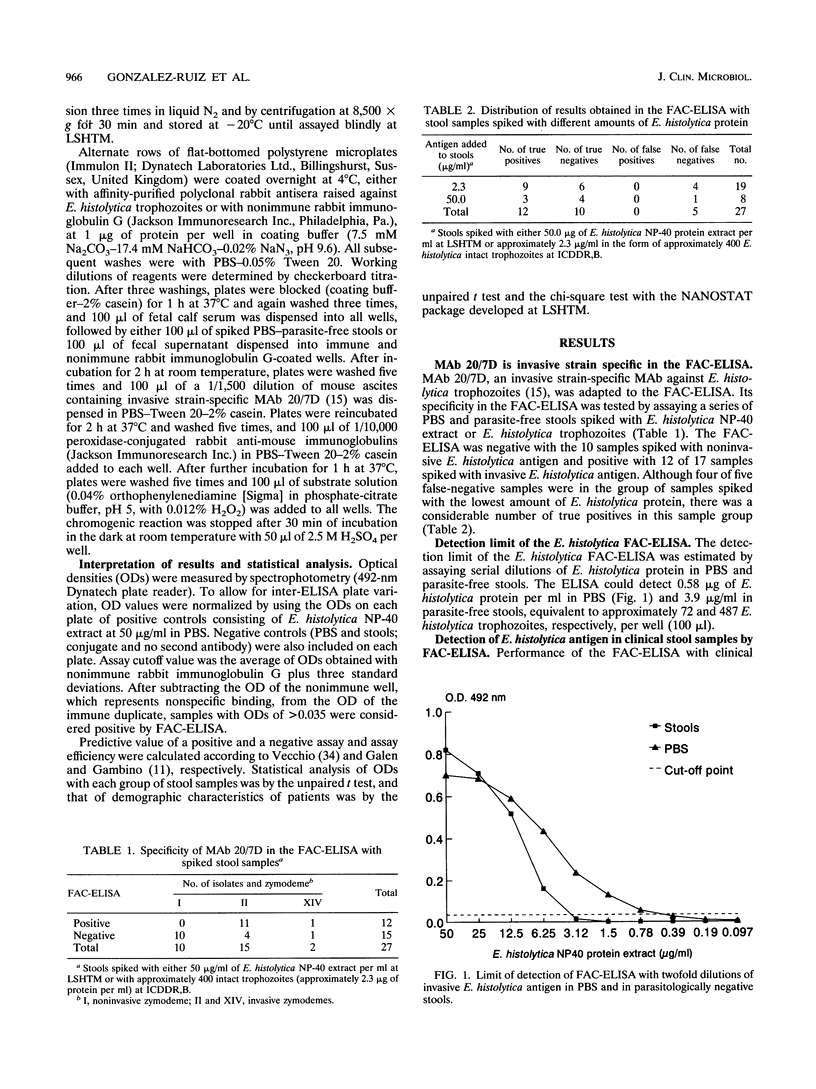
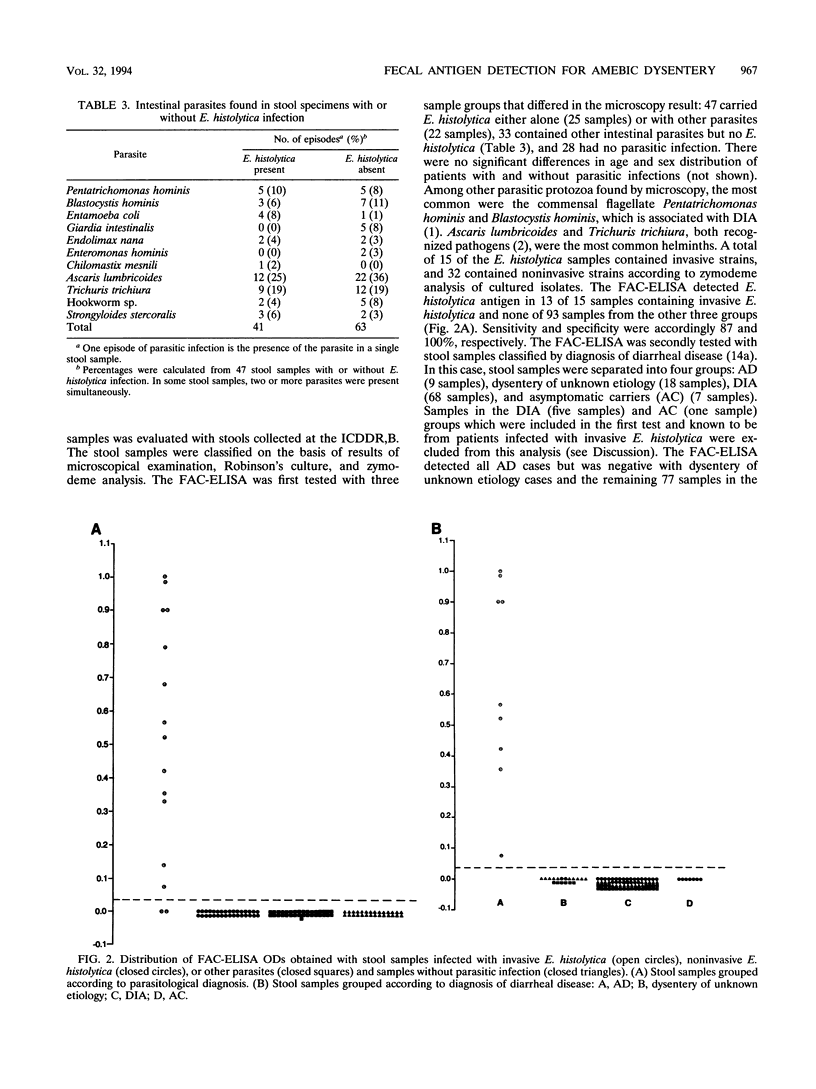
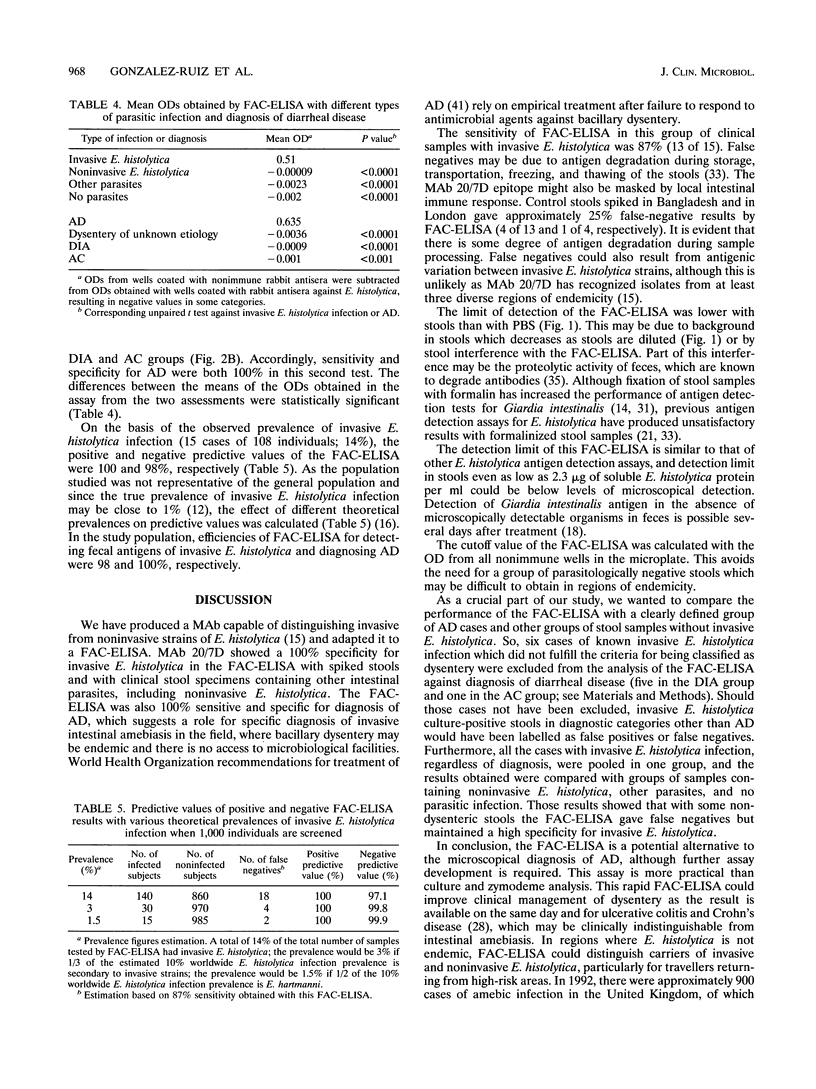
Abstract
An invasive strain-specific monoclonal antibody against Entamoeba histolytica has been used in a capture enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) for the detection of invasive E. histolytica fecal antigen in clinical specimens and for the diagnosis of amebic dysentery in patients from Bangladesh. The fecal antigen capture ELISA (FAC-ELISA) did not cross-react with other parasite species in the clinical specimens or with noninvasive E. histolytica present in those specimens and in experimentally seeded stools. The limit of detection of the assay for invasive E. histolytica crude antigen diluted in phosphate-buffered saline or in stools was 0.58 and 3.9 micrograms/ml, respectively, which is the equivalent of approximately 72 and 487 E. histolytica trophozoites per well, respectively. The sensitivity, specificity, and efficiency of the FAC-ELISA were 87, 100, and 98%, respectively, for the detection of invasive E. histolytica antigens and 100, 100, and 100%, respectively, for the diagnosis of amebic dysentery. The FAC-ELISA is a potential alternative for the field diagnosis of amebic dysentery and for epidemiological studies to define the distribution of invasive E. histolytica.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Blanc D. S. Determination of taxonomic status of pathogenic and nonpathogenic Entamoeba histolytica zymodemes using isoenzyme analysis. J Protozool. 1992 Jul-Aug;39(4):471–479. doi: 10.1111/j.1550-7408.1992.tb04834.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark C. G., Diamond L. S. Ribosomal RNA genes of 'pathogenic' and 'nonpathogenic' Entamoeba histolytica are distinct. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1991 Dec;49(2):297–302. doi: 10.1016/0166-6851(91)90073-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cruz-Reyes J. A., Spice W. M., Rehman T., Gisborne E., Ackers J. P. Ribosomal DNA sequences in the differentiation of pathogenic and non-pathogenic isolates of Entamoeba histolytica. Parasitology. 1992 Apr;104(Pt 2):239–246. doi: 10.1017/s0031182000061679. