INTRODUCTION
Reading EKGs is an integral skill in Emergency Medicine, especially given the fact that determining the presence and amount of ST segment elevation (STE) is one of the key factors to initiating fibrinolytic eligibility. STE is generally measured in reference to the J point (the end of the QRS segment and the beginning of the ST segment). However, it may not be clear in clinical practice where the J point starts, where one measures ST segment elevation in relation to the J point and finally what the exact degree of elevation of the ST segment makes one a candidate for thrombolysis. Further complicating the issue are numerous other causes of J point and ST segment elevation that are not myocardial-infarction related. This short review will focus on identifying the J point in order to determine an accurate measurement of ST segment elevation and its relationship to fibrinolytic eligibility.
The J Point: Where is it?
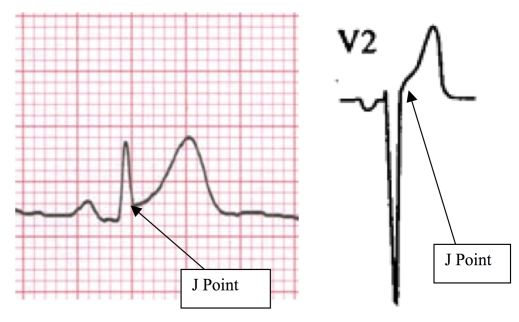
One standard text defines J point elevation as: “the point where the QRS ends and the ST segment begins.”1 Where exactly that “point” resides is rarely stated. One of the more specific descriptors states that the J point is the “first point of the inflection on the upstroke of the S wave.”2 This description gives one at least some hope of finding a specific point from which to measure. However, we know of no study that has specifically determined the interrater reliability of J point measurements. Studies of the interrater reliability of degree of STE have been performed and generally show considerable disagreement.2,3 Since this “point” may be subtle and depend on a variety of factors (the investigator’s vision for example), it may be surmised that the interrater reliability of J point measurement may be less than perfect (Figure 1).
Figure 1.
Examples of J point determination
STE and the J point
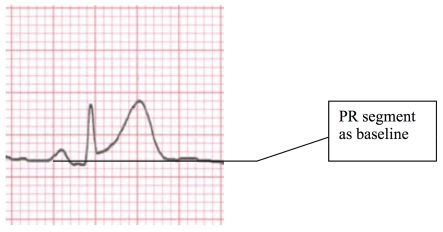
In theory the ST segment is normally neither elevated nor depressed. STE should be measured from the upper edge of the P-R segment (not the T-P segment) to the upper edge of the ST segment at the J point.4 In most patients, however, the T-P segment and P-R segment lie on the same plane.5 Likewise, ST segment depression should be measured from the lower edge of the P-R segment to the lower edge of the ST segment at the J point. If the ST segment is measured with reference to the T-P segment, atrial repolarization with a prominent negative T wave may result in an inaccurate measurement.4 (See Figure 2).
Figure 2.
The ECG Baseline
It is unclear whether STE measured at the J point or 60 milliseconds after the J point is superior when evaluating fibrinolytic or PTCA criteria.6,7,8,9,10 A recent retrospective study showed that fewer EKGs met enrollment criteria when based on STE at the J point versus at 60 ms after the J point. Fewer EKGs met an ST score (sum of STE in leads V1-V6) of 6 mm when measured at the J point versus J point plus 60 milliseconds (70% vs. 88%).6 This controversy is not likely to be resolved any time soon and, in most cases, is probably not important. It is a reminder, however, that criteria that appear to be set in stone, well defined, and closely followed by all experts, are in fact open to interpretation and bias.
What Degree of STE Equals Fibrinolytic Criteria?
Marriot’s criteria states that cardiac injury is present when the J point is either elevated by 1 mm or greater in two or more limb leads (or pre-cordial leads V4 to V6), by 2 mm or greater in two or more pre-cordial leads V1 to V3, or is depressed by 1 mm or greater in two or more pre-cordial 5 Recently, there has been a move away from leads V1 to V3. requiring a 2 mm elevation in the anterior pre-cordial leads. The American College of Emergency Physicians (ACEP) Clinical Policies Committee’s 2000 revision states that fibrinolytic criteria includes “ST-segment elevations greater than 0.1 mV in two or more contiguous leads that are not characteristic of early repolarization or pericarditis, nor of a repolarization abnormality from LVH or BBB in patients with clinical presentation suggestive of AMI.”10 This was a level “B” recommendation, and the review notes that the fibrinolytic trials have used different criteria. This move to a 1 mm elevation in any lead is supported by Pope and colleagues who found that a full 30% of patients who have ST-segment elevation of 1 mm or greater had a final diagnosis of AMI in their multicenter study. Alarmingly, the authors also note a small but important incidence (11%) of failure by the ED clinician to detect ST-segment elevations of 1 to 2 mm in the EKGs of patients who had AMI.11
It is interesting that many of the largest mega-trials used quite different criteria for fibrinolytic eligibility (Table 1). Indeed some of the mega-trials used no explicit ST segment criteria. The current criteria are derived from retrospective analysis of a combination of mega-trials and therefore have been open to interpretation. The use of 1mm in any 2 contiguous leads has also been deemed acceptable by the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association (ACC/AHA) guidelines.12 Regardless, it is best to interpret the ST segment in relation to the clinical history. The higher the pre-test probability of AMI the more comfort one should have in accepting 1mm versus 2mm of ST segment elevation as the criteria for thrombolysis.
