Abstract
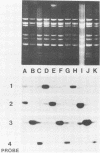
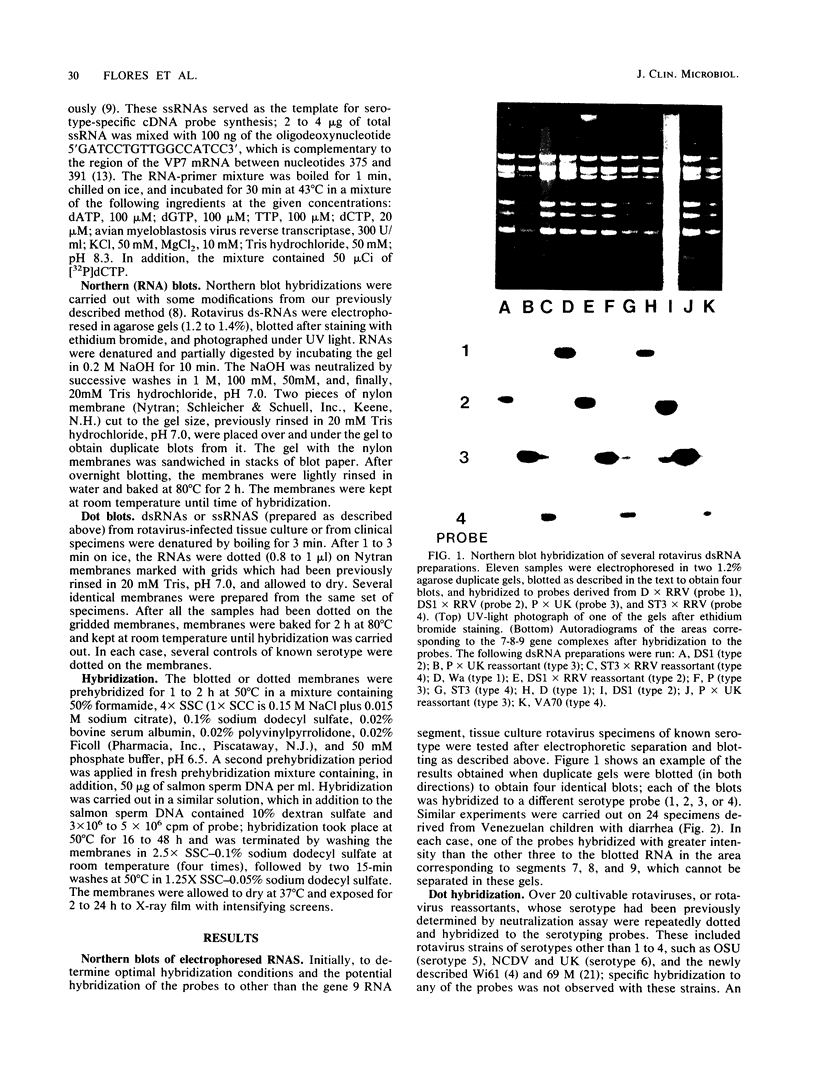
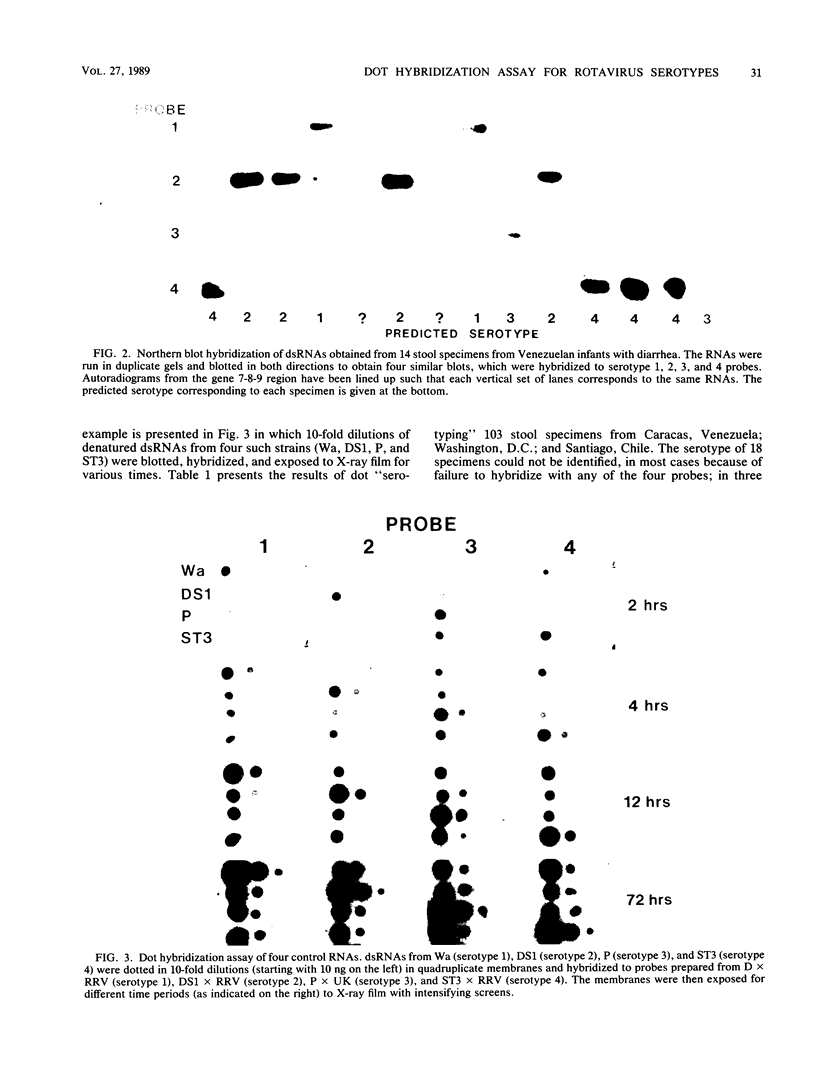
We have developed a hybridization assay that permits distinction of rotavirus serotypes 1, 2, 3, and 4. The serotype of rotaviruses from stool samples or tissue culture was recognized by hybridization of specific probes to (i) blots of viral double-stranded RNAs electrophoresed in agarose gels (Northern blots) or (ii) heat-denatured double-stranded RNAs directly dotted on nylon membranes. The probes consisted of 32P-labeled cDNA synthesized by reverse transcription of in vitro derived rotavirus mRNA from rotavirus serotypes 1 to 4. To prepare these probes, mRNAs were primed with a 17-mer nucleotide common to all four serotypes whose sequence is complementary to bases 375 to 391 of the rotavirus gene encoding the VP7 glycoprotein (gene 8 or 9 depending on the rotavirus strain). The resulting downstream transcripts encompassed areas of major sequence divergence among the four serotypes. Hybridization at high stringency (50 degrees C, 50% formamide, 4 x SSC [1 x SSC is 0.15 M NaCl plus 0.015 M sodium citrate]) was performed for 16 to 48 h. Autoradiograms of the washed membranes allowed recognition of the rotavirus serotype present in the blotted or dotted specimens since each of them hybridized preferentially to one of the four probes. Twenty-four laboratory specimens and 103 clinical specimens from Washington, D.C., Venezuela, and Chile were "serotyped" with this assay. The results were similar to those obtained with a monoclonal antibody serotyping assay.
Full text
PDF
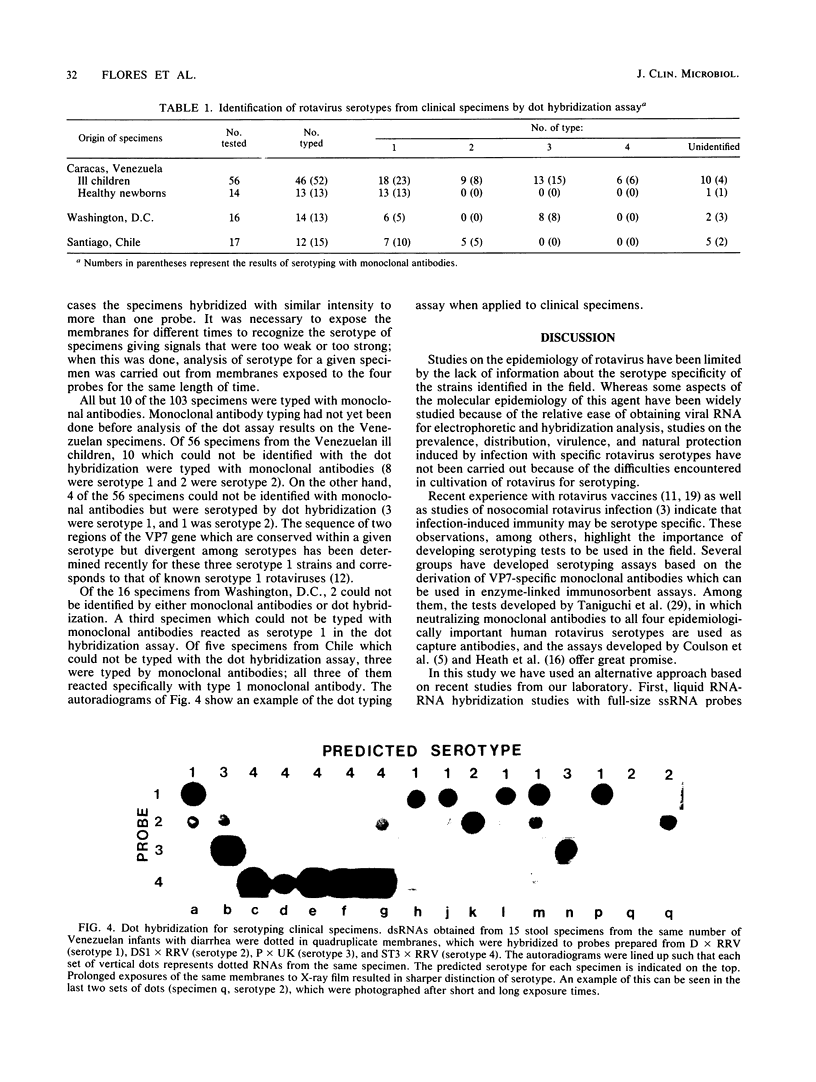


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Avendaño L. F., Calderón A., Macaya J., Prenzel I., Duarte E. Rotavirus viral RNA electrophoresis in hospitalized infants with diarrhea in Santiago, Chile. Pediatr Res. 1982 Apr;16(4 Pt 1):329–330. doi: 10.1203/00006450-198204000-00018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beards G. M., Pilfold J. N., Thouless M. E., Flewett T. H. Rotavirus serotypes by serum neutralisation. J Med Virol. 1980;5(3):231–237. doi: 10.1002/jmv.1890050307. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chiba S., Yokoyama T., Nakata S., Morita Y., Urasawa T., Taniguchi K., Urasawa S., Nakao T. Protective effect of naturally acquired homotypic and heterotypic rotavirus antibodies. Lancet. 1986 Aug 23;2(8504):417–421. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(86)92133-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark H. F., Hoshino Y., Bell L. M., Groff J., Hess G., Bachman P., Offit P. A. Rotavirus isolate WI61 representing a presumptive new human serotype. J Clin Microbiol. 1987 Sep;25(9):1757–1762. doi: 10.1128/jcm.25.9.1757-1762.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coulson B. S., Unicomb L. E., Pitson G. A., Bishop R. F. Simple and specific enzyme immunoassay using monoclonal antibodies for serotyping human rotaviruses. J Clin Microbiol. 1987 Mar;25(3):509–515. doi: 10.1128/jcm.25.3.509-515.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dimitrov D. H., Graham D. Y., Estes M. K. Detection of rotaviruses by nucleic acid hybridization with cloned DNA of simian rotavirus SA11 genes. J Infect Dis. 1985 Aug;152(2):293–300. doi: 10.1093/infdis/152.2.293. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flores J., Boeggeman E., Purcell R. H., Sereno M., Perez I., White L., Wyatt R. G., Chanock R. M., Kapikian A. Z. A dot hybridisation assay for detection of rotavirus. Lancet. 1983 Mar 12;1(8324):555–558. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(83)92811-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flores J., Midthun K., Hoshino Y., Green K., Gorziglia M., Kapikian A. Z., Chanock R. M. Conservation of the fourth gene among rotaviruses recovered from asymptomatic newborn infants and its possible role in attenuation. J Virol. 1986 Dec;60(3):972–979. doi: 10.1128/jvi.60.3.972-979.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flores J., Myslinski J., Kalica A. R., Greenberg H. B., Wyatt R. G., Kapikian A. Z., Chanock R. M. In vitro transcription of two human rotaviruses. J Virol. 1982 Sep;43(3):1032–1037. doi: 10.1128/jvi.43.3.1032-1037.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flores J., Perez-Schael I., Boeggeman E., White L., Perez M., Purcell R., Hoshino Y., Midthun K., Chanock R. M., Kapikian A. Z. Genetic relatedness among human rotaviruses. J Med Virol. 1985 Oct;17(2):135–143. doi: 10.1002/jmv.1890170206. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flores J., Perez-Schael I., Gonzalez M., Garcia D., Perez M., Daoud N., Cunto W., Chanock R. M., Kapikian A. Z. Protection against severe rotavirus diarrhoea by rhesus rotavirus vaccine in Venezuelan infants. Lancet. 1987 Apr 18;1(8538):882–884. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(87)92858-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flores J., Taniguchi K., Green K., Perez-Schael I., Garcia D., Sears J., Urasawa S., Kapikian A. Z. Relative frequencies of rotavirus serotypes 1, 2, 3, and 4 in Venezuelan infants with gastroenteritis. J Clin Microbiol. 