. W., Holmes R. K., O'Brien A. D. Two toxin-converting phages from Escherichia coli O157:H7 strain 933 encode antigenically distinct toxins with similar biologic activities. Infect Immun. 1986 Jul;53(1):135–140. doi: 10.1128/iai.53.1.135-140.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallace R. B., Miyada C. G. Oligonucleotide probes for the screening of recombinant DNA libraries. Methods Enzymol. 1987;152:432–442. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)52050-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinstein D. L., Jackson M. P., Samuel J. E., Holmes R. K., O'Brien A. D. Cloning and sequencing of a Shiga-like toxin type II variant from Escherichia coli strain responsible for edema disease of swine. J Bacteriol. 1988 Sep;170(9):4223–4230. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.9.4223-4230.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Willshaw G. A., Smith H. R., Scotland S. M., Field A. M., Rowe B. Heterogeneity of Escherichia coli phages encoding Vero cytotoxins: comparison of cloned sequences determining VT1 and VT2 and development of specific gene probes. J Gen Microbiol. 1987 May;133(5):1309–1317. doi: 10.1099/00221287-133-5-1309. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]