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diamond L. S. Techniques of axenic cultivation of Entamoeba histolytica Schaudinn, 1903 and E. histolytica-like amebae. J Parasitol. 1968 Oct;54(5):1047–1056. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Entamoeba hartmanni: missing or misidentified? J Infect Dis. 1991 Sep;164(3):612–613. doi: 10.1093/infdis/164.3.612. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farri T. A., Sargeaunt P. G., Warhurst D. C., Williams J. E., Bhojnani R. Electrophoretic studies of the hexokinase of Entamoeba histolytica groups I to IV. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg. 1980;74(5):672–673. doi: 10.1016/0035-9203(80)90165-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GEIMAN Q. M., BECKER C. E. In vitro growth and metabolism of Endamoeba histolytica. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1953 Oct 14;56(5):1048–1056. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1953.tb30285.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gathiram V., Jackson T. F. Frequency distribution of Entamoeba histolytica zymodemes in a rural South African population. Lancet. 1985 Mar 30;1(8431):719–721. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(85)91263-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldin A. J., Apt W., Aguilera X., Zulantay I., Warhurst D. C., Miles M. A. A capture ELISA detects Giardia lamblia antigens in formalin-treated faecal samples. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg. 1992 Mar-Apr;86(2):164–165. doi: 10.1016/0035-9203(92)90552-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gonzalez-Ruiz A., Haque R., Rehman T., Aguirre A., Jaramillo C., Castañon G., Hall A., Guhl F., Ruiz-Palacios G., Warhurst D. C. A monoclonal antibody for distinction of invasive and noninvasive clinical isolates of Entamoeba histolytica. J Clin Microbiol. 1992 Nov;30(11):2807–2813. doi: 10.1128/jcm.30.11.2807-2813.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- González-Ruiz A., Haque R., Aguirre A., Castañn G., Hall A., Guhl F., Ruiz-Palacios G., Miles M. A., Warhurst D. C. Value of microscopy in the diagnosis of dysentery associated with invasive Entamoeba histolytica. J Clin Pathol. 