1988 Oct;26(10):2092–2095. doi: 10.1128/jcm.26.10.2092-2095.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green K. Y., Midthun K., Gorziglia M., Hoshino Y., Kapikian A. Z., Chanock R. M., Flores J. Comparison of the amino acid sequences of the major neutralization protein of four human rotavirus serotypes. Virology. 1987 Nov;161(1):153–159. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(87)90181-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green K. Y., Sears J. F., Taniguchi K., Midthun K., Hoshino Y., Gorziglia M., Nishikawa K., Urasawa S., Kapikian A. Z., Chanock R. M. Prediction of human rotavirus serotype by nucleotide sequence analysis of the VP7 protein gene. J Virol. 1988 May;62(5):1819–1823. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.5.1819-1823.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenberg H. B., Wyatt R. G., Kapikian A. Z., Kalica A. R., Flores J., Jones R. Rescue and serotypic characterization of noncultivable human rotavirus by gene reassortment. Infect Immun. 1982 Jul;37(1):104–109. doi: 10.1128/iai.37.1.104-109.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heath R., Birch C., Gust I. Antigenic analysis of rotavirus isolates using monoclonal antibodies specific for human serotypes 1, 2, 3 and 4, and SA11. J Gen Virol. 1986 Nov;67(Pt 11):2455–2466. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-67-11-2455. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoshino Y., Sereno M. M., Midthun K., Flores J., Kapikian A. Z., Chanock R. M. Independent segregation of two antigenic specificities (VP3 and VP7) involved in neutralization of rotavirus infectivity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Dec;82(24):8701–8704. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.24.8701. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoshino Y., Wyatt R. G., Greenberg H. B., Flores J., Kapikian A. Z. Serotypic similarity and diversity of rotaviruses of mammalian and avian origin as studied by plaque-reduction neutralization. J Infect Dis. 1984 May;149(5):694–702. doi: 10.1093/infdis/149.5.694. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin M., Imai M., Ikegami N., Bellamy A. R., Summers D., Nuss D. L., Deibel R., Furuichi Y. cDNA probes of individual genes of human rotavirus distinguish viral subgroups and serotypes. J Virol Methods. 1987 Mar;15(4):285–289. doi: 10.1016/0166-0934(87)90151-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsuno S., Hasegawa A., Mukoyama A., Inouye S. A candidate for a new serotype of human rotavirus. J Virol. 