Abstract
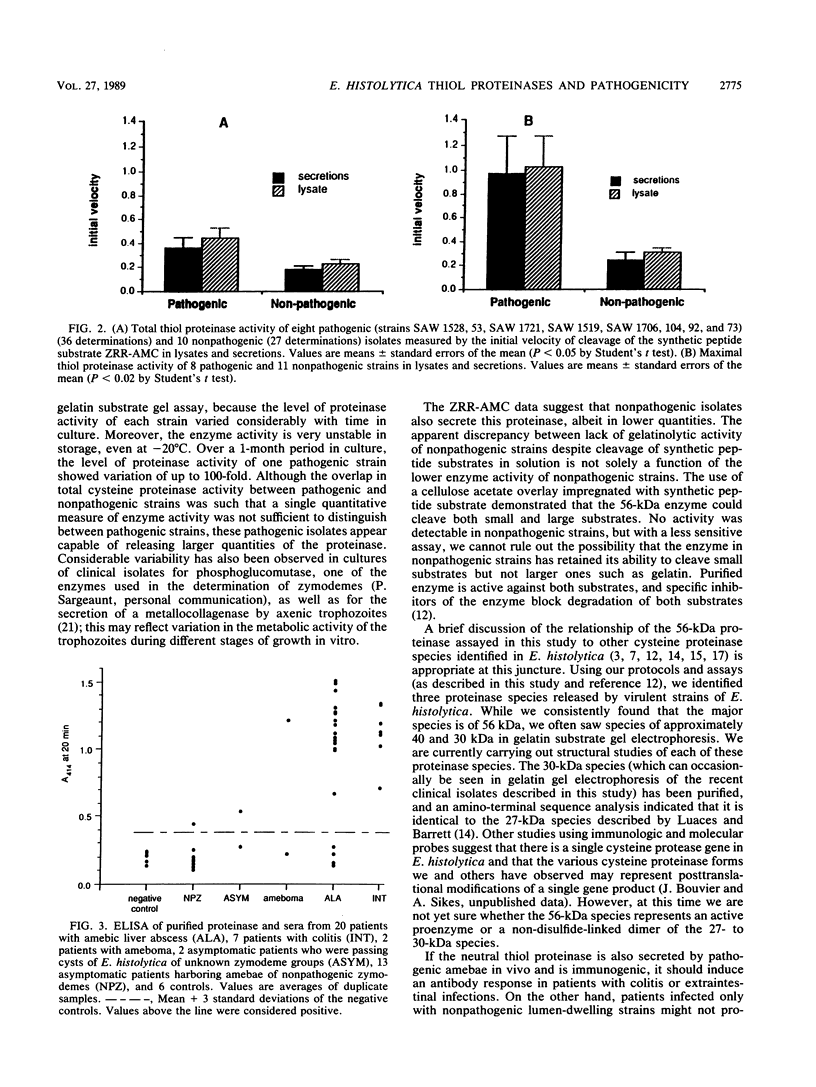
Expression of the 56-kilodalton (kDa) neutral thiol proteinase has been shown to correlate with the potential of clinical isolates of Entamoeba histolytica to produce invasive disease. A 56-kDa band was identified by gelatin substrate gel electrophoresis in 10 of 10 isolates from patients with colitis or amebic liver abscesses, but in only 1 of 10 isolates from asymptomatic patients. Pathogenic isolates appear capable of releasing significantly larger quantities of the proteinase, as measured by cleavage of a synthetic peptide substrate, ZRR-AMC (benzyloxy-carbonyl-arginine-arginine-4-amino-7-methylcoumarin). We have also shown that the proteinase is released during the course of clinical invasive amebic disease, as demonstrated by the presence of circulating antibodies detectable by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. These studies support the importance of the 56-kDa thiol proteinase in the pathogenesis of invasive amebiasis.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allason-Jones E., Mindel A., Sargeaunt P., Williams P. Entamoeba histolytica as a commensal intestinal parasite in homosexual men. N Engl J Med. 1986 Aug 7;315(6):353–356. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198608073150603. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barrett A. J., Kembhavi A. A., Brown M. A., Kirschke H., Knight C. G., Tamai M., Hanada K. L-trans-Epoxysuccinyl-leucylamido(4-guanidino)butane (E-64) and its analogues as inhibitors of cysteine proteinases including cathepsins B, H and L. Biochem J. 1982 Jan 1;201(1):189–198. doi: 10.1042/bj2010189. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Becker I., Pérez-Tamayo R., Montfort I., Alvizouri A. M., Pérez-Montfort R. Entamoeba histolytica: role of amebic proteinases and polymorphonuclear leukocytes in acute experimental amebiasis in the rat. Exp Parasitol. 1988 Dec;67(2):268–280. doi: 10.1016/0014-4894(88)90074-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diamond L. S., Harlow D. R., Cunnick C. C. A new medium for the axenic cultivation of Entamoeba histolytica and other Entamoeba. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg. 1978;72(4):431–432. doi: 10.1016/0035-9203(78)90144-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gadasi H., Kobiler D. Entamoeba histolytica: correlation between virulence and content of proteolytic enzymes. Exp Parasitol. 1983 Feb;55(1):105–110. doi: 10.1016/0014-4894(83)90003-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldmeier D., Sargeaunt P. G., Price A. B., Munday P. E., Billington O., Dixon I., Borriello P., Carder J. M., Shaw A., Hilton J. Is Entamoeba histolytica in homosexual men a pathogen? Lancet. 1986 Mar 22;1(8482):641–644. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(86)91723-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Healy G. R. Immunologic tools in the diagnosis of amebiasis: epidemiology in the United States. Rev Infect Dis. 1986 Mar-Apr;8(2):239–246. doi: 10.1093/clinids/8.2.239. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joyce M. P., Ravdin J. I. Antigens of Entamoeba histolytica recognized by immune sera from liver abscess patients. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1988 Jan;38(1):74–80. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1988.38.74. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katzenstein D., Rickerson V., Braude A. New concepts of amebic liver abscess derived from hepatic imaging, serodiagnosis, and hepatic enzymes in 67 consecutive cases in San Diego. Medicine (Baltimore) 1982 Jul;61(4):237–246. doi: 10.1097/00005792-198207000-00003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keene W. E., Petitt M. G., Allen S., McKerrow J. H. The major neutral proteinase of Entamoeba histolytica. J Exp Med. 1986 Mar 1;163(3):536–549. doi: 10.1084/jem.163.3.536. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krogstad D. J. Isoenzyme patterns and pathogenicity in amebic infection. N Engl J Med. 1986 Aug 7;315(6):390–391. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198608073150609. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luaces A. L., Barrett A. J. Affinity purification and biochemical characterization of histolysin, the major cysteine proteinase of Entamoeba histolytica. Biochem J. 1988 Mar 15;250(3):903–909. doi: 10.1042/bj2500903. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lushbaugh W. B., Hofbauer A. F., Pittman F. E. Proteinase activities of Entamoeba histolytica cytotoxin. Gastroenterology. 1984 Jul;87(1):17–27. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mathews H. M., Moss D. M., Visvesvara G. S. Analysis of antigens from membrane and soluble fractions of Entamoeba histolytica. J Protozool. 1986 Aug;33(3):328–334. doi: 10.1111/j.1550-7408.1986.tb05619.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGowan K., Deneke C. F., Thorne G. M., Gorbach S. L. Entamoeba histolytica cytotoxin: purification, characterization, strain virulence, and protease activity. J Infect Dis. 1982 Nov;146(5):616–625. doi: 10.1093/infdis/146.5.616. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mirelman D. Ameba-bacterium relationship in amebiasis. Microbiol Rev. 1987 Jun;51(2):272–284. doi: 10.1128/mr.51.2.272-284.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mirelman D., Bracha R., Wexler A., Chayen A. Changes in isoenzyme patterns of a cloned culture of nonpathogenic Entamoeba histolytica during axenization. Infect Immun. 1986 Dec;54(3):827–832. doi: 10.1128/iai.54.3.827-832.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mirelman D. Effect of culture conditions and bacterial associates on the zymodemes of Entamoeba histolytica. Parasitol Today. 1987 Feb;3(2):37–37. doi: 10.1016/0169-4758(87)90210-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muńoz M. L., Calderón J., Rojkind M. The collagenase of Entamoeba histolytica. J Exp Med. 1982 Jan 1;155(1):42–51. doi: 10.1084/jem.155.1.42. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reed S. L., Curd J. G., Gigli I., Gillin F. D., Braude A. I. Activation of complement by pathogenic and nonpathogenic Entamoeba histolytica. J Immunol. 1986 Mar 15;136(6):2265–2270. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinson G. L. The laboratory diagnosis of human parasitic amoebae. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg. 1968;62(2):285–294. doi: 10.1016/0035-9203(68)90170-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sargeaunt P. G. The reliability of Entamoeba histolytica zymodemes in clinical diagnosis. Parasitol Today. 1987 Feb;3(2):40–37. doi: 10.1016/0169-4758(87)90211-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sargeaunt P. G., Williams J. E. Electrophoretic isoenzyme patterns of the pathogenic and non-pathogenic intestinal amoebae of man. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg. 1979;73(2):225–227. doi: 10.1016/0035-9203(79)90219-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sargeaunt P. G., Williams J. E., Grene J. D. The differentiation of invasive and non-invasive Entamoeba histolytica by isoenzyme electrophoresis. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg. 1978;72(5):519–521. doi: 10.1016/0035-9203(78)90174-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strachan W. D., Chiodini P. L., Spice W. M., Moody A. H., Ackers J. P. Immunological differentiation of pathogenic and non-pathogenic isolates of Entamoeba histolytica. Lancet. 1988 Mar 12;1(8585):561–563. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(88)91355-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wyler D. J. Fibronectin in parasitic diseases. Rev Infect Dis. 1987 Jul-Aug;9 (Suppl 4):S391–S399. doi: 10.1093/clinids/9.supplement_4.s391. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]