1994 Mar;47(3):236–239. doi: 10.1136/jcp.47.3.236. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- González-Ruiz A., Miles M. A., Warhurst D. C. Predictive value of diagnostic tests and prevalence of invasive Entamoeba histolytica infection. J Infect Dis. 1993 Aug;168(2):513–515. doi: 10.1093/infdis/168.2.513. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green E. L., Miles M. A., Warhurst D. C. Immunodiagnostic detection of Giardia antigen in faeces by a rapid visual enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. Lancet. 1985 Sep 28;2(8457):691–693. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(85)92932-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haque R., Hall A., Tzipori S. Zymodemes of Entamoeba histolytica in Dhaka, Bangladesh. Ann Trop Med Parasitol. 1990 Dec;84(6):629–632. doi: 10.1080/00034983.1990.11812519. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jain U., Patel M. T., Desai P. K., Kaliraj P. Development of simple and stable ELISA for detection of copro antigen in intestinal amoebiasis. Indian J Exp Biol. 1990 Jul;28(7):671–675. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krogstad D. J., Spencer H. C., Jr, Healy G. R., Gleason N. N., Sexton D. J., Herron C. A. Amebiasis: epidemiologic studies in the United States, 1971-1974. Ann Intern Med. 1978 Jan;88(1):89–97. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-88-1-89. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sargeaunt P. G., Williams J. E. Electrophoretic isoenzyme patterns of Entamoeba histolytica and Entamoeba coli. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg. 1978;72(2):164–166. doi: 10.1016/0035-9203(78)90053-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sargeaunt P. G., Williams J. E., Grene J. D. The differentiation of invasive and non-invasive Entamoeba histolytica by isoenzyme electrophoresis. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg. 1978;72(5):519–521. doi: 10.1016/0035-9203(78)90174-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sargeaunt P. G., Williams J. E., Neal R. A. A comparative study of Entamoeba histolytica (NIH :200, HK9, etc.), "E. histolytica-like" and other morphologically identical amoebae using isoenzyme electrophoresis. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg. 1980;74(4):469–474. doi: 10.1016/0035-9203(80)90058-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spencer H. C., Sullivan J. J., Mathews H. M., Sauerbrey M., Bloch M., Chin W., Healy G. R. Serologic and parasitologic studies of Entamoeba histolytica in El Salvador, 1974-1978. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1981 Jan;30(1):63–68. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1981.30.63. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spice W. M., Ackers J. P. Large-scale production of Entamoeba histolytica trophozoites in polyxenic culture. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg. 1990 Sep-Oct;84(5):693–694. doi: 10.1016/0035-9203(90)90149-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stibbs H. H. Monoclonal antibody-based enzyme immunoassay for Giardia lamblia antigen in human stool. J Clin Microbiol. 1989 Nov;27(11):2582–2588. doi: 10.1128/jcm.27.11.2582-2588.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TOBIE J. E. Experimental infection of the rabbit with Endamoeba histolytica. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1949 Nov;29(6):859-70, illust. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1949.s1-29.859. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ungar B. L., Yolken R. H., Quinn T. C. Use of a monoclonal antibody in an enzyme immunoassay for the detection of Entamoeba histolytica in fecal specimens. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1985 May;34(3):465–472. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1985.34.465. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vecchio T. J. Predictive value of a single diagnostic test in unselected populations. N Engl J Med. 1966 May 26;274(21):1171–1173. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196605262742104. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walsh J. A. Problems in recognition and diagnosis of amebiasis: estimation of the global magnitude of morbidity and mortality. Rev Infect Dis. 1986 Mar-Apr;8(2):228–238. doi: 10.1093/clinids/8.2.228. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