1985 May;54(2):623–624. doi: 10.1128/jvi.54.2.623-624.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Midthun K., Flores J., Taniguchi K., Urasawa S., Kapikian A. Z., Chanock R. M. Genetic relatedness among human rotavirus genes coding for VP7, a major neutralization protein, and its application to serotype identification. J Clin Microbiol. 1987 Jul;25(7):1269–1274. doi: 10.1128/jcm.25.7.1269-1274.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Midthun K., Greenberg H. B., Hoshino Y., Kapikian A. Z., Wyatt R. G., Chanock R. M. Reassortant rotaviruses as potential live rotavirus vaccine candidates. J Virol. 1985 Mar;53(3):949–954. doi: 10.1128/jvi.53.3.949-954.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perez-Schael I., Daoud G., White L., Urbina G., Daoud N., Perez M., Flores J. Rotavirus shedding by newborn children. J Med Virol. 1984;14(2):127–136. doi: 10.1002/jmv.1890140206. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodriguez W. J., Kim H. W., Brandt C. D., Fletcher A. B., Parrott R. H. Rotavirus: a cause of nosocomial infection in the nursery. J Pediatr. 1982 Aug;101(2):274–277. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(82)80140-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaw R. D., Stoner-Ma D. L., Estes M. K., Greenberg H. B. Specific enzyme-linked immunoassay for rotavirus serotypes 1 and 3. J Clin Microbiol. 1985 Aug;22(2):286–291. doi: 10.1128/jcm.22.2.286-291.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Street J. E., Croxson M. C., Chadderton W. F., Bellamy A. R. Sequence diversity of human rotavirus strains investigated by northern blot hybridization analysis. J Virol. 1982 Aug;43(2):369–378. doi: 10.1128/jvi.43.2.369-378.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taniguchi K., Urasawa T., Morita Y., Greenberg H. B., Urasawa S. Direct serotyping of human rotavirus in stools by an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay using serotype 1-, 2-, 3-, and 4-specific monoclonal antibodies to VP7. J Infect Dis. 1987 Jun;155(6):1159–1166. doi: 10.1093/infdis/155.6.1159. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wyatt R. G., James H. D., Jr, Pittman A. L., Hoshino Y., Greenberg H. B., Kalica A. R., Flores J., Kapikian A. Z. Direct isolation in cell culture of human rotaviruses and their characterization into four serotypes. J Clin Microbiol. 1983 Aug;18(2):310–317. doi: 10.1128/jcm.18.2.310-317.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]