Abstract
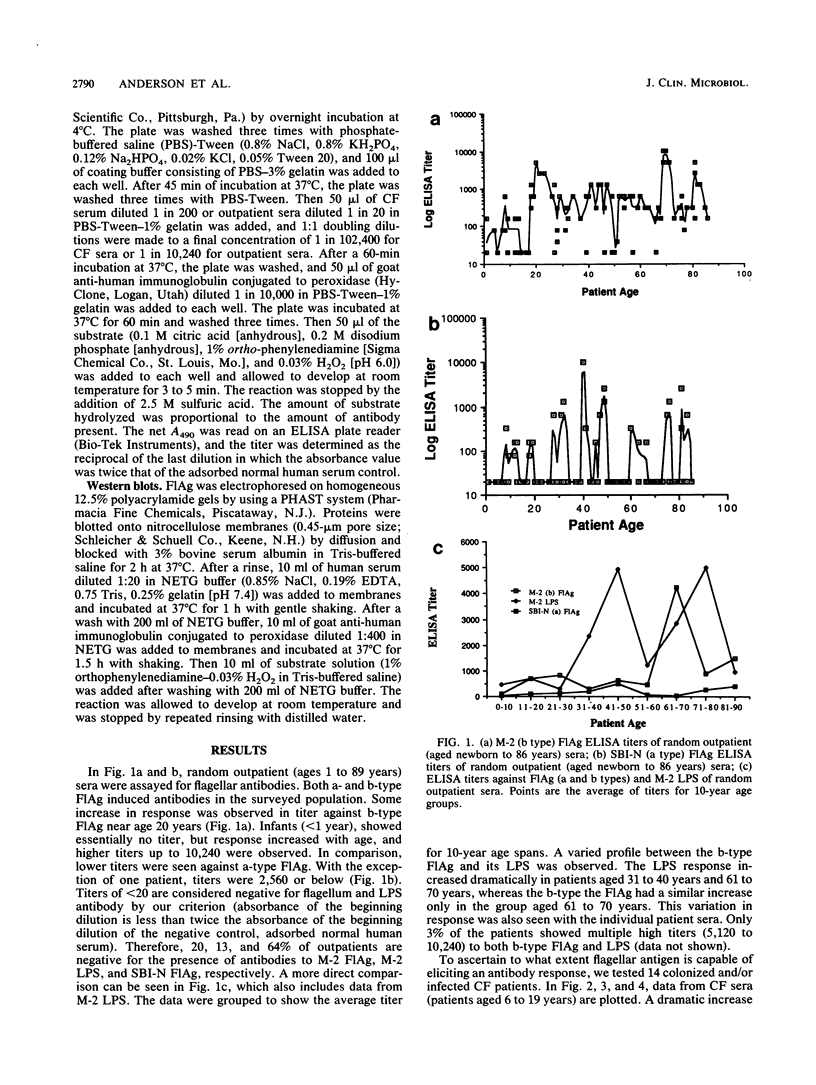
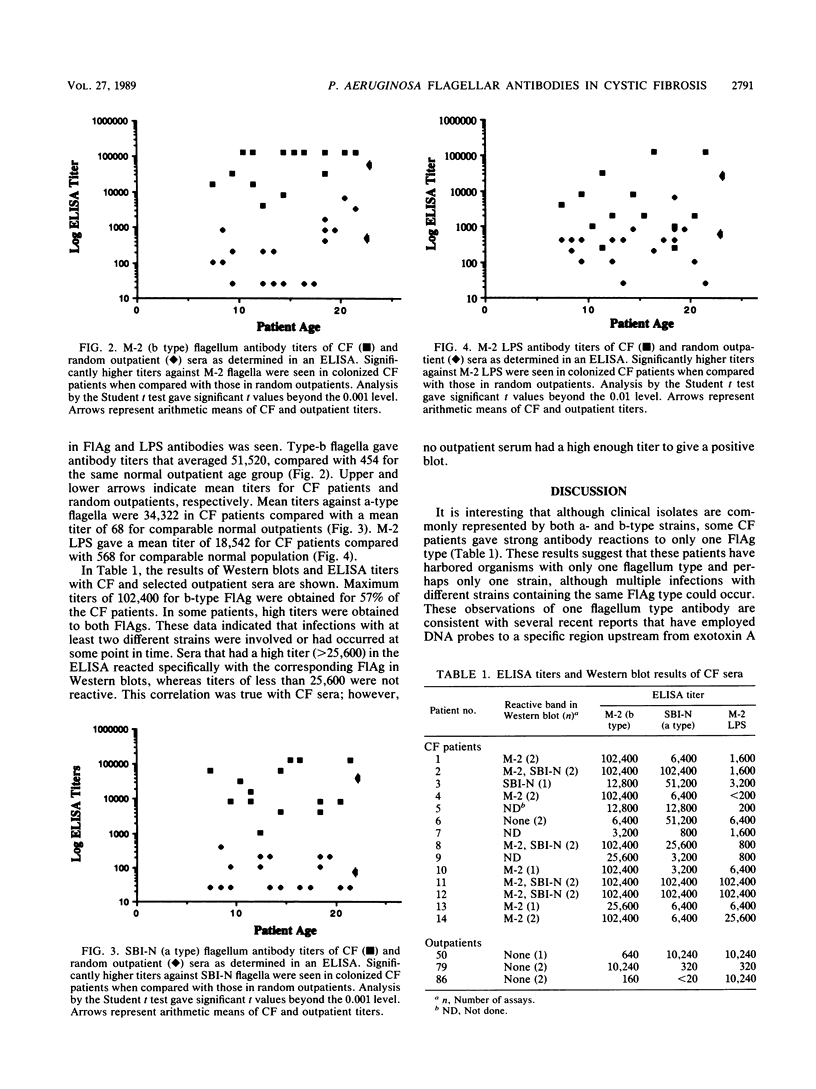
An enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay specific for flagellum type (a or b) of Pseudomonas aeruginosa was used to detect serum immunoglobulin antibodies in 98 random outpatients and 14 colonized cystic fibrosis patients. Antibodies were detected to both types of flagella in addition to M-2 lipopolysaccharide. Titers to both flagellar antigens (FlAg) were 10 to 100 times higher in cystic fibrosis patients than in random outpatients of a comparable age group. Mean antibody titers against b-type FlAg were 454 for outpatients (ages newborn to 21 years), whereas the mean titer for cystic fibrosis patients (ages 6 to 21 years) was 51,520. Titers against a-type FlAg were generally lower, with mean outpatient titers of 68 and mean cystic fibrosis patient titers of 34,323. Differences were also seen in antibody titer against M-2 lipopolysaccharide, but these differences did not correspond to M-2 FlAg titers. In 98 random outpatients (ages newborn to 86 years), FlAg titers generally increased with age. To demonstrate further specificity of the enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for flagellum antibody, Western blots were performed with selected high-titer cystic fibrosis patient sera. Sera that had a high titer (greater than 25,600) for b- or a-type FlAg showed a corresponding reactive band. These results demonstrate that flagellum antibodies are produced in humans in response to P. aeruginosa infection.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allison J. S., Dawson M., Drake D., Montie T. C. Electrophoretic separation and molecular weight characterization of Pseudomonas aeruginosa H-antigen flagellins. Infect Immun. 1985 Sep;49(3):770–774. doi: 10.1128/iai.49.3.770-774.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson T. R., Montie T. C. Opsonophagocytosis of Pseudomonas aeruginosa treated with antiflagellar serum. Infect Immun. 1987 Dec;55(12):3204–3206. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.12.3204-3206.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ansorg R. Flagellaspezifisches H-Antigenschema von Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Zentralbl Bakteriol Orig A. 1978 Nov;242(2):228–238. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aronoff S. C., Stern R. C. Serum IgG antibody to outer membrane antigens of Pseudomonas cepacia and Pseudomonas aeruginosa in cystic fibrosis. J Infect Dis. 1988 May;157(5):934–940. doi: 10.1093/infdis/157.5.934. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bryan L. E., Kureishi A., Rabin H. R. Detection of antibodies to Pseudomonas aeruginosa alginate extracellular polysaccharide in animals and cystic fibrosis patients by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. J Clin Microbiol. 