Table 1.
ECG Entrance Criteria in Select Mega-Trials
| Study | Publication Year | Duration of Symptoms Required | Maximum Time to Onset Prior to Presentation | EKG Change Requirements | Other Requirements/Modifiers |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ISIS - 1 (13) | 1986 | ----- | 12 hr | None | MI suspected by MD |
| ISIS - 1 (14) | 1988 | ----- | 24 hr | None | MI suspected by MD |
| GISSI - 2 (15) | 1990 | ----- | 6 hr |
|
|
| ISIS - 3 (16) | 1992 | ----- | ----- | None | MD thought there was a “clear” indication for Fibrinolytics |
| GUSTO (17) | 1993 | 20 min | 6 hr |
|
|
| GUSTO III (18) | 1997 | 30 min | 6 hr |
|
|
| ASSENT - 2 (19) | 1999 | ----- | 6 hr |
|
|
| InTIME - II (20) | 2000 | 30 min | 6 hr |
|
|
| ASSENT - 3 (21) | 2001 | ----- | 6hr |
|
|
| GUSTO V (22) | 2001 | 30 min | 6hr | “EKG criteria for STEMI or New LBBB” (with references to GUSTO, GUSTO III & ASSENT – 2) |
SUMMARY
The exact location of the J point, as well as its use for determining STE is open to some debate. Even the exact place to measure ST segment elevation for fibrinolytics is a point of contention, as is the degree of ST segment elevation that warrants consideration of fibrinolytic therapy. Interpreting ST segment elevation must be made in the context of the clinical setting. Like any test, the pre-test probability of the disease (myocardial infarction in this case) is essential in interpreting the results of the test (degree, type and amount of ST segment elevation).
Footnotes
Reprints available through open access at www.westjem.org
REFERENCES
- 1.Goldberger . An Imprint of Elsevier, Chapter 2- Basic. 7. ECG w\Waves; Mosby: 2006. Clinical Electrocardiography: A Simplified Approach. [Google Scholar]
- 2.Carley SD, Gamo R, Driscoll PA, et al. What’s the point of ST elevation? Emergency Medicine Journal. 2002;19:126–128. doi: 10.1136/emj.19.2.126. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Tandberg D, Kastendieck KD, Meskin S. Observer variation in measured ST-Segment elevation. Annals of Emergency Medicine. 1999;34:448–452. doi: 10.1016/s0196-0644(99)80045-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Smith SW, Whitmam W. Acute coronary syndromes. Emergency Medicine Clinics of North America. 2006;24:53–89. doi: 10.1016/j.emc.2005.08.008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Wagner GS. Marriott’s Practical Electrocardiography. 9. Baltimore, MD: Williams & Wilkins; 1994. [Google Scholar]
- 6.Smith SW. ST elevation in anterior acute myocardial infarction differs with different methods of measurement. Academic Emergency Medicine. 2006;13:406–412. doi: 10.1197/j.aem.2005.10.019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Willems JL, Willems RJ, Willems GM, et al. Significance of initial ST segment elevation and depression for the management of thrombolytic therapy in acute myocardial infarction. Circulation. 1990;82:1147–1158. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.82.4.1147. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Bush HS, Ferguson JJ, Angelini P, et al. Twelve-lead electrocardiographic evaluation of ischemia during percutaneous transluminal coronary angioplasty and its correlation with acute reocclusion. American Heart Journal. 1991;121:1591–1599. doi: 10.1016/0002-8703(91)90001-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Tamura A, Mikuriya Y, Kataoka H, et al. Emergent coronary angiographic findings of patients with ST leads, or both, during anterior wall acute myocardial infarction. American Journal of Cardiology. 1995;76:516–517. doi: 10.1016/s0002-9149(99)80142-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Fesmire F, Brady W, Hahn S, et al. Clinical Policy: Indications for reperfusion therapy in Emergency Department patients with suspected acute myocardial infarction. Annals of Emergency Medicine. 2006;48:358–383. doi: 10.1016/j.annemergmed.2006.07.006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Pope J, Ruthazer R, Beshansky J, et al. Clinical features of emergency department patients presenting with symptoms of acute cardiac ischemia: a multicenter study. Journal of Thrombosis and Thrombolysis. 1998;6:63–74. doi: 10.1023/A:1008876322599. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Writing Committee Members et al. ACC/AHA guidelines for the management of patients with ST-elevation myocardial infarction – executive summary: A report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Task Force on practice guidelines (writing committee to revise the 1999 guidelines for the management of patients with acute myocardial infarction) Journal of the American College of Cardiology. 2004;44:671–719. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2004.07.002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]