1983 Aug;18(2):276–282. doi: 10.1128/jcm.18.2.276-282.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Darveau R. P., Hancock R. E. Procedure for isolation of bacterial lipopolysaccharides from both smooth and rough Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Salmonella typhimurium strains. J Bacteriol. 1983 Aug;155(2):831–838. doi: 10.1128/jb.155.2.831-838.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drake D., Montie T. C. Flagella, motility and invasive virulence of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Gen Microbiol. 1988 Jan;134(1):43–52. doi: 10.1099/00221287-134-1-43. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drake D., Montie T. C. Protection against Pseudomonas aeruginosa infection by passive transfer of anti-flagellar serum. Can J Microbiol. 1987 Sep;33(9):755–763. doi: 10.1139/m87-130. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Döring G., Albus A., Høiby N. Immunologic aspects of cystic fibrosis. Chest. 1988 Aug;94(2 Suppl):109S–115S. doi: 10.1378/chest.94.2_supplement.109s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Döring G., Buhl V., Høiby N., Schiøtz P. O., Botzenhart K. Detection of proteases of Pseudomonas aeruginosa in immune complexes isolated from sputum of cystic fibrosis patients. Acta Pathol Microbiol Immunol Scand C. 1984 Oct;92(5):307–312. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1984.tb00092.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Döring G., Obernesser H. J., Botzenhart K., Flehmig B., Høiby N., Hofmann A. Proteases of Pseudomonas aeruginosa in patients with cystic fibrosis. J Infect Dis. 1983 Apr;147(4):744–750. doi: 10.1093/infdis/147.4.744. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fomsgaard A., Høiby N., Shand G. H., Conrad R. S., Galanos C. Longitudinal study of antibody response to lipopolysaccharides during chronic Pseudomonas aeruginosa lung infection in cystic fibrosis. Infect Immun. 1988 Sep;56(9):2270–2278. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.9.2270-2278.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Granström M., Ericsson A., Strandvik B., Wretlind B., Pavlovskis O. R., Berka R., Vasil M. L. Relation between antibody response to Pseudomonas aeruginosa exoproteins and colonization/infection in patients with cystic fibrosis. Acta Paediatr Scand. 1984 Nov;73(6):772–777. doi: 10.1111/j.1651-2227.1984.tb17774.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hollsing A. E., Granström M., Vasil M. L., Wretlind B., Strandvik B. Prospective study of serum antibodies to Pseudomonas aeruginosa exoproteins in cystic fibrosis. J Clin Microbiol. 1987 Oct;25(10):1868–1874. doi: 10.1128/jcm.25.10.1868-1874.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luzar M. A., Thomassen M. J., Montie T. C. Flagella and motility alterations in Pseudomonas aeruginosa strains from patients with cystic fibrosis: relationship to patient clinical condition. Infect Immun. 1985 Nov;50(2):577–582. doi: 10.1128/iai.50.2.577-582.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Montie T. C., Anderson T. R. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for detection of Pseudomonas aeruginosa H (flagellar) antigen. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 1988 Apr;7(2):256–260. doi: 10.1007/BF01963097. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Montie T. C., Doyle-Huntzinger D., Craven R. C., Holder I. A. Loss of virulence associated with absence of flagellum in an isogenic mutant of Pseudomonas aeruginosa in the burned-mouse model. Infect Immun. 1982 Dec;38(3):1296–1298. doi: 10.1128/iai.38.3.1296-1298.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Montie T. C., Drake D., Sellin H., Slater O., Edmonds S. Motility, virulence, and protection with a flagella vaccine against Pseudomonas aeruginosa infection. Antibiot Chemother (1971) 1987;39:233–248. doi: 10.1159/000414349. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ogle J. W., Janda J. M., Woods D. E., Vasil M. L. Characterization and use of a DNA probe as an epidemiological marker for Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Infect Dis. 1987 Jan;155(1):119–126. doi: 10.1093/infdis/155.1.119. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ogle J. W., Reller L. B., Vasil M. L. Development of resistance in Pseudomonas aeruginosa to imipenem, norfloxacin, and ciprofloxacin during therapy: proof provided by typing with a DNA probe. J Infect Dis. 1988 Apr;157(4):743–748. doi: 10.1093/infdis/157.4.743. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pasloske B. L., Joffe A. M., Sun Q., Volpel K., Paranchych W., Eftekhar F., Speert D. P. Serial isolates of Pseudomonas aeruginosa from a cystic fibrosis patient have identical pilin sequences. Infect Immun. 1988 Mar;56(3):665–672. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.3.665-672.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pedersen S. S., Espersen F., Høiby N. Diagnosis of chronic Pseudomonas aeruginosa infection in cystic fibrosis by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. J Clin Microbiol. 1987 Oct;25(10):1830–1836. doi: 10.1128/jcm.25.10.1830-1836.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piedra P., Ogra P. L. Immunologic aspects of surface infections in the lung. J Pediatr. 1986 May;108(5 Pt 2):817–823. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(86)80751-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wood R. E., Boat T. F., Doershuk C. F. Cystic fibrosis. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1976 Jun;113(6):833–878. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1976.113.6.833. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


